29.1 Infiltration – Definition and Importance
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Definition of Infiltration
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're learning about infiltration. What do you understand by the term 'infiltration'?

I think it has to do with water soaking into the ground.

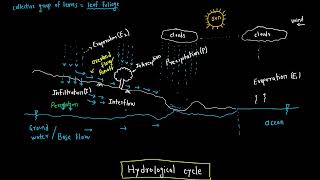
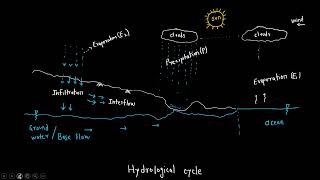
Exactly! Infiltration is the movement of water through the soil surface into the subsurface layers. Can anyone tell me why this process is important?

It affects how much water goes into the groundwater.

Yes, it influences groundwater recharge rates as well as runoff generation. Remember, the acronym 'GRO' can help you remember: Groundwater, Runoff, and Overall water quality!

So, it's also about soil erosion?

Correct! Infiltration not only impacts groundwater but also controls soil erosion and preserves water quality.

Does it play a role in agriculture too?

Absolutely! It impacts crop water availability, which is crucial for agricultural planning. Let’s summarize: Infiltration is vital for groundwater recharge, runoff management, and crop viability.
Hydrological Importance of Infiltration
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Infiltration affects several important hydrological processes. What are some of these?

It helps with recharge of groundwater and reduces flooding.

Correct! It determines how much water ends up as runoff and how much contributes to groundwater. This directly influences flood forecasting. Can anyone think of how it might affect agricultural planning?

If infiltration is high, crops would have more water?

That's right! High infiltration means more water is available for crops, which is essential for irrigation planning. Remember the mnemonic 'WIG'—Water In Ground—for its importance in farming.

What about water quality?

Great question! Infiltration can filter pollutants from surface water, improving water quality. So, to sum up: Infiltration influences groundwater, crop availability, and even soil health.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Infiltration is crucial for understanding the movement of water through soil, affecting runoff, groundwater recharge, and overall soil health. It is significant in hydrological design, flood forecasting, and agriculture, directly impacting crop water availability and environmental quality.
Detailed
Infiltration is defined as the movement of water from the surface of the soil into the subsurface layers. This process is instrumental in the hydrological cycle, determining how much water will run off the land versus how much will percolate into the soil, thereby influencing groundwater recharge. Importantly, infiltration affects soil erosion, water quality, and agricultural planning, as it controls the availability of moisture for crops. Understanding and modeling infiltration capacity is essential for effective flood management, irrigation planning, and maintaining sustainable watershed practices.
Youtube Videos







Key Concepts
-
Infiltration: The movement of water into the soil.
-
Groundwater Recharge: Importance in maintaining water supplies.
-
Runoff: The impact of infiltration on water movement.
-
Soil Erosion: The effects of water infiltration on soil stability.
-
Water Quality: How infiltration impacts the cleanliness of water.
Examples & Applications
When it rains, a significant amount of water may infiltrate into the ground, replenishing underground aquifers.
In agriculture, areas with higher infiltration rates may require less irrigation, conserving water.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When it rains on the ground so brown, infiltration keeps water around!
Stories
Once upon a time, a raindrop fell on a thirsty farm. It soaked into the ground, nourishing the plants and helping them grow, reminding us of how crucial infiltration is to life.
Memory Tools
Think 'GRO': Groundwater, Runoff, Overall quality—key areas influenced by infiltration.
Acronyms
I.I.C
Infiltration Influences Crops—helps us remember its importance in agriculture.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Infiltration
The process of water entering the soil from the ground surface.
- Groundwater Recharge
The process of water moving downward from surface water to groundwater.
- Runoff
Water that flows over the land surface and does not infiltrate into the soil.
- Soil Erosion
The removal of the upper layer of soil, which can be influenced by water movement and vegetation.
- Water Quality
The chemical, physical, and biological characteristics of water, often concerning its suitability for various uses.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
