Parts of Automobile Body
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Body Shell
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’re focusing on the **body shell** of an automobile. Can anyone tell me what the body shell does?

It holds everything together, right?

Absolutely! The body shell provides structural support for the engine, passengers, and luggage. Think of it as the vehicle's skeleton. It also plays a crucial role in safety during collisions.

Does the body shell influence the car's design?

Yes, it does! The design of the body shell affects aerodynamics and aesthetics. Remember, a good design improves fuel efficiency and performance.

So, it's not just about looks?

Exactly! Functionality and safety are key. Let's summarize this section: the body shell is essential for support, safety, and influencing overall vehicle design.
Hood and Bumpers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s talk about the **hood** and **bumpers**. What do you think the primary function of the hood is?

Is it just to cover the engine?

Yes! The hood protects the engine and provides access for maintenance. It's essential for both safety and convenience when servicing the vehicle.

What about the bumpers?

Great question! Bumpers are designed to absorb impacts and protect against collisions. They are crucial for rider safety. Remember, testing the bumpers in low-impact scenarios ensures they perform well.

So, the bumpers help reduce damage?

Exactly! They minimize repair costs and protect the integrity of the car's frame. Let's recap: the hood provides engine access and protection while bumpers safeguard against impacts.
Doors and Roof
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, who can explain the significance of **doors** and the **roof**?

Doors let us in and out of the car!

Correct! Doors not only provide access to the passenger areas, but they are also designed to enhance safety in the event of a collision.

And the roof?

The roof protects passengers from weather and also adds structural rigidity to the vehicle. It's like the capstone that holds everything in place.

So both are essential for safety?

Exactly! Doors and roofs contribute significantly to the overall strength and safety of the vehicle. To summarize: doors allow access while ensuring safety, and the roof provides weather protection and support.
Windows and Mirrors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s discuss **windows** and **mirrors**. Why do you think they are crucial in a vehicle?

They help us see what’s around us!

Exactly! Windows and mirrors provide visibility, which is essential for safe driving.

Are all windows the same?

Not at all! The windshield is specially designed for safety and protection. It's often laminated to prevent shattering. Mirrors, on the other hand, are important for eliminating blind spots.

So they help in preventing accidents?

Exactly! Good visibility reduces the risk of accidents. To wrap it up: windows and mirrors are vital for enhancing driver awareness and promoting safety.
Grille and Trim
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let’s cover the **grille** and **trim**. What roles do they play in a vehicle?

The grille helps with airflow, right?

Correct! The grille allows air to enter the radiator, which is vital for engine cooling. It's functional yet also adds character to the vehicle's front design.

What about the trim?

Trim not only enhances the car's aesthetics but also plays a role in protecting edges and surfaces. It helps prevent rust and wear.

So, it’s both functional and looks good?

Exactly! The combination of functionality and design makes for a well-rounded vehicle. Summary: the grille ensures engine cooling, while trim supports aesthetics and protection.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The automobile body comprises various essential components such as the body shell, hood, bumpers, doors, roof, trunk, and more. Each part serves distinct functions ranging from structural support to aesthetics and safety, influencing the vehicle's performance and design.
Detailed
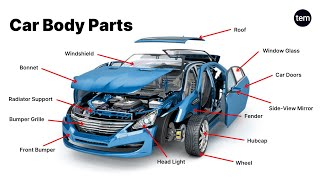
Parts of Automobile Body
The automobile body is a critical structure designed to support the vehicle's components and protect its occupants. Key components include:
- Body Shell: This outer structure houses the engine, passengers, and luggage.
- Hood (Bonnet): It covers the engine compartment and allows access for maintenance.
- Bumpers: Positioned front and rear, they absorb impact during minor collisions.
- Fenders (Mudguards): These protect the wheels and lower body from dirt and debris.
- Doors: Provide entry to the passenger compartment.
- Roof: Offers protection from weather and adds structural rigidity.
- Trunk (Boot/Decklid): Serves as a storage compartment at the rear of the vehicle.
- Grille: Facilitates airflow to the radiator, crucial for engine cooling.
- Pillars (A, B, C): Structural supports for the roof and door mounts.
- Windows/Windshield: Glass panels ensuring visibility and shielding occupants.
- Mirrors, Lights, Trim: Essential for vehicle safety and enhancing aesthetics.
Understanding these components is fundamental for appreciating vehicle dynamics, design, safety, and overall performance.
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Body Shell
Chapter 1 of 11
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The outer structural shell accommodates engine, passengers, luggage, and components.
Detailed Explanation
The body shell of an automobile is the main framework that holds everything together. It provides structural support for various components such as the engine, passenger seats, luggage areas, and any other integral parts of the vehicle. Essentially, it forms the shape of the car and protects the inside from external elements.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the body shell like the walls of a house. Just as the walls support the roof and hold in the rooms while protecting inhabitants from the weather, the body shell keeps all the car's components secure and safe from outside conditions.
Hood (Bonnet)
Chapter 2 of 11
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Hinged cover at the front; protects the engine and provides access.
Detailed Explanation
The hood, also known as the bonnet in some regions, is a hinged cover that sits at the front of the vehicle. Its primary function is to protect the engine and components underneath while also providing access for maintenance, such as checking the oil or replacing the battery.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the hood as a book cover. Just as a cover protects the pages and keeps them safe while still allowing you to open it to read, the hood protects the engine while allowing access for repairs and checks.
Bumpers
Chapter 3 of 11
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Located at front and rear, absorb minor impact and protect against collisions.
Detailed Explanation
Bumpers are located at both the front and rear of the vehicle and are designed to absorb minor impacts and reduce damage during collisions. They play a crucial role in protecting both the car itself and the occupants inside; they are designed to crumple in a way that dissipates energy from an impact.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of bumpers like the padding in a helmet. Just as padding absorbs the impact in case of a fall to protect the head, bumpers absorb collision forces to safeguard the car and its passengers.
Fenders (Mudguards)
Chapter 4 of 11
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Shield wheels and lower body from mud and debris.
Detailed Explanation
Fenders, or mudguards, are located over the wheels of the car. Their main purpose is to shield the lower part of the vehicle from mud, debris, and water that can be kicked up by the tires while driving. This helps to keep the car clean and improves visibility by preventing debris from being flung onto the windows.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine wearing a raincoat while walking in the rain. Just as the coat protects you from getting wet, fenders help protect the car's body from dirt and moisture.
Doors
Chapter 5 of 11
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Provide access to passenger compartment.
Detailed Explanation
The doors of a vehicle are vital for providing access to the passenger compartment. They allow occupants to enter and exit the car. Doors are designed to swing open and closed securely and often include mechanisms like locks to ensure safety while driving.
Examples & Analogies
Think of car doors like the doors of your house. They provide a way in and out while securing your personal space from the outside.
Roof
Chapter 6 of 11
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Protects from weather and adds structural rigidity.
Detailed Explanation
The roof of an automobile provides protection from various weather conditions, such as rain, snow, and sun. Additionally, it adds structural integrity to the vehicle, helping it maintain shape and strength, especially during rolls or impacts.
Examples & Analogies
The car roof is similar to the roof of a building. Just as a building's roof keeps people inside safe from the elements, the car roof ensures passengers remain safe and comfortable.
Trunk (Boot) / Decklid
Chapter 7 of 11
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Rear storage compartment.
Detailed Explanation
The trunk, also known as the boot in some countries, is located at the rear of the vehicle. It provides a storage space for luggage, groceries, and other items. The trunk is designed to be easily accessible, often featuring a lid that can be opened independently from the rest of the car.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of the trunk as a suitcase. Just like a suitcase holds your belongings while traveling, the trunk keeps everything safe and secure while you drive.
Grille
Chapter 8 of 11
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Allows air entry to the radiator.
Detailed Explanation
The grille is located at the front of the vehicle and serves a crucial function by allowing air to enter the engine bay and reach the radiator. This airflow is necessary for cooling the engine, which can generate a lot of heat during operation.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the grille like a ventilation system in a house. Just as vents allow fresh air to circulate and keep the house comfortable, the grille lets air flow in to keep the engine cool.
Pillars (A, B, C)
Chapter 9 of 11
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Support roof and mount doors/glass.
Detailed Explanation
Pillars are the vertical supports in the car's body structure, designated as A, B, and C pillars. They hold up the roof and provide mounting points for doors and windows. These pillars are integral to the car's safety, helping to maintain the integrity of the passenger compartment during a collision.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the pillars as the structural frame of a building. Just like the frame supports the roof and walls, pillars in a car hold everything in place.
Windows/Windshield
Chapter 10 of 11
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Glass panels for visibility and protection.
Detailed Explanation
Windows and the windshield are made of glass and provide visibility for the driver and passengers. They protect occupants from wind, rain, and debris while allowing views of the outside. The windshield is particularly designed to be strong and resist impacts.
Examples & Analogies
Think of car windows like the glass in a greenhouse. Just as greenhouse glass allows sunlight in while protecting plants, car windows provide a clear view while safeguarding people from outside elements.
Mirrors, Lights, and Trim
Chapter 11 of 11
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Essential for safety, function, and aesthetics.
Detailed Explanation
Mirrors, lights, and exterior trim components enhance both safety and aesthetics. Mirrors provide visibility for changing lanes and reversing, while lights are critical for visibility during dark conditions and signaling intent to other drivers. Trim adds design elements that contribute to the overall look of the car.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of these components like the finishing touches on a suit. Just as cufflinks and a tie add style while also being functional, mirrors and lights enhance the car's performance while looking good.
Key Concepts
-
Body Shell: The outer structure that supports and protects the vehicle components.
-
Hood: A hinged cover that safeguards the engine and allows access for maintenance.
-
Bumpers: Components designed to absorb impact and minimize damage during collisions.
-
Fenders: Protective elements that prevent debris from affecting the vehicle body.
-
Trunk: The rear section for storage, often referred to as the boot.
-
Grille: The area that allows air to flow to the engine for cooling.
-
Pillars: Structural components providing support for the roof and mounting points for doors and windows.
-
Windows: Glass components that provide visibility and protection for occupants.
-
Trim: Decorative and protective elements that enhance the vehicle's appearance.
Examples & Applications
The body shell is like a skeleton that supports the car's organs (engine, seats, and storage) while providing safety during accidents.
The hood acts like a shield protecting the engine, much like a knight’s armor, allowing easy access for maintenance tasks.
Bumpers can be likened to airbags for the car’s exterior, designed to absorb shocks from minor collisions.
Fenders prevent dirt and debris from splashing on the vehicle’s body, similar to how eyelashes protect our eyes.
The trunk serves as the car’s luggage holder, just like a backpack holds all necessary supplies for travelers.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
The hood’s a cover, strong and nice, to check the oil, it’s my device.
Stories
Once there was a car with a body shell that stood strong like a fortress, protecting all its treasures — the engine, passengers, and their luggage from harm’s way.
Memory Tools
To remember the parts of the body shell, think A-H-B-F-D-R-T-G: A for the body shell, H for the hood, B for bumpers, F for fenders, D for doors, R for the roof, T for trunk, G for grille.
Acronyms
S-B-F-D-R-G (Shell, Bumper, Fender, Door, Roof, Grille) can help you recall the main body parts.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Body Shell
The outer structural shell of a vehicle that accommodates the engine, passengers, and luggage.
- Hood (Bonnet)
A hinged cover at the front that protects the engine and provides access for maintenance.
- Bumper
A component located at the front and rear of the vehicle that absorbs impact and protects against collisions.
- Fender (Mudguard)
A part that shields the wheels and lower body from mud and debris.
- Trunk (Boot/Decklid)
The rear storage compartment of a vehicle.
- Grille
A component that allows airflow to the radiator for engine cooling.
- Pillars (A, B, C)
Vertical supports that help hold the roof and mount doors or glass.
- Windows/Windshield
Glass panels that provide visibility and protect occupants in a vehicle.
- Trim
Decorative, protective elements on a vehicle that enhance aesthetics.
- Mirrors
Reflective surfaces that help drivers see behind and beside them to improve safety.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
