Introduction to Business Analysis
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Definition and Purpose of Business Analysis
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will start with the definition and purpose of Business Analysis. Can anyone tell me what they think Business Analysis might be?

Is it about solving problems in business?

Exactly! Business Analysis is about solving problems by understanding needs and recommending solutions. It's like being a detective in a business environment. Remember this definition: BA is about enabling change through identifying and proposing solutions that deliver value. Now, why do you think this is important?

Because businesses need to adapt to stay competitive!

Perfect! The purpose is also to improve efficiency and ensure that stakeholders are aligned. Let's practice recalling those key outcomes. Can someone summarize what they are?

Improved efficiency, better communication, and defined project scopes!

Spot on! Remember the acronym ECD: Efficiency, Communication, Defined scope. Now let's move on!
Role of a Business Analyst
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's now dive into the specific role of the Business Analyst. What do you think is the core function of a BA?

They gather and document requirements, right?

Yes! They collect, analyze, and document requirements. BAs also conduct interviews. How might you prepare for such an interview?

I would make a list of questions and learn about the business first.

Excellent approach! Preparing is key. BAs also support testing and validation. Can anyone tell me why this is crucial?

To make sure the final product meets what the business needed!

Exactly! BAs ensure that the solutions are practical. Time for a quick recap: What are the primary responsibilities of a BA?

Gathering requirements, conducting interviews, creating documentation, and supporting testing!

Great job! Let’s keep up this enthusiasm as we discuss the necessary soft skills!
Soft Skills Required for Business Analysts
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s explore the soft skills that a Business Analyst needs. Who can list some of them?

Critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication!

Excellent! These skills are essential. Can anyone think of how critical thinking might help in business analysis?

It helps in analyzing data and drawing conclusions!

Absolutely! Each of these skills contributes to successfully identifying needs. To remember them, think C-P-C-P: Critical thinking, Problem-solving, Communication, and then facilitation. Now, can you give an example of how one of these skills might be applied?

When negotiating requirements with stakeholders!

Exactly! Negotiation relies on strong communication skills. Let’s summarize what we’ve covered so far about the necessary soft skills.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section defines Business Analysis as a practice aimed at facilitating change within organizations by recognizing business needs, analyzing them, and proposing solutions. Furthermore, it discusses the role of Business Analysts, their responsibilities, and the importance of collaboration among various project roles.
Detailed
Introduction to Business Analysis
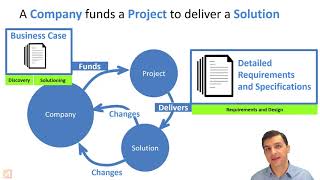
Business Analysis is defined as the practice of enabling change in an organization by identifying needs and proposing solutions that deliver value to stakeholders. Its primary purpose is to understand the business structure, identify areas for improvement, bridge the gap between business needs and technology solutions, and ensure stakeholder alignment on requirements and outcomes.
Key Outcomes of Business Analysis
- Improved Efficiency: Helps in enhancing the effectiveness of business processes.
- Enhanced Communication: Strengthens stakeholder communication and understanding.
- Defined Project Scope: Ensures better-defined project scopes leading to reduced risks of failure.
Role of a Business Analyst
A Business Analyst (BA) is critical as a liaison between business stakeholders and technical teams, translating business needs into functional specifications. Key responsibilities include gathering and documenting requirements, conducting stakeholder interviews, creating Business Requirement Documents (BRDs) and Functional Requirement Documents (FRDs), supporting testing, and communicating across departments.
Soft Skills Required
- Critical Thinking: Ability to analyze situations logically.
- Problem-Solving: Finding effective solutions to complex problems.
- Communication and Negotiation: Interfacing with different stakeholders.
- Facilitation and Active Listening: Leading discussions and understanding diverse perspectives.
Comparative Roles: BA vs PM vs QA vs Product Owner
Understanding the differences between various roles in a project context:
- A Business Analyst focuses on understanding and solving business problems.
- A Project Manager is responsible for the execution and management of timelines and budgets.
- A QA Engineer validates that the solution meets requirements.
- A Product Owner prioritizes features and oversees product outcomes.
Example Scenario
In a software project, the BA identifies user needs, the PM ensures timely delivery, the QA guarantees functionality, and the Product Owner aligns the product with users' requirements.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Business Analysis
Chapter 1 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Business Analysis is the practice of enabling change in an organization by defining needs and recommending solutions that deliver value to stakeholders. It is a disciplined approach to identifying business problems and opportunities, analyzing needs, and determining solutions.
Detailed Explanation
Business Analysis (BA) is fundamentally about understanding and addressing the needs of an organization. This definition outlines that the main goal of BA is to enable change. To achieve this, business analysts assess the current state of the business, identify necessary changes, and advocate for solutions that will add value for stakeholders, such as customers, employees, and management. A disciplined approach means that BA requires structured methods for gathering information, analyzing data, and developing recommendations.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a business analyst like a doctor for a business. Just as a doctor diagnoses health issues and prescribes treatments, a business analyst identifies problems within a business and suggests improvements or solutions to enhance its performance.
Purpose of Business Analysis
Chapter 2 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The purpose of business analysis is to:
- Understand the business structure, policies, and operations
- Identify areas of improvement
- Bridge the gap between business needs and technology solutions
- Ensure stakeholder alignment on requirements and outcomes
Detailed Explanation
The purpose of business analysis encompasses several key elements. Understanding the business structure means comprehending how different parts of the organization interact, which is essential for identifying inefficiencies or problems. Identifying areas for improvement helps the organization become more effective and competitive. Bridging the gap between business needs and technology solutions ensures that technical teams understand what business stakeholders are looking for in a solution. Finally, ensuring stakeholder alignment is critical because if everyone is not on the same page regarding what the requirements are, the solutions may not meet the needs effectively.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're planning a community event. You need to understand the venue's rules (business structure), find out the best way to attract attendees (areas for improvement), work with the technical team to set up online registration (bridge the gap), and make sure everyone involved understands their roles for the event to be successful (stakeholder alignment).
Key Outcomes of Business Analysis
Chapter 3 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Key outcomes of business analysis include:
- Improved efficiency and effectiveness of business processes
- Enhanced stakeholder communication and understanding
- Well-defined project scopes and reduced risk of failure
Detailed Explanation
The outcomes of business analysis are integral to an organization's success. Improved efficiency means that processes operate faster and with fewer errors. Effectiveness refers to achieving the desired results. Enhanced communication among stakeholders ensures everyone understands the project's direction and goals, leading to better collaboration. Additionally, well-defined project scopes mean that a project has a clear purpose and established boundaries, which reduces the likelihood of challenges arising during execution, ultimately improving the chances of project success.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a family planning a road trip. If they take time to lay out their route (well-defined scope), everyone knows when to pack (improved efficiency), and they communicate throughout the trip about stops and preferences (enhanced understanding), leading to a more enjoyable traveling experience and less chance of ending up lost!
Role of a Business Analyst
Chapter 4 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A Business Analyst (BA) acts as a bridge between business stakeholders and technical teams. They translate business requirements into functional specifications and ensure that the final solution meets business needs.
Detailed Explanation
The role of a business analyst is vital in connecting the needs of the business with the capabilities of technology. They gather specific requirements from stakeholders, analyze them, and create functional specifications that detail what the technology must do. This role ensures that technology solutions are aligned with business needs and that technical teams understand what is necessary for successful implementation.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a translator at a United Nations meeting who takes a speech in English and translates it into French for the French delegates. Similarly, the BA translates the 'language' of business needs into a 'language' that technical teams can understand and work with.
Primary Responsibilities of a Business Analyst
Chapter 5 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Primary responsibilities include:
- Gather, analyze, and document requirements
- Conduct stakeholder interviews and workshops
- Create BRDs, FRDs, user stories, and process models
- Support testing and validation
- Communicate requirements across departments
Detailed Explanation
The primary responsibilities of a business analyst involve a variety of tasks essential for the success of projects. Gathering requirements means collecting both what the stakeholders need and what the business aims to achieve. Analyzing and documenting these requirements makes sure they are clear and comprehensive. Conducting interviews and workshops helps to elicit even more insights from stakeholders. Creating business requirements documents (BRDs), functional requirements documents (FRDs), user stories, and process models are crucial for detailing how the system should work. Supporting testing ensures that the solution meets the newly defined requirements, while communicating across departments keeps everyone informed and engaged in the process.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a chef preparing a new dish. They start by gathering ingredients and recipes (gather requirements), taste testing (support testing), and then sharing the dish with the staff (communicating across departments) to ensure it’s as delicious as envisioned.
Essential Soft Skills for Business Analysts
Chapter 6 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Soft skills needed for a Business Analyst include:
- Critical thinking
- Problem-solving
- Communication and negotiation
- Facilitation and active listening
Detailed Explanation
Soft skills are just as important as technical skills for business analysts. Critical thinking helps them assess situations and come up with logical solutions. Problem-solving ensures they can find ways to tackle challenges that arise. Communication and negotiation are necessary for discussing requirements with stakeholders and coming to agreements that work for everyone involved. Facilitation and active listening skills enable them to conduct effective meetings and ensure that all voices are heard during the requirements-gathering process.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a successful mediator who resolves disputes between two parties. They need to think critically about the situation, listen to both sides, and communicate effectively to negotiate a compromise—all of which are attributes required for a successful business analyst.
Comparison of Roles: BA, PM, QA, and Product Owner
Chapter 7 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Role Focus Area Key Responsibility
Business Analyst: Business needs & solutions; Understands problems and defines solutions
Project Manager: Project execution; Plans, tracks, and manages timelines & budgets
QA Engineer: Quality assurance; Validates that the solution works as expected
Product Owner: Product vision & backlog; Prioritizes features and owns product outcomes
Detailed Explanation
This section compares the roles of different key players in project management and product development: Business Analysts focus on identifying needs and proposing solutions; Project Managers ensure that projects stay on track and within budget; QA Engineers are responsible for testing and ensuring quality; and Product Owners prioritize what features should be developed based on business goals and customer needs. Each role plays a distinct yet interconnected part in delivering successful outcomes.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a theater production. The Business Analyst is like the scriptwriter, ensuring the story aligns with audience needs; the Project Manager is the director, keeping the production on schedule and within budget; the QA Engineer is the actor ensuring the performance meets the audience's expectations; and the Product Owner is the producer, making decisions on which scenes will be included based on what will resonate most with viewers.
Key Concepts
-
Efficiency: Enhancing the effectiveness of business processes.
-
Stakeholder Alignment: Ensuring that all parties involved understand and agree on requirements.
-
Role of a Business Analyst: Acts as a bridge between business needs and technical solutions.
Examples & Applications
A Business Analyst who interviews stakeholders to gather requirements for a new software application.
In a recent project, the BA identified process inefficiencies that led to a 30% increase in operational efficiency.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
BA's role is to bridge a gap, find solutions and help the map.
Stories
Imagine a ship captain steering through rough waters, making decisions based on the crew’s insights — that’s like a BA navigating through business needs.
Memory Tools
Use the acronym BAR: Business Analysis, Requirements, and Solutions to remember the process.
Acronyms
Remember 'ECD' for Efficiency, Communication, Defined scope as key outcomes.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Business Analysis
The practice of enabling organizational change by defining needs and recommending solutions that deliver value.
- Business Analyst (BA)
A professional responsible for gathering, analyzing, and documenting business needs to recommend technical solutions.
- Project Manager (PM)
A person responsible for planning, executing, and closing projects to meet defined objectives within a specified time.
- Quality Assurance (QA)
The process or set of processes intended to ensure that a product or service meets specified requirements.
- Product Owner
An individual who is responsible for defining the features of the product and prioritizing them based on business objectives.
- BRD
Business Requirements Document, which outlines the requirements of a specific business need or project.
- FRD
Functional Requirements Document, detailing how the system will operate to fulfill the business requirements.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
