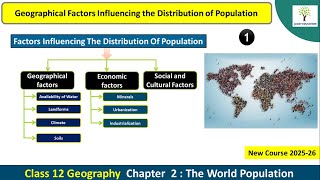
Factors Influencing the Distribution of Population
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Geographical Factors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's begin with geographical factors. Can someone tell me why availability of water is vital for population distribution?

Because people need water for drinking and agriculture?

Exactly! Areas abundant in freshwater sources like rivers often have higher populations. They are essential for agriculture, industries, and daily living, contributing to population density.

What about landforms? Do they affect where people live?

Great question! Landforms like flat plains are preferred for farming and infrastructure, while mountainous areas are less populated due to challenging living conditions. Remember, flat areas mean easier travel and farming!
Climate and Population Density
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Climate also plays a significant role. Can anyone think of a type of climate that may deter habitation?

Deserts! It's really hot and there’s not much water.

Precisely! Desert regions are often sparsely populated due to extreme conditions. On the flip side, regions with temperate or Mediterranean climates attract dense populations. Think about how comfortable living conditions can influence where people choose to settle!

So, does the climate also affect agricultural productivity?

Absolutely! Favorable climates lead to successful agriculture, supporting larger populations. This interaction between climate and agriculture is critical.
Urbanization and Migration
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's discuss urbanization. Why do you think many people migrate to cities?

Cities have more job opportunities and better access to healthcare.

Exactly! Urban areas provide employment, education, and amenities that attract people from rural areas. This is a classic push and pull phenomenon in migration.

Can you give an example of a mega city in the world?

Sure! Places like Tokyo or New York are mega cities that attract millions due to their diverse opportunities. Isn’t it fascinating how such dynamics affect population distribution?
Socio-Cultural Factors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's also look at socio-cultural factors. Can someone share how culture might influence where people live?

Places with significant historical or cultural importance can attract people.

Exactly! Religious and cultural sites can lead to increased populations in certain areas. Conversely, social unrest can drive people away from regions, creating a significant impact on demographics.

What policies can governments use to manage population distribution?

Governments might incentivize movement to less populated regions by offering tax breaks or improved infrastructure. This is a strategic response to balance population dynamics.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The uneven distribution of population is shaped by a variety of geographical, social, economic, and political factors. Key considerations include climate, availability of water, soil fertility, urbanization, industrial growth, and the influence of migration due to push and pull factors.
Detailed
Factors Influencing the Distribution of Population
The section explores how the world's population, which exceeds 6 billion, is not uniformly spread across the planet. This uneven distribution can be attributed to several crucial factors:
- Geographical Factors: Key factors include the availability of water, landforms such as flat plains versus mountainous areas, and soil types influencing agricultural productivity. Areas rich in resources tend to attract higher populations.
- Example: River valleys and plains are densely populated due to accessible water and fertile land, while deserts and mountainous terrains are sparsely populated.
- Climate: Comfortably mild climates tend to attract people, while extreme weather conditions deter habitation. Regions with moderate climates or conducive agricultural conditions are more densely populated.
- Example: Mediterranean regions flourish due to their favorable climate.
- Socioeconomic Factors: Urbanization leads to population density in cities due to better employment, education, and healthcare opportunities, leading rural populations to migrate to urban areas.
- Example: The rise of mega cities attracts vast numbers of migrants.
- Industrial Growth: Regions with industrial activities attract skilled labor, contributing to increased population density.
- Example: Industrial belts like the Kobe-Osaka region in Japan showcase high population density due to significant job opportunities.
- Social and Cultural Factors: Areas with cultural significance draw people, while socio-political unrest may lead to emigration.
Understanding these factors helps to comprehend global population dynamics and the implications for resource distribution and policy-making.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Availability of Water
Chapter 1 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Water is the most important factor for life. So, people prefer to live in areas where fresh water is easily available. Water is used for drinking, bathing and cooking – and also for cattle, crops, industries and navigation. It is because of this that river valleys are among the most densely populated areas of the world.
Detailed Explanation
Water is essential for survival and plays a crucial role in agriculture and industry. Regions with abundant fresh water sources, like rivers and lakes, attract more people because these resources support farming, drinking water, and industrial activities. Thus, river valleys are typically more populated compared to arid regions with limited water access.
Examples & Analogies
Think of how you might choose to live near a lake or river where you can fish, swim, and have fresh drinking water, rather than in a dry desert. Similarly, communities thrive around water sources as they enable farming and provide necessary resources for life.
Landforms
Chapter 2 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
People prefer living on flat plains and gentle slopes. This is because such areas are favorable for the production of crops and to build roads and industries. The mountainous and hilly areas hinder the development of transport networks and hence initially do not favor agricultural and industrial development.
Detailed Explanation
Flat land offers better opportunities for agriculture, infrastructure development, and construction of industries. In contrast, mountainous areas present challenges for farming due to steep terrains and can limit transport routes which are essential for trade and movement. As a result, populations tend to concentrate in flatter areas where human activities can flourish.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to build a school on a hill versus on flat land. On a hill, you'd face many obstacles like steep slopes, making it hard for children to get there. Hence, schools (and people) are usually found on flat land where it's easy to reach.
Climate
Chapter 3 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
An extreme climate such as very hot or cold deserts are uncomfortable for human habitation. Areas with a comfortable climate, where there is not much seasonal variation, attract more people. Areas with very heavy rainfall or extreme and harsh climates have low population.
Detailed Explanation
Climate significantly impacts human settlement. Mild climates with consistent temperatures attract people, making them more livable. Conversely, extreme conditions such as harsh winters or scorching summers deter settlement, resulting in lower population density in such regions. Thus, areas with moderate climates are often more densely populated due to the comfort they provide for living.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how tourists flock to sunny beach resorts but avoid harsh, snowy mountains during winter. Just like tourists prefer comfortable environments for their vacations, people seek reasonable climates for their everyday lives, leading to denser populations in warmer, more hospitable regions.
Soils
Chapter 4 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Fertile soils are important for agricultural and allied activities. Therefore, areas which have fertile loamy soils have more people living on them as these can support intensive agriculture.
Detailed Explanation
The quality of soil directly affects the ability to grow crops. Fertile soils yield better harvests, supporting more significant populations. People tend to settle in these areas to take advantage of the agricultural opportunities that fertile land provides, as opposed to less productive land, which can sustain fewer people.
Examples & Analogies
If you think of a garden, the freshness of soil determines how many flowers or vegetables can grow. Just like a well-maintained garden will attract a gardener to live near it, fertile lands draw people who can make a living from farming and agriculture.
Urbanisation and Employment Opportunities
Chapter 5 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Cities offer better employment opportunities, educational and medical facilities, better means of transport and communication. Good civic amenities and the attraction of city life draw people to the cities. It leads to rural to urban migration and cities grow in size.
Detailed Explanation
Urban areas draw populations due to the promise of improved life quality, such as jobs, education, and healthcare access. This urban to rural trend causes cities to expand as people leave rural areas seeking better opportunities. As cities grow, they can further attract more residents, creating a cycle of urbanization and population concentration.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a magnet that attracts iron filings. Cities act like that magnet for people, pulling them in with the promise of jobs, schools, and healthcare - just as the filings are drawn to the magnet, people migrate to cities for better opportunities.
Social and Cultural Factors
Chapter 6 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Some places attract more people because they have religious or cultural significance. In the same way, people tend to move away from places where there is social and political unrest. Many times, governments offer incentives to people to live in sparsely populated areas or move away from overcrowded places.
Detailed Explanation
Cultural and social factors significantly influence where people want to live. Regions with rich cultural heritage or religious importance pull in residents and tourists. Conversely, social unrest or instability drives people away from areas they find unsafe. Governments may also encourage population distribution by offering incentives in areas that need more residents, aiming to balance population densities.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine someone moving to a lively city known for its festivals and galleries, seeking a vibrant culture to enrich their life. Conversely, if they came from a place experiencing conflict, they would immediately seek safety and stability - illustrating how these social and cultural aspects strongly affect population distribution.
Key Concepts
-
Population distribution: The layout of populations with respect to geographical space.
-
Population density: The ratio of people in a given area.
-
Urbanization: The movement towards cities driven by socio-economic factors.
-
Migration: The movement of people which alters population dynamics.
-
Push and Pull Factors: Reasons behind migration that can either repel or attract individuals.
Examples & Applications
River valleys like the Nile and the Ganges are densely populated due to fertile land and water availability.
Countries like Bangladesh demonstrate high rural-to-urban migration due to burgeoning job opportunities in cities.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Water and soil, fertile and green, attract populations, a habitat seen!
Stories
Imagine a farmer named Jim who moved from a dry desert to the lush plains. He found water, good soil, and a welcoming village. Soon, others joined him, creating a bustling community!
Memory Tools
Use 'CWS' to remember key factors affecting population: Climate, Water, Soil.
Acronyms
Remember 'DUPS' to recall the factors
Density
Urbanization
Push/Pull factors
Soil.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Population Distribution
The manner in which people are spread across a given area.
- Population Density
The number of people per unit area, usually expressed in persons per square kilometer.
- Urbanization
The movement of people from rural areas to urban areas, resulting in city growth.
- Migration
The movement of people from one place to another, often influenced by push and pull factors.
- Push Factors
Conditions that drive people away from their original location, such as unemployment or conflict.
- Pull Factors
Attractive conditions that draw people to a new location, like job opportunities or better living standards.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
