Definition of Durability
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Durability
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's start discussing the definition of durability. Importantly, durability refers to concrete's ability to resist various forms of deterioration over its service life. Can anyone tell me why durability is crucial in concrete construction?

Isn't it important so that structures last longer and don't require constant repairs?

Exactly! It directly influences the longevity and lifecycle cost of the structure. We often hear that durability is a combination of strength and resistance to the environment. Who can summarize that relationship?

Durability equals strength plus resistance to things like water and chemicals.

Perfect! This relationship emphasizes that a strong concrete structure might still fail if it doesn’t withstand environmental stresses. Let's move on to the importance of durability.
Implications of Durability
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we've defined durability, let’s explore its importance. Why do you think durability affects the life and maintenance of structures?

It probably reduces the need for repairs and saves money in the long run.

Exactly! Durable structures reduce maintenance and repair costs significantly and enhance safety and sustainability. Can anyone name a type of environment where durability becomes even more critical?

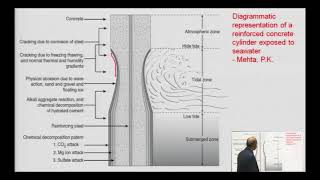
Marine environments, where salt and moisture can damage the concrete quickly.

Great example! Structures in aggressive environments need to be designed with high durability in mind. Always remember, strong initial construction does not guarantee long-term performance unless durability is properly accounted for.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section explains that the durability of concrete is not only about its strength but also about its ability to withstand various environmental factors that may lead to deterioration. Understanding durability is crucial for developing long-lasting concrete structures.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Durability is paramount for the longevity and performance of concrete structures. Defined as the ability of concrete to resist weathering, chemical attacks, and other forms of deterioration while retaining its engineering properties, durability significantly impacts the lifecycle cost of a structure.
According to IS 456:2000, "A durable concrete is one that performs satisfactorily under the expected exposure conditions during its service life." The relationship can be summarized with the equation: Durability = Strength + Resistance to Environment. This emphasizes that both the inherent strength of concrete and its resistance to environmental challenges like water, chemicals, and temperature fluctuations are essential components of durability.
The significance of understanding durability extends beyond initial design to include maintenance, safety, and sustainability aspects essential in civil engineering.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding Durability of Concrete
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Durability of concrete refers to its ability to resist weathering action, chemical attack, abrasion, or any other process of deterioration while maintaining its desired engineering properties over its service life.
Detailed Explanation
This definition establishes that durability is about how well concrete can withstand various factors that could lead to its deterioration. It highlights that concrete must not only retain its strength but also resist environmental factors that can cause damage, like weather, chemicals, and wear and tear. Essentially, durability encompasses a concrete structure’s ability to last over time without significant deterioration.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a high-quality smartphone. It can be powerful with great specifications, but if it can't withstand drops, water, or dust, it won't last long. Similarly, concrete that is strong but not durable may fail prematurely just like the phone that breaks easily.
IS 456:2000 Definition
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
According to IS 456:2000, “A durable concrete is one that performs satisfactorily under the expected exposure conditions during its service life.”
Detailed Explanation
IS 456:2000 is a standard in the concrete industry that defines what durable concrete is. It indicates that not only should concrete be strong but it must also perform well in the conditions it is expected to face during its use. This reinforces that the environmental context and exposure conditions are critical factors in determining a concrete's durability.
Examples & Analogies
Think about clothing materials. A winter coat made of lightweight fabric may look good but won't keep you warm in heavy snow. Similarly, concrete needs to be suited for its environment – just being strong isn't enough if it can't handle exposure to weather or chemicals.
Equating Durability to Resistance
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Durability = Strength + Resistance to Environment (Water, Chemicals, Temperature, etc.)
Detailed Explanation
This equation provides a simplified understanding of durability. It states that durability is not just about the concrete's inherent strength but also how well it can resist external environmental factors like water, chemicals, and extreme temperatures. A durable concrete structure effectively combines both robust material properties and environmental resistance.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a superhero. Just having incredible strength is not enough; the superhero must also have protective abilities that defend against attacks. Similarly, for concrete, both strength and the ability to fend off environmental 'attacks' contribute to its overall durability.
Key Concepts
-
Durability: Ability to resist deterioration over time.
-
Strength: The inherent ability of concrete to withstand imposed loads.
-
Environmental Resistance: Concrete's ability to endure environmental stresses such as chemicals and moisture.
Examples & Applications
A concrete bridge designed for a coastal environment would require additional durability measures such as a lower water-cement ratio and more robust materials to resist chloride attack.
In a sewage treatment plant, concrete must be durable against chemical attacks, which may involve using specific types of pozzolanic materials.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Strength is firm, durability's key, resist the storms, and you shall see!
Stories
Once a bridge stood tall by the sea, unaware of salt's destructive spree. It seemed strong at first, but cracks began to show, a lesson learned: durability, you'd better know!
Memory Tools
SPECK: Strength, Permeability, Environment, Curing, Key properties.
Acronyms
DURE
Durability
Usefulness
Resistance
Efficiency in concrete.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Durability
The ability of concrete to resist weathering action, chemical attack, and physical deterioration while maintaining its intended engineering properties.
- Permeability
The ability of concrete to resist the ingress of water, air, and aggressive chemicals.
- WaterCement Ratio
The ratio of the weight of water to the weight of cement used in a concrete mix, which influences strength and durability.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
