Infiltration: Definition and Importance
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Infiltration
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing infiltration. Can anyone tell me what infiltration means in the context of hydrology?

I think it’s about how water enters the soil.

That's correct! Infiltration is the movement of water through the soil surface into the ground. We refer to the speed of this movement as the infiltration rate. It's a vital part of the hydrologic cycle.

Why is that important?

Good question! Infiltration affects surface runoff, groundwater recharge, and even agricultural water management. These factors are crucial for effective water resource management. Remember, infiltration helps replenish aquifers!

So, it really impacts farming and our water supply?

Exactly! It determines how much water is available for crops and can also help reduce flooding.

If infiltration is so important, what happens if the ground is too saturated?

Another great point! When the ground is saturated, infiltration capacity decreases, leading to more surface runoff and potentially flooding. It's all interconnected.

To summarize, infiltration is about how water moves into the soil, impacting our water resources. Remember this: 'Water goes in, plants grow, we thrive!'
Infiltration Capacity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s focus on infiltration capacity. Can anyone tell me what infiltration capacity is?

Is it the maximum rate the soil can absorb water?

Exactly! The infiltration capacity refers to the maximum rate at which a soil can absorb water under specific conditions. This varies greatly among different soil types.

What types of soils would have high infiltration capacity?

Great question! Sandy soils typically have high infiltration capacities compared to clayey soils, which absorb water much slower. We can remember this with the mnemonic: 'Sand sinks, clay clings!'

Does vegetation affect how well the soil can absorb water?

Absolutely! Vegetation slows down surface water flow and enhances infiltration by creating paths for water, like roots forming macropores. More plants mean more infiltration!

So if more water gets absorbed, less runs off during storms?

Precisely! Vegetation is key in controlling runoff and thus reducing flood risks. Well-done!

To summarize, infiltration capacity varies with soil type and vegetation, affecting water management and flood control.
Practical Applications of Infiltration
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s talk about the applications of infiltration in fields like agriculture and urban planning. Why is infiltration important for these areas?

It helps us manage water better, right?

Yes! Understanding infiltration helps in optimizing irrigation and designing drainage systems. For example, areas with high infiltration capacity are ideal for planting crops.

And in cities?

In urban areas, we design permeable pavements to enhance infiltration and reduce flooding during heavy rains. If we reduce impervious surfaces, we increase infiltration!

So, if less water runs off, it can help recharge aquifers too?

Exactly! More infiltration means more groundwater recharge, which is essential for sustainable water sources.

What other effects does poor infiltration have?

Poor infiltration can lead to increased soil erosion and lower crop yields. Remember, healthy soil means healthy plants, which leads to healthy food!

To summarize, infiltration is not just a hydrological term; it has real-world applications that impact how we manage our water resources.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Infiltration refers to the movement of water through the soil surface into the ground. The rate of infiltration influences surface runoff, groundwater recharge, and agricultural practices, highlighting its significance in hydrology and water resource management.
Detailed
Infiltration: Definition and Importance
Infiltration is crucial for understanding water management. It is the process through which water moves from the surface into the soil. The rate at which this occurs is termed the infiltration rate, while the infiltration capacity refers to the maximum rate at which a specific type of soil can absorb water under given conditions. This section emphasizes several key points:
- Significance in Hydrology: Infiltration is pivotal as it influences surface runoff, groundwater recharge, aquifer replenishment, and soil erosion. This knowledge is vital in designing effective drainage systems, irrigation strategies, and flood control measures.
- Impacts on Agricultural Water Management: Understanding infiltration helps optimize agricultural practices and improves soil moisture retention, thereby fostering effective water management.
The chapter will further elaborate on the various factors affecting infiltration capacity and the classification of infiltration capacities, showcasing its importance in hydrological studies.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Infiltration
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
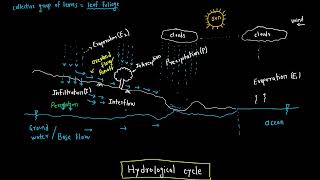
Infiltration is defined as the movement of water through the soil surface into the ground. The rate at which infiltration occurs is termed as the infiltration rate, while the infiltration capacity is the maximum rate at which a given soil can absorb water under given conditions.
Detailed Explanation
Infiltration refers to how water from rain or other sources moves downward from the surface of the soil into the ground. The 'infiltration rate' is how quickly this movement occurs, while the 'infiltration capacity' describes the maximum potential rate of this process, depending on various soil and environmental conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a sponge submerged in water. At first, it absorbs water rapidly (high infiltration rate), but once it's full, it can't soak up any more water (infiltration capacity). This is similar to how soil can absorb rainwater until it reaches maximum saturation.
Significance of Infiltration
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Significance in Hydrology:
- Influences surface runoff and flood hazards.
- Governs groundwater recharge and aquifer replenishment.
- Affects soil erosion and agricultural water management.
- Determines the design of hydraulic structures like stormwater drains.
Detailed Explanation
Infiltration plays a critical role in various hydrological processes. It influences how much water runs off the surface during rain, which can lead to floods. It also impacts how groundwater is replenished, ensuring that aquifers have enough water. Furthermore, good infiltration helps control soil erosion and is vital for managing agricultural irrigation effectively. Additionally, understanding infiltration helps engineers design stormwater systems to prevent flooding.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a garden during a heavy rainstorm. If the soil has high infiltration, the water soaks in quickly, reducing flooding and helping the plants. In contrast, if the soil can't absorb water fast enough, excess water pools, potentially damaging the plants or creating runoff problems, similar to how a poorly designed drainage system can lead to flooding in a neighborhood.
Key Concepts
-
Infiltration: The process of water movement into the soil.
-
Infiltration Rate: The speed at which water enters the soil.
-
Infiltration Capacity: The maximum rate at which a soil can absorb water.
-
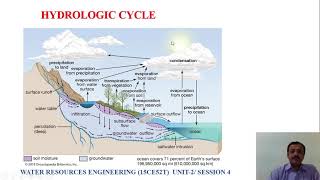
Hydrologic Cycle: The continuous movement of water through the environment.
-
Groundwater Recharge: The infiltration of water that replenishes underground aquifers.
Examples & Applications
Sandy soils typically have a high infiltration capacity, allowing for rapid water absorption.
Conversely, clayey soils have lower infiltration capacity, leading to increased runoff during rain.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When water flows on the ground, into the soil it can be found.
Stories
Imagine a thirsty plant during a rainstorm. The rainwater seeps down to its roots, nourishing it. This is infiltration at work!
Memory Tools
Sandy soils sink, clay clings - remember their different behaviors.
Acronyms
I.C.E. - Infiltration, Capacity, Efficiency.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Infiltration
The process by which water moves into the soil from the ground surface.
- Infiltration Rate
The speed at which water is absorbed into the soil.
- Infiltration Capacity
The maximum rate at which a given soil can absorb water under specific conditions.
- Hydrologic Cycle
The continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth.
- Groundwater Recharge
The process by which water infiltrates into the ground and replenishes aquifers.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
