Introduction to Operational Amplifiers
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Op-Amps
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into operational amplifiers, or Op-Amps. Can anyone tell me what an Op-Amp does?

I think it's a kind of amplifier, right?

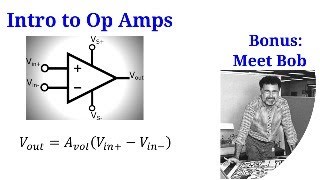
Exactly! Op-Amps are high-gain voltage amplifiers with unique properties. They have differential inputs and a single-ended output. This allows them to amplify the difference between two input voltage levels.

What do you mean by differential inputs?

Great question! Differential inputs mean that the Op-Amp monitors two voltages at once, amplifying only the difference. This is crucial for many applications, like filtering noisy signals.

What are some applications of Op-Amps?

Op-Amps are widely used in signal conditioning, filtering, and even in mathematical calculations like integrators and differentiators. Let's remember that using the acronym 'SCF' could help us recall their common uses: Signal Conditioning, Filtering, and mathematical Functions.

I see! So, Op-Amps are pretty versatile!

Absolutely! To recap, Op-Amps amplify voltage, have differential inputs, and are used in many applications, summarizing their importance in electronics.
IC 741 Specifications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's talk about the IC 741, a classic operational amplifier. Who knows its key features?

It has a high gain, right?

Correct! The IC 741 has a high gain of around 100,000. This means it can amplify small input signals significantly. Can anyone suggest why a dual polarity supply is beneficial?

Maybe it allows for both positive and negative voltage output?

Exactly! The dual polarity supply enables the Op-Amp to handle both positive and negative voltages, allowing for a wider range of applications. Additionally, it has a low offset voltage, making it more accurate in amplifying signals.

Does that affect the performance a lot?

Yes, low offset voltage is crucial, especially in precision applications. It minimizes the error in output, ensuring that the amplified signal accurately represents the input.

Got it! So, the IC 741 is a reliable component for many circuits.

Precisely! Just remember, the critical features of the IC 741 are its high gain, dual polarity supply, and low offset voltage.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Op-Amps, notably the IC 741, serve crucial roles in analog circuits through signal conditioning and mathematical operations. Their characteristics, such as high gain and low offset voltage, make them versatile components in electronics.
Detailed
Introduction to Operational Amplifiers
Operational amplifiers (Op-Amps) are critical components in electronics, known for their high gain and versatility. Specifically, the Op-Amp is a DC-coupled device that amplifies voltage signals with differential inputs, typically featuring a single-ended output.
An example of a widely used Op-Amp is the IC 741, which is notable for its high gain (approximately 100,000), dual polarity supply capability, and low offset voltage. These characteristics enable Op-Amps to be utilized in various applications such as signal conditioning, filtering, and performing mathematical operations that are essential in complex circuit designs.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
What is an Operational Amplifier?
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● An operational amplifier (Op-Amp) is a high-gain, DC-coupled voltage amplifier with differential inputs and usually a single-ended output.
Detailed Explanation
An operational amplifier, commonly referred to as an Op-Amp, is a type of electronic component that is designed to amplify voltage. It is characterized by its high gain, meaning it can increase the amplitude of a small input voltage to a much larger output voltage. The Op-Amp has two input terminals: the non-inverting terminal (+) and the inverting terminal (-). It also typically has a single output terminal. The 'DC-coupled' aspect means it can amplify both AC and DC signals without affecting the DC component of the signal.
Examples & Analogies
Think of an operational amplifier like a microphone and speaker system. When you speak into the microphone (input), it picks up your voice and sends the sound to the speaker (output) at a louder volume. Just like the microphone gathers small sound waves (voltage) and amplifies them into loud waves, an Op-Amp takes small voltage signals and amplifies them to larger levels.
Applications of Op-Amps
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Widely used in signal conditioning, filtering, and mathematical operations.
Detailed Explanation
Op-Amps are versatile components that find applications in numerous areas of electronics. Signal conditioning refers to improving the quality of a signal, such as amplifying it and altering its form to make it more suitable for processing. Filtering involves removing unwanted components from a signal, allowing only the desired signals to pass through. Additionally, Op-Amps perform mathematical operations like addition, subtraction, integration, and differentiation, making them fundamental in analog computing and signal processing.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine Op-Amps as chefs in a kitchen. In their role, they take raw ingredients (input signals), process them by altering flavors and textures (conditioning), and create delicious dishes (final output) that meet specific tastes (desired outcomes). Just as chefs might combine ingredients and use different techniques to achieve the perfect meal, Op-Amps manipulate electrical signals for various applications.
Key Concepts
-
High-Gain Amplifier: Op-Amps have a high voltage amplification factor, often exceeding 100,000.
-
Differential Inputs: They accept two voltages and amplify their difference, which is significant in many applications.
-
IC 741 Features: This classic Op-Amp has a dual polarity supply and low offset voltage, making it a reliable choice for analog circuits.
Examples & Applications
An Op-Amp is used in an inverting amplifier configuration to reduce the input signal polarity by 180°.
The IC 741 can be employed in a summer circuit to add multiple input signals into one output.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Op-Amps amplify the strain, powering signals without a gain!
Stories
Once in the land of circuits, there lived an Op-Amp called 741 who could change everything around it just by measuring differences.
Memory Tools
Remember 'SCF' for Op-Amp applications: Signal Conditioning, Filtering, and Functions.
Acronyms
IC 741 = 'I Can amplify 741 ways.'
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Operational Amplifier (OpAmp)
A high-gain voltage amplifier with differential inputs and a single-ended output.
- IC 741
A widely used general-purpose operational amplifier with features like high gain and low offset voltage.
- Differential Inputs
Inputs that accept two different voltage levels to amplify the difference between them.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
