Hotspot Mitigation for Virtual Machine Migration
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Hotspot Mitigation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Alright class, today we're diving into hotspot mitigation in virtual environments. Can someone explain what we mean by 'hotspot' in resource management?

Isn't it when the demand for resources becomes too high for a physical server?

Exactly! A hotspot occurs when the demand for CPU, memory, or disk I/O from various VMs exceeds the host's capacity, causing performance issues. This brings us to the need for hotspot mitigation strategies. Why do you think it's crucial to address these hotspots?

To prevent slowdowns and ensure that services remain available, right?

Correct, it’s all about maintaining consistent performance. Let's remember this with the acronym 'PEAR' — Performance, Efficiency, Availability, Reliability. It summarizes our goals for hotspot management. Can anyone think of a situation that might lead to a hotspot?

Maybe during a sudden spike in website traffic?

Yes, bursting loads during events like sales can cause this! Great connections, let’s move onward.
Live VM Migration Process
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s delve into live VM migration. Can someone lead off with the first step?

Um, I think it starts with connecting the source and destination hypervisors?

Correct! This step sets up the communication channel between the two hosts. After that, we prepare the new environment. What happens next?

We copy the VM’s memory iteratively?

Absolutely! This pre-copy phase transfers most of the memory in several iterations. One key element here is tracking dirty pages. Who can explain what that means?

Dirty pages are those that get modified after being copied, right? So we need to keep updating them.

Exactly! It’s a crucial factor in minimizing the time the VM is paused during migration. Finally, what do we do at the end?

After copying everything, we cut over the network and storage connections and resume the VM!

Great recap! Remember, the transition to the new host should be imperceptible for users, ensuring service continuity.
Resource Provisioning and Management
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s talk about resource provisioning methods next. Who remembers the difference between static and dynamic provisioning?

Static provisioning allocates resources based on estimations, while dynamic adjusts resources based on real-time usage.

Exactly! Dynamic provisioning is key in cloud environments. Can anyone name a technology or framework focused on proactive hotspot mitigation?

The Sandpiper architecture?

Yes! The Sandpiper architecture includes components like the Resource Profiling Engine and Hotspot Detector. Why do you think these components are important?

They help to analyze usage data and predict future hotspots to avoid performance issues.

Great insight! By predicting demand, we can mitigate hotspots before they arrive, ensuring efficient resource use.
Comprehensive Strategies
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s summarize the comprehensive hotspot mitigation strategies. Who can list some we’ve discussed?

We talked about dynamic resource allocation and intelligent VM placement!

And proactive monitoring and predictive analytics!

Exactly! Load balancing and disaster recovery orchestration are also essential strategies. Remember, the aim is to optimize performance and ensure user satisfaction. Any questions before we wrap up?

Just to clarify, how does auto-scaling fit into all of this?

Great question! Auto-scaling helps dynamically adjust VM instances based on load, ensuring that resource usage is efficient even as demand fluctuates. Excellent participation today, everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section outlines the importance of hotspot mitigation for resource management in virtualized environments, detailing various workload characteristics, dynamic provisioning methods, the Sandpiper architecture, and outlining the steps of live VM migration as a critical strategy for achieving performance optimization.
Detailed
In-depth Summary of Hotspot Mitigation for Virtual Machine Migration
In virtualized data centers and cloud infrastructures, resource management challenges arise due to dynamic workloads that can create resource 'hotspots.' A hotspot occurs when the aggregate demand for a resource by virtual machines (VMs) exceeds the available capacity on a physical host, leading to performance degradation.
Workload Characteristics
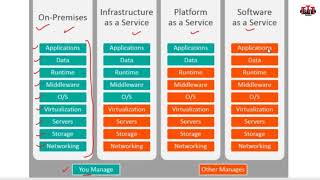
Workloads can be constant, bursting, cyclical, I/O intensive, or CPU intensive, each posing distinct challenges for resource allocation. The shift from static to dynamic resource provisioning allows for better performance. Static provisioning leads to underutilization, while dynamic provisioning tailors resources based on current demand.
Sandpiper Architecture
The Sandpiper architecture is a conceptual framework aimed at proactive hotspot mitigation. It includes a Resource Profiling Engine for continuous monitoring, a Hotspot Detector to anticipate potential hotspots, and a VM Placement and Migration Manager that facilitates optimal VM hosting decisions. This architecture enhances energy efficiency and resource utilization.
Migration Techniques
Live VM migration enables the seamless transfer of VMs between hosts without downtime, which is essential for maintaining service availability. The migration process involves preparing the destination host, iteratively copying memory (pre-copy phase), pausing the VM to transfer any remaining data (stop-and-copy), followed by cutover to the new host and resuming operations.
Overall Strategies
The section emphasizes diverse strategies for mitigating hotspots, including intelligent VM placement based on current usage, proactive monitoring to predict demand, and load balancing to distribute resource demands evenly. Collectively, these strategies contribute to enhanced performance and efficient resource management in cloud environments.
Youtube Videos








Key Concepts
-
Hotspot: A situation where resource demand exceeds supply, leading to performance issues.
-
Dynamic Provisioning: Automated resource allocation method responding to real-time demand.
-
Live VM Migration: Moving VMs between hosts without downtime, ensuring service continuity.
-
Sandpiper Architecture: A framework designed for proactive resource management and hotspot mitigation.
-
Resource Profiling Engine: Monitors resource utilization to predict and identify hotspots.
Examples & Applications
An e-commerce site experiences high traffic during flash sales, creating CPU and memory hotspots that require VM migration.
A finance application running batch processing at month-end demonstrates cyclical loads, necessitating dynamic resource adjustments to avoid hotspots.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Hotspots cause a fuss, when resources are in excess; migrate VMs to give them rest, for performance that's the best!
Stories
Imagine a busy restaurant (the physical host) where too many customers (VMs) arrive. If the waiters (resources) can’t serve everyone, some customers might leave unhappy. To solve this, the manager (the migration process) quickly moves some customers to another restaurant that has more staff available!
Memory Tools
Remember 'PEAR' for hotspot management: Performance, Efficiency, Availability, and Reliability; these are the key goals!
Acronyms
HML - Hotspot Mitigation Methodology
Detect hotspots
Migrate VMs
Live monitor resource usage.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Hotspot
A resource contention scenario where the demand from virtual machines exceeds the capacity of a physical host, leading to performance degradation.
- Live VM Migration
The process of moving a running VM from one physical host to another with no service downtime.
- Dynamic Provisioning
An automated resource allocation method that adjusts resources based on real-time monitoring and demand.
- Sandpiper Architecture
A conceptual framework focused on proactive resource management and hotspot mitigation in virtualized environments.
- Resource Profiling Engine
A component that monitors resource utilization metrics in real-time to detect and predict hotspots.
- PreCopy Live Migration
A method of VM migration that involves iteratively transferring the memory state of a VM while it continues running.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
