Evapotranspiration – Definition and Concept
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Evapotranspiration
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're going to learn about evapotranspiration, or ET for short. Can anyone tell me what ET consists of?

Isn't ET made up of evaporation and transpiration?

That's correct! Evapotranspiration is the total water loss from a surface due to evaporation from soil and water bodies and transpiration from plants. Why do you think it's important for us to study ET?

Because it helps us understand how much water plants need?

Exactly! ET is essential for water resource management, especially in agriculture. Let's remember the acronym ET—E for Evaporation and T for Transpiration. Can anyone define both processes?

Evaporation is the physical loss of water as vapor, and transpiration is when plants take in water through their roots and release it as vapor!

Well done! Evaporation mainly happens from the soil and water surfaces, while transpiration occurs through tiny leaves' stomata.
Factors Affecting Evapotranspiration
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand the mechanisms of ET, let’s talk about what factors can affect it. Student_4, can you think of any climatic factors that affect ET?

Temperature and sunlight?

Yes! Temperature, solar radiation, wind speed, and humidity all significantly affect evaporation and transpiration rates. Can anyone guess how soil and vegetative factors come into play?

The type of crop and how much moisture is in the soil?

Exactly! Soil texture, moisture availability, and the type of vegetation all influence ET. That's why it's crucial to manage these factors carefully.

And what about irrigation or farming practices?

Great point! Management practices like irrigation techniques and mulching can significantly impact how plants use water. Remember, effective water management is vital, especially in arid areas.
Importance of Evapotranspiration Measurement
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's highlight why we must accurately measure ET. Student_3, what could be the consequences of not understanding ET?

Maybe we could overwater crops or waste water?

Exactly! With an accurate understanding of ET, farmers can better plan their water usage. Can anyone share what some methods for estimating ET might be?

Isn't there the Blaney-Criddle Method?

Yes! Methods like the Blaney-Criddle, Pan Evaporation, and FAO Penman-Monteith are commonly used. These methods use different data inputs to calculate ET. It is crucial to choose the appropriate method based on specific needs.

So, knowing ET helps really manage water for crops!

Exactly! Understanding and accurately measuring ET helps sustain water resources in agriculture, especially in regions where water is scarce. Let's keep that in mind as we move on to the next topic.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
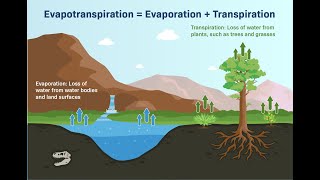
Evapotranspiration (ET) is the total loss of water from soil and plant surfaces to the atmosphere through evaporation and plant transpiration. Understanding ET is crucial for effective water resource management, especially in agriculture and arid regions.
Detailed
Evapotranspiration – Definition and Concept
Evapotranspiration (ET) plays a critical role in the hydrologic cycle, combining two significant processes: evaporation and transpiration.
- Evaporation refers to the physical loss of water as vapor from sources like soil, water bodies, and plant surfaces.
- Transpiration is a biological process wherein plants absorb water from the soil through roots and release it as vapor through small openings in leaves called stomata.
ET is influenced by various environmental factors, including climate, soil conditions, and vegetation, and is typically assessed in terms of reference or actual crop conditions. Understanding ET is vital for planning agricultural water demands, hydrological modeling, irrigation scheduling, and overall water resource management, particularly in regions facing water scarcity.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Evapotranspiration
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Evapotranspiration is defined as the total water loss from a vegetated surface due to the combined processes of:
Detailed Explanation
Evapotranspiration, commonly abbreviated as ET, refers to the total amount of water that is lost from a vegetated area. This loss of water occurs due to two main processes: evaporation and transpiration. Understanding this definition helps us appreciate how both natural processes contribute to the overall loss of water from soil and plants into the atmosphere.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a sponge left out in the sun. As it heats up, water slowly evaporates from its surface. Similarly, the soil and plants lose water into the air through evaporation and transpiration, just as the sponge dries out.
Evaporation Explained
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Evaporation: Physical loss of water as vapor from soil, plant surfaces, and water bodies.
Detailed Explanation
Evaporation is the process where liquid water changes into water vapor and enters the atmosphere. This can occur from various surfaces such as soil, rain puddles, leaves, and water bodies. Several factors, including temperature, sunlight, and wind speed, influence the rate of evaporation. Generally, higher temperatures and more sunlight lead to increased evaporation rates.
Examples & Analogies
Think of how a wet sidewalk dries up on a sunny day. The heat from the sun and the breeze help the water evaporate quickly, turning it from liquid to vapor, just like how the surface of soil in a garden loses moisture.
Transpiration Explained
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Transpiration: Biological process through which plants absorb water via roots and release it as vapor through stomata.
Detailed Explanation
Transpiration is a vital biological process performed by plants. Water absorbed by plant roots is transported to the leaves and then released as vapor through small openings called stomata. This process not only helps in cooling the plant but also contributes to the overall water cycle. The amount of water released can vary based on plant type, environmental conditions, and the plant's growth stage.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how you feel when you sweat. Just like sweating cools your body and releases moisture into the air, plants lose water through transpiration, helping them regulate their temperature and moisture levels.
Factors Affecting Evapotranspiration
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
ET depends on various climatic, soil, and vegetative factors and is measured over a reference crop or actual crop conditions.
Detailed Explanation
Evapotranspiration is influenced by a variety of factors, including climate (like temperature and humidity), soil type (how much water it can hold), and vegetation characteristics (such as type and amount of foliage). To understand and estimate ET accurately, measurements are often made using a standard or reference crop as a baseline. This allows us to compare how different conditions can affect water loss.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a garden with different types of plants. Some plants may lose more water due to their size or leaf structure, just as a wet sponge dries out differently based on its surroundings and the conditions it is exposed to.
Key Concepts
-
Evapotranspiration (ET): The combination of evaporation and transpiration representing total water loss to the atmosphere.
-
Evaporation: The process where water transitions from liquid to vapor, largely influenced by climatic conditions.
-
Transpiration: The biological release of water vapor by plants from their stomata.
Examples & Applications
In a warm, sunny climate, ET may be high due to increased evaporation and transpiration, leading to greater agricultural water consumption.
In a shaded forest area, lower sunlight leads to reduced evaporation, while transpiration continues to modify local humidity.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Evapotranspiration, a cycle so neat, / Water to vapor, a natural treat.
Stories
Imagine a plant drinking from the soil. As it grows, it releases water vapor into the sky, completing the circle of water in nature.
Memory Tools
To remember ET: Evaporation Takes place, Transpiration Keeps going – ET!
Acronyms
ET
for Evaporation from surfaces
for Transpiration from plant leaves.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Evapotranspiration (ET)
The total loss of water from soil and vegetation to the atmosphere, encompassing both evaporation and transpiration.
- Evaporation
The physical process of water turning into vapor from soil, water bodies, and plant surfaces.
- Transpiration
The process by which plants absorb water from the soil and release it as vapor through stomata.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
