Factors Affecting Friction
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Friction
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’re exploring friction! Friction is the force that opposes motion between surfaces. Who can tell me why we notice friction when we slide a book across a table?

Maybe because the surfaces are not perfectly smooth?

Exactly! Surface texture affects friction. Rough surfaces increase the friction due to more *interlocking*. Remember the phrase 'Rough equals Tough!'

What about smooth surfaces? Like glass?

Good question! Smooth surfaces have less friction, making sliding easier. This shows how different surfaces can change the game of motion!
What Influences Friction
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's talk about what influences friction. Can anyone tell me one thing that might increase friction?

Maybe the weight of the objects?

Correct! The *normal force*, or how hard the surfaces press against each other, greatly impacts friction. More weight increases that force, thus increasing friction.

So, if we push down harder on a brick, it will be harder to slide?

Right! Always remember: *Press hard, slide harder!*
Material Differences
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s do a comparison of materials. If I wrapped a brick in jute and then in plastic, what do you think would happen when we pull them?

I think the jute will create more friction.

That’s right! The rough texture of jute means more friction compared to the smooth plastic. Remember the acronym: *Jute's a Juggernaut of Friction!*

So friction changes depending on the materials, right?

Exactly! Different materials can either help or hinder movement depending on their interaction!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section discusses how friction opposes motion between surfaces, influenced by their texture, the force pressing them together, and the nature of their interaction. Specific activities illustrate these principles, emphasizing that friction is not uniform across different surfaces.
Detailed
Factors Affecting Friction
Friction is a force that resists the motion of two surfaces sliding against each other. It depends on various factors:
1. Surface Texture: Rough surfaces typically produce more friction than smooth surfaces due to greater interlocking of irregularities on their surfaces. For example, pushing a brick over different materials demonstrates varying frictional forces influenced by material textures.
2. Normal Force: The frictional force increases when surfaces are pressed together more strongly. This relationship is observed through activities involving bricks that show that a heavier brick requires more force to start its movement due to greater friction.
3. Type of Materials: Different materials exhibit different frictional properties. For instance, fabric like jute creates more friction when wrapped around a brick compared to a smooth plastic surface.
This section also underscores the importance of friction in everyday life and its various applications, from safety in walking to mechanisms in machines. The activities framed in this section illustrate these concepts in a practical, engaging way.
Youtube Videos







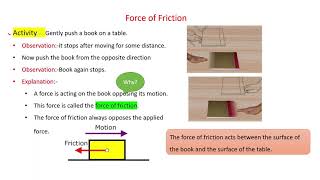
Key Concepts
-
Friction is a resistive force that opposes motion between sliding surfaces.
-
Surface texture greatly influences the amount of friction produced.
-
The normal force, or the weight applied to the surfaces, directly affects friction.
-
Different materials can create varying levels of friction depending on their textures.
Examples & Applications
Pushing a brick across a wooden table versus a glass table: the brick moves more easily over glass due to lower friction.
The difference in sliding a box over sandpaper compared to moving it over smooth tile shows how material texture impacts friction.
Using lubricants like oil on machinery helps decrease friction and enhance efficiency.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Friction is a sneaky foe, opposing motion, fast or slow!
Stories
Imagine two friends trying to slide down a slide; the rougher the slide, the harder it is for them to go down. That's friction!
Memory Tools
Remember the acronym FRICTION: Forces Resist Interlocking Contact To Oppose Normal motion.
Acronyms
FRICTION
Forces Resist Interface Contact To Increase Or Neutralize motion.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Friction
A force that opposes the relative motion between two surfaces in contact.
- Normal Force
The force perpendicular to the surfaces in contact that affects friction.
- Interlocking
The engagement of surface irregularities that increases friction.
- Static Friction
The frictional force that needs to be overcome to start moving an object at rest.
- Sliding Friction
The frictional force acting on an object in motion sliding against another surface.
- Rolling Friction
The resistance encountered when an object rolls over a surface.
- Lubricants
Substances used to reduce friction between surfaces.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
