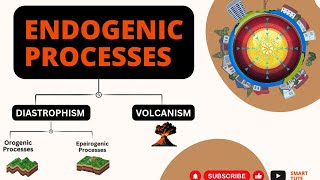
Diastrophism
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Diastrophism
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're exploring diastrophism – processes that move and elevate the earth's crust. Can anyone tell me what diastrophism involves?

Isn't it related to earthquakes and mountain building?

Exactly! Diastrophism includes orogenic processes, epeirogenic movements, earthquakes, and plate tectonics. It fundamentally describes how the crust changes over time. Remember: Diastrophism = *Dynamic crust movement*.

What do you mean by orogenic and epeirogenic processes?

Good question! Orogeny refers specifically to mountain-building efforts, while epeirogeny involves the broad uplift of large crustal areas without significant folding. Think of orogeny as specific and dramatic while epeirogeny is more general.

How do these processes affect the earth's features?

They shape landscapes! Orogenic processes create mountains, while epeirogenic movements can uplift plateaus. Both play critical roles in the topography we see.

So, these movements provide the earth with variety, right?

Exactly! The interplay of these forces results in the diverse geological features we encounter. Keep this in mind: *Forces create forms!*
Key Processes: Orogeny and Epeirogeny
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's explore orogeny and epeirogeny further. Who can summarize the difference between them?

Orogeny is about mountain-building, and epeirogeny is about uplifting larger parts of the crust?

Precisely! Orogeny involves severe deformations and folding while epeirogeny is a gentler process. What do you think each process contributes to the earth's surface?

Orogeny would create rugged terrains, while epeirogeny might lead to even plateaus.

Well done! And don't forget earthquakes—they can occur from both slow plate movements and sudden stress releases. Together, they shape our planet dramatically.

Are these processes happening all the time?

Great observation! Yes, the earth's crust is always dynamic, evolving slowly yet continuously. Let's remember: *Change is constant!.*
Impact of Diastrophism
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

How do you think diastrophism affects our environment and life on Earth?

It probably affects where we can build cities and how we farm!

Absolutely! Regions shaped by diastrophism provide different resources and risks. Remember: *Geology dictates geography!*

Is diastrophism only harmful?

Not at all! While it can cause challenges like earthquakes, it can also create rich soils and landscapes that support life. Think of it as both a sculptor and a destroyer.

And it shows the interdependence of natural processes!

Exactly! Everything is connected. Remember this: *Every force has its form*!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section on diastrophism defines the endogenic forces shaping the earth's crust through activities such as mountain building (orogeny), uplifts (epeirogeny), and tectonic movements. It emphasizes the dynamic nature of Earth's surface shaped over extensive periods, critically influencing geological and biological processes.
Detailed
Diastrophism: An In-Depth Summary
Diastrophism refers to all processes that elevate, move, or build parts of the earth's crust under the influence of endogenic forces. This section delves into critical geological processes categorized under diastrophism, including:
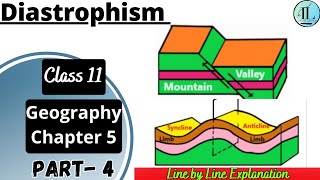
- Orogeny: Involves severe folding and the mountain-building process, primarily affecting long and narrow belts of the crust.
- Epeirogeny: Involves the uplift or warping of large sections of the crust without severe deformation.
- Earthquakes: Localized movements due to the release of built-up stress within the crust.
- Plate Tectonics: Concerns horizontal movements of crustal plates that contribute to various geological phenomena.
Through these processes, interactions in the crust lead to variations in pressure, volume, and temperature (PVT), which in turn instigate metamorphic changes in rocks. Importantly, understanding diastrophism is crucial for grasping how geological formations evolve and how they interact with human activity and natural systems.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Diastrophism
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
All processes that move, elevate or build up portions of the earth’s crust come under diastrophism.
Detailed Explanation
Diastrophism refers to the various processes that alter the Earth's crust. This includes any movement that causes deformation, whether that means raising land to create mountains or altering the shape of existing rock formations.
Examples & Analogies
Think of diastrophism like kneading dough. Just as the dough changes shape under pressure and manipulation, the Earth’s crust is constantly being pushed and pulled, reshaping the surface.
Types of Diastrophic Processes
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
(i) orogenic processes involving mountain building through severe folding and affecting long and narrow belts of the earth’s crust; (ii) epeirogenic processes involving uplift or warping of large parts of the earth’s crust; (iii) earthquakes involving local relatively minor movements; (iv) plate tectonics involving horizontal movements of crustal plates.
Detailed Explanation
The types of diastrophic processes include:
1. Orogenic Processes - These are responsible for mountain formation through the folding of the Earth's crust.
2. Epeirogenic Processes - These result in the lifting or warping of broad regions, which does not typically cause folding.
3. Earthquakes - These involve minor but significant movements associated with stress release in the crust.
4. Plate Tectonics - The horizontal movement of large plates on the Earth's surface that can cause various geological phenomena.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a massive, soft cheese block. If you push one side, it may lift up, creating folds (orogeny). If you press down gently on a broader section, it can warp but not fold (epeirogeny). Earthquakes are like sudden cracks appearing in this cheese as it shifts.
Effects of Diastrophism
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Through the processes of orogeny, epeirogeny, earthquakes and plate tectonics, there can be faulting and fracturing of the crust. All these processes cause pressure, volume and temperature (PVT) changes which in turn induce metamorphism of rocks.
Detailed Explanation
Diastrophism can lead to various geological changes like faulting and fracturing, which can alter landscapes dramatically. As rocks are subjected to different stresses, changes in pressure, volume, and temperature occur, leading to a transformation known as metamorphism, where existing rocks change forms.
Examples & Analogies
Think about a stress ball under pressure. As you squeeze it, the shape changes. Similarly, as tectonic forces act on rocks within the Earth, their structure can change significantly under extreme conditions.
Distinction between Orogeny and Epeirogeny
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Orogeny is a mountain building process whereas epeirogeny is a continental building process.
Detailed Explanation
The distinction is important in geological terms: orogeny involves more localized, intense pressure leading to mountain formation, while epeirogeny is about broader uplifts or depressions of larger areas of the continental crust without necessarily causing mountains.
Examples & Analogies
Think of building a tall sandcastle with concentrated effort at one spot (orogeny) compared to gently raising a whole patch of sand on a beach (epeirogeny), which might not create prominent structures but alters the height of the sand overall.
Key Concepts
-
Diastrophism: The dynamic processes that shape and uplift the Earth's crust through orogenic and epeirogenic forces.
-
Orogeny: A specific mountain-building process associated with severe crustal deformation.
-
Epeirogeny: A gentler uplift of large crustal areas not associated with severe folding.
Examples & Applications
The Himalayas were formed through intense orogenic processes.
The uplift of the Midcontinent Rift in the United States exemplifies epeirogenic processes.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Orogeny makes mountains tall, while epeirogeny uplifts all.
Stories
Imagine the land as a sleeping giant; orogenic processes awaken its mountains, while epeirogenic forces stretch it like a blanket, creating smooth plateaus.
Memory Tools
O.E.: Orogenic raises peaks, Epeirogenic lifts plains.
Acronyms
DREAM
Diastrophism Raises Earth's Amazing Mountains.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Diastrophism
Processes that move, elevate, or build up portions of the Earth’s crust.
- Orogeny
Mountain-building processes involving severe folding of the earth's crust.
- Epeirogeny
Uplift or warping of large areas of the earth's crust without severe deformation.
- Plate Tectonics
The theory explaining the movement of the Earth's lithosphere due to convection currents.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
