Cotton Textiles
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Cotton Textiles
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome everyone! Let's start with an introduction to cotton textiles. Can anyone tell me the historical methods used for producing cotton textiles?

They used to make them by hand, right? Like spinning and weaving by artisans?

Exactly! Hand spinning and handloom weaving were the traditional methods. These practices date back centuries. However, the introduction of power looms in the 18th century transformed the industry. Can anyone suggest why this technology was significant?

It allowed for faster production and larger quantities?

That's right! The ability to produce larger quantities quickly helped meet growing demand. Memory Aid: Think of 'POWER'—'P' for Production, 'O' for Output, 'W' for Weaving, 'E' for Efficiency, 'R' for Revolutionizing textile manufacturing. Now, why did traditional industries face challenges during the colonial period?

Because they couldn't compete with the machine-made cloth from England?

Correct! It was a tough period for our traditional industries. Remember, understanding these roots helps appreciate the industry's current landscape.
Economic and Employment Aspects
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's shift focus to the economic impact. How does the cotton textile industry contribute to employment?

It provides jobs to many people across different roles. Farmers, weavers, and workers involved in processing, for example.

Exactly! The industry is crucial for job creation, especially in rural areas. Can anyone think of how it also contributes to foreign exchange?

By exporting textiles to other countries?

Right again! Exporting manufactured cotton textiles not only brings in revenue but also strengthens trade relations. Here's a quick mnemonic to remember: 'TEXTILE'—'T' for Trade, 'E' for Export, 'X' for eXport revenues, 'T' for Transforming economies, 'I' for Income generation, 'L' for Livelihoods, 'E' for Employment!

That's helpful!
Geographical Distribution
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss where cotton textiles are mainly produced. Can anyone name some key regions?

Maharashtra and Gujarat are the big ones, right?

Yes! Those states have ideal conditions like raw material availability, labor, and climate. However, weaving is also decentralized. What does that mean?

It means that it happens in various areas rather than being concentrated in one place.

Exactly! And this decentralization helps incorporate traditional skills into the industry. To remember, think of 'COTTON'—'C' for Climate, 'O' for Origin of materials, 'T' for Transportation, 'T' for Traditional skills, 'O' for Occupation for many, and 'N' for Network of industries!

That simplifies it!
Challenges and Future Outlook
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's talk about challenges. What are some issues that affect the cotton textile industry today?

One issue is the quality of fabrics. Despite spinning high-quality yarn, weaving doesn’t always match that quality.

Exactly! This mismatch is problematic for competitiveness. Can anyone suggest how we might improve this?

Maybe more investment in training for weavers or upgrading technology?

Great suggestions! Memory Aid: Think of 'IMPROVE'—'I' for Investment in skills, 'M' for Modernization, 'P' for Partnerships with weavers, 'R' for Research in textile technology, 'O' for Open markets, 'V' for Value addition, 'E' for Export enhancement!

This is really interesting!
Conclusion and Review
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

As we conclude, can someone summarize what we've learned about cotton textiles?

We learned about its history, economic importance, where it's produced, and the challenges it faces!

Fantastic summary! Remember the key terms and mnemonics we've shared to aid your memory. The cotton textile industry is essential not just for its economic impact but for its role in preserving cultural heritage through traditional skills. Keep exploring these themes as you study!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The cotton textile industry plays a pivotal role in India's economy, being a major source of employment, export, and value addition in manufacturing. From its ancient hand-spinning roots to modern power looms, the industry has evolved significantly while remaining closely linked to agriculture and rural development.
Detailed
Cotton Textiles
The cotton textile industry is a cornerstone of India's manufacturing landscape. Traditionally, cotton textiles were produced through hand spinning and weaving techniques. However, with the introduction of power looms in the 18th century, the industry underwent significant transformation.
The industry's historical context is vital, as colonial influences disrupted traditional practices, particularly when competing with imported mill-made cloth. Post-independence, the sector has focused on revitalizing traditional methods while embracing technological advancements.
Key Aspects of Cotton Textiles
- Economic Contributions: As a major contributor to industrial production and foreign exchange, the cotton textile industry supports employment and aids in poverty alleviation, particularly in rural areas.
- Agricultural Ties: The industry is intrinsically linked to Indian agriculture, relying on cotton as a raw material, thereby providing livelihood to farmers and countless workers engaged in various stages of cotton processing.
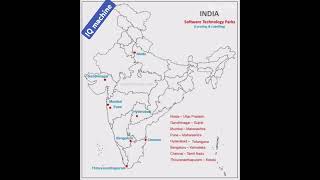
- Geographical Distribution: Initially concentrated in Maharashtra and Gujarat due to favorable conditions for cotton cultivation and processing, the industry is also decentralized to include traditional weaving practices across other regions.
- Challenges: Despite India's strengths in spinning, weaving often utilizes lower-quality yarn. Efforts to enhance weaving quality and integration of traditional crafts remain essential for the industry's growth.
- Future Outlook: Continuous modernization and better quality assurance are needed to remain competitive in the global textile market. The goal is to meet international standards, ensuring both self-sufficiency and export potential.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Historical Background of Cotton Textiles in India
Chapter 1 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In ancient India, cotton textiles were produced with hand spinning and handloom weaving techniques. After the 18th century, power-looms came into use. Our traditional industries suffered a setback during the colonial period because they could not compete with the mill-made cloth from England.
Detailed Explanation
Cotton textiles have a long history in India, starting from hand-spun and handwoven fabrics used by artisans. With the advancement of technology by the 18th century, machines like power-looms revolutionized production. However, during British colonialism, Indian textile industries faced challenges as they struggled to compete against cheaper, mass-produced textiles from England, which led to a decline in traditional methods.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it this way: Imagine a small bakery that makes delicious handcrafted bread. When a large factory starts producing cheap bread en masse, many customers flock to the factory bread because it's cheaper, making it hard for the small bakery to compete. This is similar to what happened to Indian textile producers when British mills began exporting cheaper textiles.
Geographical Distribution and Factors Influencing Cotton Textiles
Chapter 2 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In the early years, the cotton textile industry was concentrated in the cotton growing belt of Maharashtra and Gujarat. Availability of raw cotton, market, transport including accessible port facilities, labour, moist climate, etc. contributed towards its localisation.
Detailed Explanation
The initial success of the cotton textile industry in India largely depended on its geographical location, particularly in regions like Maharashtra and Gujarat, where the climate and agricultural conditions favored cotton cultivation. Key factors for this localization included the presence of raw materials (cotton), access to markets and transportation systems (like ports) for shipping products, and a moist climate that was favorable for textile production.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a farmer who grows apples in a region known for its fertile soil and optimal climate for apples. This means he can harvest and sell better apples compared to farmers in a desert. Similarly, the local conditions in Maharashtra and Gujarat allowed for better textile production due to favorable farming and shipping conditions.
Integration with Agriculture and Employment Generation
Chapter 3 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The industry has close links with agriculture and provides a living to farmers, cotton boll pluckers and workers engaged in ginning, spinning, weaving, dyeing, designing, packaging, tailoring and sewing.
Detailed Explanation
The cotton textile industry is intrinsically linked to agriculture as it relies on cotton, a vital agricultural product. This industry not only creates jobs for a wide range of workers in various stages of production—from picking cotton to sewing finished garments—but also enhances the livelihoods of farmers by creating a demand for raw cotton, thus forming a complete ecosystem.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the cotton textile industry like a tree with different branches—the trunk represents the farmers growing cotton, and each branch represents a step in the cotton processing journey like ginning or weaving. Each branch supports different birds (workers) and creates a larger ecosystem where all depend on each other to thrive.
Centralization and Decentralization in Production
Chapter 4 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
While spinning continues to be centralised in Maharashtra, Gujarat and Tamil Nadu, weaving is highly decentralised to provide scope for incorporating traditional skills and designs of weaving in cotton, silk, zari, embroidery, etc.
Detailed Explanation
In the cotton textile industry, the process of spinning yarn from cotton is primarily centralized in a few regions known for their production efficiency, while weaving remains decentralized. This decentralization allows various artisans from different regions to incorporate their unique traditional skills and designs, preserving cultural heritage in the textiles produced.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a big factory that makes toys in one location (like spinning) and many small craftspeople making unique toys in their own neighborhoods (like weaving). Each neighborhood has its own style, creativity, and tradition which keeps the craft diverse and interesting.
Challenges in Weaving Quality Production
Chapter 5 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Weaving supplies low quality of fabric as it cannot use much of the high quality yarn produced in the country. Weaving is done by handloom, powerloom and in mills.
Detailed Explanation
Although India excels in spinning high-quality yarn, the weaving process sometimes results in lower fabric quality. This happens because the weaving sector has not adopted the same level of technology that spinning has. Weaving occurs through various methods such as handlooms, powerlooms, and mills, but inefficiencies in these processes can lead to compromised product quality.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a chef who makes a fantastic cake batter (like spinning high-quality yarn) but poorly bakes it or uses old baking equipment (like outdated weaving technology), resulting in a cake that doesn't taste as great as the batter would suggest. The final product suffers because of the weaving process.
Employment and Economic Significance
Chapter 6 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The handspun khadi provides large scale employment to weavers in their homes as a cottage industry.
Detailed Explanation
Khadi, which is handspun and hand-woven cloth, is a significant part of the textile industry in India. It is not only eco-friendly but also provides ample job opportunities because it allows weavers to work from home, thus contributing to both the economy and rural livelihoods.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a community bakery where local residents come together to bake bread at home. They can produce bread without the need for a central factory, allowing them to earn an income while still taking care of family and community needs, similar to how khadi supports local weavers.
Key Concepts
-
Economic Importance: Cotton textiles significantly contribute to India's GDP and employment.
-
Historical Evolution: Transition from traditional handcrafting to modern mechanized production.
-
Agricultural Link: The industry is closely tied to agriculture, fostering rural development.
Examples & Applications
The production of khadi, handspun cotton fabric promoted by Mahatma Gandhi, reflects the traditional textile manufacturing approach.
Maharashtra's cotton mills exemplify industrial adaptation, producing fabrics on a large scale.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Cotton soft and fine, through looms it does align, spinning threads so bright, for clothes that feel just right.
Stories
Once in a village, artisans spun cotton by hand, creating beautiful fabrics that told stories of their land. With power looms, they wove faster, keeping tradition alive while embracing the future.
Memory Tools
To remember the significance: COTTON - C for Contribution, O for Opportunities, T for Trade, T for Technology, O for Occupation, N for National Identity.
Acronyms
POWER - P for Production, O for Output, W for Weaving, E for Efficiency, R for Revolution.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Cotton Textiles
Fabrics produced from cotton fibers, significant in India's manufacturing sector.
- Power Loom
A mechanized loom powered by electricity, allowing faster textile production.
- Textile Industry
The sector involved in the production of fabrics through spinning, weaving, and finishing.
- Agrobased Industry
Industries that rely on agricultural products as raw materials.
- Decentralized Weaving
The distribution of weaving operations across various regions instead of in centralized locations.
- Employment Generation
The creation of jobs in various sectors, significantly driven by industries.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
