Regional Studies/Area Studies
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Geography
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome class! Today, we're diving into geography as a vital discipline. Can anyone tell me what geography means?

Isn't it just about maps and places?

Great starting point! Geography indeed involves maps, but it's more than that. It combines the study of both physical features and human activities. Let's remember this: 'Geography = Earth + Description.'

Oh, so it includes how humans interact with the environment too!

Exactly! Geography explores that interaction, which is essential for understanding our world. Why do you think this relationship matters?

Maybe because it helps us understand different cultures?

Exactly! Understanding cultures and their environment is crucial for global citizenship. Remember: our interactions shape our surroundings.
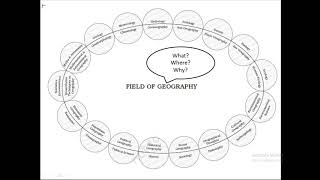
Branches of Geography
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's delve into the branches of geography. Can anyone name some branches?

Isn’t it physical and human geography?

Correct! Physical geography focuses on natural features, while human geography examines societal aspects. Together they provide a holistic view. Can someone tell me what biogeography studies?

It studies the distribution of plants and animals, right?

Exactly, well done! And why is understanding these distributions important?

To know how different life forms interact with their environment?

Yes! It’s about understanding ecosystems. Let's remember the acronym 'PHESC' for Physical, Human, Economic, Social, and Cultural aspects of geography.
Areal Differentiation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

We often use the term 'areal differentiation' in geography. What do you think it means?

Does it mean studying differences in landscapes and cultures?

Correct! It's about recognizing variations across different spaces. This helps us understand not just the 'what' and 'where', but also the 'why' of these differences. Why do you think knowing the 'why' is important?

So we can address issues like resource allocation?

Exactly! This knowledge is key for effective planning and management. Remember: 'Identify, Analyze, Explain'—this process is crucial in geography.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section delves into geography as a multidimensional discipline, emphasizing its role in exploring the relationship between physical and human aspects of the earth's surface. It discusses the systematic and regional approaches to geography, including area studies and examines the implications of geographical knowledge in real-world contexts.
Detailed
Regional Studies/Area Studies
This section examines geography as an integrating discipline that synthesizes knowledge from both natural and social sciences, leading to an understanding of spatial attributes and variations. Geography is framed as the study of areal differentiation, incorporating elements such as physical landscape and human activity. Notably, the section asserts that geography is not merely descriptive but investigates the dynamic interactions between humans and their environment.
The text also discusses the various branches of geography, including physical and human geography, alongside area studies that analyze specific macro, meso, and micro regions. By leveraging modern scientific techniques, such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS), geography enhances our comprehension of resource distribution, cultural variations, and societal development. Ultimately, the section emphasizes the relevance of geographical studies in national development and sheds light on the critical questions geography seeks to answer: what exists, where it exists, and why it exists.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding Regional Studies
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Regional Studies/Area Studies comprise Macro, Meso and Micro Regional Studies.
Detailed Explanation
Regional Studies focus on analyzing the characteristics of specific areas or regions. They can be divided into three scales: Macro, Meso, and Micro.
- Macro Regional Studies look at broad regions that encompass large geographical areas such as continents.
- Meso Regional Studies focus on smaller regions within a country or a larger area, such as states or provinces.
- Micro Regional Studies examine very localized areas, such as neighborhoods or districts within cities.
Each level of study allows geographers to analyze and understand the complexities and unique features of these places, which can include their culture, economy, and physical geography.
Examples & Analogies
Think of studying geography like being a detective. In a major investigation (Macro), you would start by looking at entire countries and how they interact globally. Then, you'd narrow down to specific states or provinces (Meso) to see what unique challenges they have. Finally, you might investigate a small town (Micro), where local events and people provide insights that bigger areas might miss.
Regional Planning
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Regional Planning comprises Country/Rural and Town/Urban Planning.
Detailed Explanation
Regional Planning focuses on how to effectively manage land and resources within a specific region. It includes two primary areas:
- Country/Rural Planning, which deals with agricultural land, rural development, and infrastructure in less populated areas.
- Town/Urban Planning, which focuses on cities and towns, addressing issues like transportation, housing, and public services. This planning ensures that regions can meet the needs of their populations while also considering environmental impacts.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a gardener who is planning a garden. They must think about how much space each plant needs (Urban Planning for towns) and how to use the overall land effectively (Rural Planning for wide areas). Just as a gardener organizes plants for the best growth, planners organize space to support a healthy community.
Regional Development
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Regional Development focuses on improving the economic and social well-being of a particular region.
Detailed Explanation
Regional Development is a crucial discipline that aims to raise the living standards within a specific area by enhancing its economic activity. This includes creating job opportunities, developing better infrastructure, and improving access to health and education. The goal is to ensure that all regions, especially those that are disadvantaged, can grow sustainably and equitably.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a small village where many people are unemployed. Regional Development initiatives might introduce training programs, improve transportation to larger cities for job opportunities, and build local businesses. Think of it as giving the village the tools to build itself up, making it thrive just like how we would seek to upgrade our personal skills to get a better job.
Regional Analysis
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Regional Analysis involves examining specific regions to understand their unique features and dynamics.
Detailed Explanation
Regional Analysis looks closely at particular regions to unpack their unique characteristics and challenges. This may include studying demographic trends, economic activities, cultural aspects, and environmental considerations to get a comprehensive picture of how a region operates. It's about understanding the interplay of various elements within an area.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a chef who is trying to create a new dish. They would need to analyze their ingredients (the characteristics of the region), understand how each ingredient affects the dish (the dynamics within the region), and finally, experiment to create a delicious meal. Similarly, geographers use Regional Analysis to blend different aspects of a region to understand it fully.
Key Concepts
-
Geography: The systematic study of the earth's surface and the relationships between human beings and their environment.
-
Areal Differentiation: The analysis of how and why phenomena vary across different locations.
-
GIS: A technology used for spatial analysis and data visualization in geography.
Examples & Applications
The region-specific agricultural practices vary due to climate, soil, and cultural influences.
Urban planning utilizes geographical information to manage city growth effectively.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Geography's a map, and history's a story, together they reveal our past and glory.
Stories
Once upon a time, a young explorer named Geo traveled through vast landscapes, meeting diverse cultures that taught him about areal differentiation.
Memory Tools
G.E.O - Geography Explains Our world!
Acronyms
CAMP for key geography components
Climate
Area
Movement
People.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Geography
The study of the earth's landscapes, environments, and the relationships between people and their environment.
- Areal Differentiation
The distinction and variation of phenomena across space.
- Biogeography
The study of the spatial distribution of biological organisms and ecosystems.
- GIS
Geographic Information Systems, a technology that allows for the mapping and analysis of spatial data.
- Cultural Geography
The study of the relationship between culture and geographic space.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
