Spark Ignition (SI) Engine Fuel System
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to the Fuel System
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're diving into the Spark Ignition Engine Fuel System. Can anyone tell me what the fuel tank's role is in this system?

It stores petrol!

Exactly! And why is it designed to be robust?

To ensure safe fuel delivery?

Correct! This is vital for preventing leaks or accidents. Now, can anyone explain the function of the fuel filter?

The fuel filter removes impurities, right?

Yes, it protects the carburetor and injectors. Let’s remember 'F-F-R' for Fuel Filter's Role: Filter Fuel Right! Now, what happens after the fuel tank?
Fuel Delivery Mechanism
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's talk about the Fuel Pump. Who can tell me its purpose?

It delivers fuel from the tank to the carburetor or injectors.

That’s right! It can be mechanical or electric. Now, why is the air filter important?

It cleans the air that enters the engine?

Exactly! It prevents wear on the engine parts. Let's summarize that with 'A-F-C': Air Filter Cleans air. Who can describe what the carburetor does?
Carburetors and Fuel Injection
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss the Carburetor. What does it do?

It mixes fuel and air in precise ratios for combustion.

Correct! And how does it adjust the mixture?

By changing the throttle, temperature, and load.

Excellent! Remember, 'C-M-R' for Carburetor Mixes Ratios! Now, what’s the difference in fuel injection types?

Port fuel injection and direct injection!

That’s right! Each has benefits that enhance engine performance and emission control. Remember 'F-I-E' – Fuel Injection Enhances performance!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses the key components of the Spark Ignition Engine Fuel System, including the fuel tank, filters, pump, carburetor, and injectors. It highlights their functions and the importance of maintaining optimal conditions for combustion and vehicle performance.
Detailed
Spark Ignition (SI) Engine Fuel System
The Spark Ignition (SI) Engine Fuel System is critical for the operation of gasoline engines, ensuring that the right amount of fuel and air mix reaches the engine for efficient combustion. Key components include:
- Fuel Tank: Stores petrol and is equipped with venting to ensure safe delivery.
- Fuel Filter & Sediment Bowl: Removes contaminants, protecting the carburetor or injectors from damage.
- Fuel Pump: Responsible for delivering fuel to the carburetor or injectors, with options including mechanical and electric pumps.
- Air Filter: Cleans the intake air, preventing engine wear.
- Carburetor: Precisely mixes air and fuel for combustion, adapting the mixture to varying engine conditions.
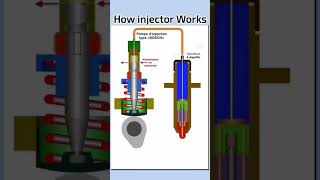
- Fuel Injection: In modern petrol engines, fuel can be injected directly into the intake port or combustion chamber, improving efficiency and emissions control.
The flow of fuel in an SI engine begins at the fuel tank, progresses through various filters and pumps, and finally combines with air to create the optimal mixture for combustion. Understanding these components clarifies how they contribute to a vehicle’s power and efficiency.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
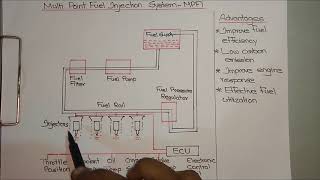
Typical SI Fuel System Flow
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Typical SI Fuel System Flow
| Step | Component | Function |
|------|-------------------|-------------------------------|
| 1 | Fuel Tank | Fuel storage |
| 2 | Fuel Filter | Removes impurities |
| 3 | Fuel Pump | Delivers fuel under pressure |
| 4 (carb)| Carburetor | Mixes air and fuel |
| 4 (injection)| Injector/Manifold | Directs fuel to cylinder/port |
| 5 | Air Filter | Filters intake air for combustion |
Detailed Explanation
The Typical SI Fuel System Flow outlines the sequential steps through which fuel travels from storage to combustion in an engine. This flowchart format makes it easy to understand each component's role. It begins with the fuel tank, where the petrol is initially stored, followed by the fuel filter, which cleans the fuel by removing impurities.
Next, the fuel pump transfers the fuel under pressure, ensuring that it reaches the carburetor or fuel injectors effectively. The carburetor (or injector in modern systems) mixes the air and fuel, preparing the mixture for combustion. Finally, the air filter ensures that the air used in this process is clean, promoting effective combustion and engine performance.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're watering a garden. First, you have a water reservoir (the fuel tank) that stores the water. Before using the water, you want to ensure it's clean, so you have a filter to strain it (the fuel filter). The pump is like a hose that carries the water to where it's needed with enough pressure. When you reach the plant, you either pour the water directly (like a carburetor) or use a precise sprayer that delivers the perfect amount of water exactly where it’s needed (like fuel injection). Finally, ensuring there's no debris in the air helps the plant grow strong, just like keeping the air filtered helps the engine run efficiently.
Key Concepts
-
Fuel Tank: Stores petrol and is vital for safety.
-
Fuel Filter: Removes impurities to protect the engine.
-
Fuel Pump: Delivers fuel efficiently.
-
Air Filter: Cleans intake air to prevent damage.
-
Carburetor: Mixes fuel and air in optimal ratios.
-
Fuel Injection: Enhances performance through precise control.
Examples & Applications
An example of how a clogged fuel filter can lead to engine sputtering due to impurities reaching the engine.
Demonstrating the difference in performance between a carbureted engine and a fuel-injected engine through acceleration tests.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the tank, the petrol flows, through the filter, out it goes. Pump it quick, ensure it’s clean, air and fuel, a mix pristine.
Stories
Once, a Fuel Tank was lonely, holding petrol all alone. It wanted friends, so it invited the Filter, which kept it clean, and the Pump, which made sure fuel flowed quickly to the Carburetor, where magic happened with air!
Acronyms
Remember F-T-F-P-A-C
Fuel Tank - Filter - Pump - Air Filter - Carburetor.
SPF (Safe Petrol Fueling) for remembering the sequence
Safety in the tank
Filtering impurities
Pumping fuel effectively.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Fuel Tank
A storage unit for petrol, designed for safety and efficiency.
- Fuel Filter
A component that removes impurities from fuel before it enters the engine.
- Fuel Pump
A device that moves fuel from the tank to the carburetor or injectors.
- Air Filter
A filter that cleans the intake air, preventing engine wear.
- Carburetor
A device that mixes air and fuel in the correct ratios for combustion.
- Fuel Injection
A system that delivers fuel directly into the engine for better performance.
- Port Injection
Fuel injection into the intake port of the engine.
- Direct Injection
Fuel injection directly into the combustion chamber.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
