EIA Procedures: Environmental Clearance for Project
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to EIA Procedures
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome class! Today, we are diving into the Environmental Impact Assessment, or EIA, procedures. Can anyone tell me why obtaining an EIA is important before starting a civil engineering project?

I think it's to make sure that we don’t harm the environment while building.

Absolutely! The primary goal is to assess and mitigate any adverse environmental impacts. Let's talk about the four main stages of the EIA process: screening, scoping, public consultation, and appraisal. Can anyone recall what screening involves?

Is that where you check if the project requires an EIA?

Correct! Screening helps determine whether an EIA is necessary based on the project's category. This leads us to the next step, scoping. It defines the issues and impacts that need to be addressed. Any questions so far?
Public Consultation and Appraisal
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's move on to the public consultation phase. Why do you think public involvement is crucial in the EIA process?

It gives the community a chance to voice their opinions and concerns, right?

Exactly! Public consultation ensures transparency and allows stakeholders to express their views. Following this, we have the appraisal phase, where experts review the EIA report. What do you think happens after this stage?

Is it when they either approve or reject the project?

Yes! The clearance or rejection letter follows the appraisal, which is a critical point in the project timeline. Let’s summarize: screening identifies the need for an EIA, scoping defines issues, public consultation engages stakeholders, and appraisal reviews findings.
Documentation and Submission
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand the stages, let’s talk about the documentation process. What forms do project proponents need to submit?

Form 1 and Form 1A, right?

That's right! Form 1 captures general project information, while Form 1A is a checklist for environmental impacts. Why is it important to have detailed information in these forms?

Because it helps decision-makers understand the potential impacts and mitigation strategies!

Exactly! Providing thorough and clear information contributes to a more effective assessment process. Does everyone feel comfortable with the documentation requirements?
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section describes the structured EIA procedures mandated by the MoEF, which includes stages such as screening, scoping, public consultation, and appraisal for various project categories, emphasizing the importance of thorough assessment to mitigate environmental impacts. It also details the steps involved in the clearance process, including project location assessment, public hearings, and documentation required for submission.
Detailed
In the realm of civil engineering, the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) procedures are critical for ensuring that projects consider their environmental implications. The EIA Notification of 2006 instituted mandatory Environmental Clearances, involving a multi-stage process: screening, scoping, public consultation, and appraisal. The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF) categorizes projects into ten sectors and specifies the documentation required based on the project's category, affecting the degree of scrutiny and the necessity for an EIA report. The steps in the EIA process include: 1) location identification; 2) assessment of whether an EIA is needed; 3) preparation and submission of EIA reports to relevant authorities like the State Pollution Control Board (SPCB); 4) conducting public hearings; and 5) receiving formal clearance from the MoEF or state government. Each step incorporates stakeholder communication and public involvement, illustrating the commitment to sustainable development and regulatory compliance in civil engineering projects. Following thorough appraisal, projects receive clearance valid for five years, ensuring that environmental responsibilities are upheld throughout the construction and operation lifecycle.
Youtube Videos

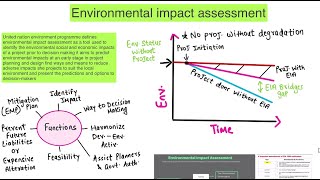




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Environmental Clearance
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
During project planning and pre-design, a critical step is acquiring the Environmental Clearance. The EIA Notification of 2006 mandated Prior Environmental Clearance, which involves four stages namely, screening; scoping; public consultation; and appraisal, for certain category of projects.
Detailed Explanation
Environmental Clearance (EC) is an essential requirement for construction projects to ensure that they comply with environmental regulations. This process is governed by the EIA Notification of 2006, which outlines that before a project can proceed, it must go through a series of four distinct stages: screening, scoping, public consultation, and appraisal.
1. Screening: This first stage involves determining whether a project requires an EIA based on its potential environmental impacts.
2. Scoping: This second stage identifies the key environmental issues that need to be considered in the EIA.
3. Public Consultation: Engaging with the community and stakeholders to gather their input on the project.
4. Appraisal: This final stage assesses the EIA report to determine whether to grant or deny the environmental clearance.
Examples & Analogies
Think of acquiring Environmental Clearance as getting permission before building a house. Just like a city might require plans to be submitted to ensure the house won't harm the neighborhood, an Environmental Clearance ensures that a construction project won't negatively impact the environment. This process allows community voices to be heard, similar to a neighborhood meeting where concerns about construction impacts are discussed.
Role of the Ministry of Environment
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF), GoI, manages and publishes EIA Notifications and develops Sector specific Standard Terms of References (ToR) and manuals for the different sectors.
Detailed Explanation
The MoEF is responsible for overseeing the implementation of the Environmental Clearance process. They publish various EIA Notifications that outline the standards and procedures required for different types of projects. Additionally, the MoEF creates sector-specific Terms of Reference (ToR) that guide project proponents on how to conduct their Environmental Impact Assessments appropriately for their respective industries.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a school principal who sets rules for different class subjects. The principal, like the MoEF, determines what each teacher needs to focus on for their subject area, ensuring everything aligns with school policies while allowing for tailored approaches that suit each subject.
Categorization of Projects
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The MoEF categorises all projects under ten sectors, i.e., (1) Mining, (2) Mineral Beneficiation, (3) Ports and Harbours, (4) Airports, (5-A) Building Construction, (5-B) Townships, (6) Asbestos, (7) Highways, (8) Coal Washery, (9) Aerial Ropeways, and (10) Nuclear power plants, Nuclear fuel processing plants and Nuclear waste management plants, and states that certain type (B) do not require to submit an EIA report for the clearance.
Detailed Explanation
The MoEF organizes projects into categories based on their environmental impact potential. There are ten sectors, including mining and highways, designated by specific rules. For certain ‘Type B’ projects, the requirements are less strict, meaning they may be exempt from needing to submit a detailed Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) report.
Examples & Analogies
Think of project categorization like sorting food in a grocery store. Some foods, like fresh produce, might have fewer regulations for handling, while others, like raw meat, have stricter guidelines due to health risks. Similarly, the MoEF categorizes projects based on their potential environmental risk.
Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) Methodology
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
EIA methodology, as explained in earlier Unit, has various steps, namely: Screening, Scoping, Impact Analysis, Mitigation, Reporting, Review of EIA, Decision-Making, and Post Monitoring, to develop a report on the state of affairs of the proposed project and its possible impact on the environment.
Detailed Explanation
EIA methodology involves a systematic process to evaluate the environmental consequences of a proposed project. Here's a breakdown of the key steps:
1. Screening: Determines whether an EIA is necessary.
2. Scoping: Identifies the significant issues to be assessed.
3. Impact Analysis: Evaluates the potential environmental effects of the project.
4. Mitigation: Suggests measures to minimize negative impacts.
5. Reporting: Compiles findings into an EIA report.
6. Review of EIA: Experts evaluate the EIA report.
7. Decision-Making: Authorities decide whether to approve the project.
8. Post Monitoring: Ongoing monitoring of impacts once the project is underway.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the EIA process as a doctor’s check-up appointment. Just as a doctor checks vital signs, health history, and conducts tests (analogous to the EIA steps) before making health recommendations, an EIA assesses possible environmental issues before allowing a project to proceed.
Step-by-Step Guide to Getting Environmental Clearance
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
To begin an Environmental Clearance for Project, following are the steps outlined by the Centre for Science and Environment, India; Step 1: Project proponent identifies the location of proposed plant after ensuring compliance with existing siting guidelines...
Detailed Explanation
The process of obtaining an Environmental Clearance is outlined in several steps:
1. Identify Location: Ensure compliance with siting guidelines.
2. Check Purview: Determine if the project needs environmental clearance.
3. Conduct EIA: If required, prepare an EIA report.
4. Public Hearing: Conduct hearings to gather public input.
5. Submit Application: File for Environmental Clearance with required documentation.
6. Environmental Appraisal: MoEF scrutinizes the application and may conduct site visits.
7. Clearance Decision: Receive approval or rejection for the project.
Examples & Analogies
This process is like filing for a building permit to construct a new house. You first check local zoning laws (step 1), confirm you comply with building codes (step 2), prepare and submit your building plans (step 5), and finally await feedback from the local council (step 7), before getting approval or denial.
Key Concepts
-
Environmental Clearance: A formal approval required to ensure that a project adheres to environmental regulations.
-
Screening: The first step to determine if an EIA is required for a project.
-
Public Hearing: A meeting conducted to gather feedback from the public regarding their concerns about a proposed project.
Examples & Applications
Example of a mining project requiring EIA based on its potential environmental impacts on surrounding ecosystems.
A case where public consultation altered the planning of a development project to better suit community needs.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
EIA steps are quite clear, screening, scoping, public cheer, then appraisal we hold dear!
Stories
Imagine a town planning a new park. First, they screen the land, then scope out the effects, consult with local families during a public meeting, and finally, the decision-makers appraise the gathered feedback before giving a green light.
Memory Tools
Remember 'SSPA' for EIA: Screening, Scoping, Public Consultation, Appraisal!
Acronyms
Use the acronym 'EIA' to remember Environmental Impact Assessment, focusing on environmental effects of construction projects.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- EIA (Environmental Impact Assessment)
A systematic process that evaluates the potential environmental impacts of a proposed project before it begins.
- MoEF (Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change)
The Indian government ministry responsible for the planning and implementation of policies related to environment and forest.
- Public Consultation
A stage in the EIA process that involves engaging stakeholders and the community to gather input and feedback.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
