Mohr-Coulomb Failure Criteria
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Shear Strength
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

So, let’s start with shear strength. Can anyone tell me what factors might influence this?

Is it just the type of soil?

Great start! Soil composition plays a major role, including mineralogy, grain size, and even pore fluid content. Remember the acronym MGP for 'Mineralogy, Grain size, Pore fluid'!

What about the way the soil is arranged?

Exactly! The structure of the soil, which includes how the particles are arranged and packed, also influences shear strength. We can think of 'S' for structure in our MGP acronym.

So all these factors work together?

Exactly! The interplay of these components defines the soil's stability under stress. To summarize, shear strength is influenced by composition, initial state, and structure.
Introduction to Mohr-Coulomb Failure Criteria
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s move to the Mohr-Coulomb Failure Criteria. What do you think it signifies?

Does it have to do with when a material fails?

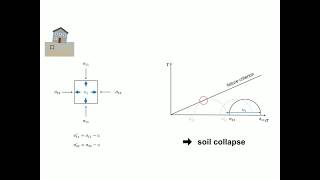
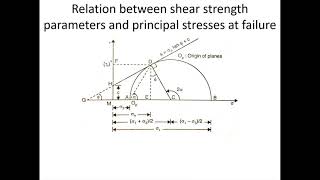
Correct! It states that failure occurs due to a critical combination of normal stress and shear stress. It’s not just about the maximum values of each.

So they have to work together?

Precisely! Think of it as a balancing act. If one exceeds its limits without considering the other, failure might not occur. A good way to remember this is by thinking of them as dance partners—each must adjust to the other's movements.

Can this help in predicting soil failure?

Yes! By analyzing the stresses involved, we can predict failure more accurately. So to summarize, the Mohr-Coulomb criteria focuses on the interplay between normal and shear stresses.
Real-World Applications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s look at real-world problems. Can anyone think of a scenario where understanding these principles is vital?

Maybe in civil engineering when building roads?

Spot on! Engineers must understand shear strength to design safe structures. Improper calculations could lead to a catastrophic failure.

So, this theory is really important in construction?

Absolutely! It helps in assessing the stability of slopes, retaining walls, and foundations. Let’s summarize: Mohr-Coulomb helps predict when structures might fail, particularly under loading conditions.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section outlines the factors influencing shear strength, including soil composition, initial state, and structure. It introduces the Mohr-Coulomb Failure Criteria, which posits that failure occurs at a critical combination of normal and shear stresses rather than exceeding their maximums.
Detailed
The Mohr-Coulomb Failure Criteria plays a crucial role in understanding soil mechanics and materials failure. It asserts that a material's failure results from a specific balance of normal and shear stress rather than merely their peak values. Factors such as soil composition (including mineralogy and grain size), the initial state of the soil (e.g., loose or dense), and the structure (particle arrangement and packing) influence shear strength. By examining these elements, one can better predict when and how a material may fail under stress.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to the Mohr-Coulomb Failure Criteria
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
This theory states that a material fails because of a critical combination of normal stress and shear stress, and not from their either maximum normal or shear stress alone.
Detailed Explanation
The Mohr-Coulomb Failure Criteria posits that material failure occurs due to a specific relationship between two types of stress: normal stress and shear stress. Normal stress acts perpendicular to a surface, while shear stress acts parallel to it. The key point here is that it is the combination of these stresses that leads to failure, rather than the individual effects of maximum normal or shear stresses. This means that understanding how these stresses interact is crucial for predicting when a material will fail.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to push a large box across a rough floor. The effort you apply to push it sideways (shear stress) and the weight of the box pressing down on the floor (normal stress) must work together. If you push too hard without addressing the weight, the box may not move. Conversely, if it’s too heavy, it’ll resist your push. Only when you consider both forces together can you predict whether the box will slide or stay put, much like how soil or rock fails under stress.
Key Concepts
-
Shear Strength: The resistance of soil to shearing forces related to its composition and structure.
-
Mohr-Coulomb Failure Criteria: A framework for understanding when materials will fail under stress, emphasizing the interaction of normal and shear stress.
Examples & Applications
A slope failure in a hillside due to excessive rain increases pore water pressure, reducing shear strength below the critical combination of stresses.
In foundation engineering, the Mohr-Coulomb criteria are applied to ensure that foundational structures can bear the expected loads without failing.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In soil and stress, we must invest, to prevent a fail we must balance the rest.
Stories
Imagine two dancers on a stage; if one leans too far without regard to the other, they will both fall. This is like the balance needed between normal and shear stress.
Memory Tools
Memory aid for shear strength: MGP = Mineralogy, Grain size, Pore fluid.
Acronyms
S for Structure helps to remember that soil arrangement influences shear strength.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Shear Strength
The resistance of a material to shear forces, influenced by various factors like composition, state, and structure.
- MohrCoulomb Failure Criteria
A theory stating that a material fails under a critical combination of normal stress and shear stress.
- Soil Composition
The makeup of soil, including mineralogy, grain size, and pore fluid characteristics.
- Soil Structure
The arrangement and organization of soil particles within a mass.
- Normal Stress
The stress acting perpendicular to a given surface.
- Shear Stress
The stress acting parallel to a given surface.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
