Conjunctions: The Joining Words (Connectors)
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Coordinating Conjunctions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into conjunctions. Let’s start with coordinating conjunctions. Who can tell me what a coordinating conjunction does?

Isn't that when they connect two equal parts of a sentence?

Exactly! They connect words, phrases, and clauses of equal rank. Remember the acronym FANBOYS: For, And, Nor, But, Or, Yet, So. Can someone give me an example using 'and'?

I like pizza and pasta!

Perfect! Now, let's try using 'but' in a sentence. Who would like to give it a shot?

I want to go to the park, but it’s raining.

Great example! Coordinating conjunctions are essential for creating balance in your sentences. So let’s summarize: they connect elements of equal importance in a sentence.
Subordinating Conjunctions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's shift gears to subordinating conjunctions. What can someone tell me about them?

They connect a dependent clause to an independent clause!

Exactly right! They describe relationships such as time, cause, and condition. Examples include 'because,' 'although,' and 'if.' Let’s practice. Can someone create a sentence using 'if'?

I will go to the party if I finish my homework.

Good job! Now, what about using 'because' in a sentence?

I was late because my bus broke down.

Nice work! Remember that subordinating conjunctions are crucial for adding complexity to your sentences, allowing you to express more detailed thoughts.
Applying Conjunctions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s apply what we've learned! I’ll say a sentence, and you tell me the conjunction used. 'I could go for a walk, but it looks like rain.' What’s the conjunction?

'But' connects the clauses!

Great! Next sentence: 'When the rain stops, we can go outside.' What’s the conjunction here?

'When.' It’s a subordinating conjunction.

Exactly! Well done. Conjunctions are everywhere, and understanding them will help your writing flow better. Let’s summarize: always identify whether you’re using coordinating or subordinating conjunctions.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Conjunctions are critical tools in English, categorized as coordinating and subordinating conjunctions. This section explores their definitions, functions, and examples, emphasizing how they enhance sentence structure and clarity.
Detailed
Conjunctions: The Joining Words (Connectors)
Conjunctions are vital components of the English language, serving as bridges that connect words, phrases, clauses, and entire sentences. They are essential for creating complex and compound sentences, which help convey more nuanced meanings and relationships between ideas. Conjunctions are divided into two main categories:
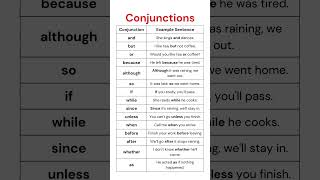
1. Coordinating Conjunctions
These conjunctions connect elements of equal grammatical rank, such as two nouns, adjectives, or independent clauses. A helpful mnemonic to remember the seven coordinating conjunctions is "FANBOYS," which stands for:
- For
- And
- Nor
- But
- Or
- Yet
- So
Examples:
- I like apples and bananas. (Joins two nouns)
- She wanted to go, but she was tired. (Joins two independent clauses)
2. Subordinating Conjunctions
These conjunctions link a dependent clause (which cannot stand alone as a complete sentence) to an independent clause. They establish a relationship of dependence, providing context or conditions.
Common Subordinating Conjunctions:
- because, although, while, if, when, since, unless, after, before
Example:
- I will eat when I finish my homework. (Joins a dependent clause to an independent clause)
Understanding conjunctions helps students develop more sophisticated writing skills by allowing them to construct sentences that reflect complex thoughts and relationships.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
What is a Conjunction?
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A conjunction is like a bridge; it connects words, phrases, clauses, or sentences.
Detailed Explanation
A conjunction is a part of speech that helps connect different elements in sentences. Just as a bridge connects two separate areas, conjunctions connect words, phrases, or even complete sentences, facilitating smoother communication.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine if every time you wanted to speak, you had to pause between each word and start a new sentence. It would make conversations very choppy and hard to follow. Just like how a bridge allows smooth passage over water, conjunctions offer a way to create fluid, understandable sentences.
Coordinating Conjunctions
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Coordinating Conjunctions: Join elements of equal grammatical rank. Remember the acronym FANBOYS: For, And, Nor, But, Or, Yet, So.
Example: I like apples and bananas. (Joins two nouns)
Example: She wanted to go, but she was tired. (Joins two independent clauses)
Detailed Explanation
Coordinating conjunctions are used to connect words or groups that are similar in structure. The acronym FANBOYS helps remember these conjunctions: 'For', 'And', 'Nor', 'But', 'Or', 'Yet', and 'So'. For instance, 'and' connects similar items like 'apples and bananas', while 'but' connects contrasting ideas, as in 'She wanted to go, but she was tired'. This function is essential for creating complex sentences with clarity.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like making a fruit salad. If you had apples and bananas, you'd mix them together to create a delightful dish. If you wanted to contrast two fruits—like sweet strawberries and sour lemons—you'd make a choice. Just as you wouldn't pick just one fruit to express your taste, conjunctions let you combine different ideas in a single sentence.
Subordinating Conjunctions
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Subordinating Conjunctions: Join a dependent (or subordinate) clause to an independent clause. The dependent clause cannot stand alone as a complete sentence.
Examples: because, although, while, if, when, since, unless, after, before.
Example: I will eat when I finish my homework. (Joins a dependent clause to an independent clause)
Detailed Explanation
Subordinating conjunctions connect dependent clauses to independent clauses. A dependent clause cannot form a complete sentence on its own; it needs the main clause to provide context. For example, 'I will eat when I finish my homework' includes 'when I finish my homework' as a dependent clause, providing timing for the action in the independent clause 'I will eat'. This structure allows for added information while maintaining grammatical correctness.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like a movie where a character's backstory is provided as a subplot. You wouldn't understand the character's motivations fully without the main scenes. Similarly, subordinating conjunctions add depth to sentences, making the overall message richer and clearer.
Key Concepts
-
Conjunctions: Essential for connecting elements in sentences.
-
Coordinating Conjunctions: Join words or clauses of equal rank.
-
Subordinating Conjunctions: Connect dependent clauses to independent clauses.
Examples & Applications
I like apples and bananas. (Joins two nouns)
She wanted to go, but she was tired. (Joins two independent clauses)
2. Subordinating Conjunctions
These conjunctions link a dependent clause (which cannot stand alone as a complete sentence) to an independent clause. They establish a relationship of dependence, providing context or conditions.
Common Subordinating Conjunctions:
because, although, while, if, when, since, unless, after, before
Example:
I will eat when I finish my homework. (Joins a dependent clause to an independent clause)
Understanding conjunctions helps students develop more sophisticated writing skills by allowing them to construct sentences that reflect complex thoughts and relationships.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Coordinating connects with ease, join words together just like breeze.
Stories
Imagine two friends at a park. One can jump high, the other can run fast. They meet in the middle, connecting their skills to play together. Just like conjunctions connect ideas!
Memory Tools
Remember FANBOYS for coordinating conjunctions: For, And, Nor, But, Or, Yet, So.
Acronyms
SWABBI for subordinating conjunctions
Since
When
Although
Because
Before
If.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Conjunction
A word that connects words, phrases, clauses, or sentences.
- Coordinating Conjunctions
Conjunctions that join elements of equal grammatical rank.
- Subordinating Conjunctions
Conjunctions that join a dependent clause to an independent clause.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
