Exponential Growth and Decay
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Exponential Functions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

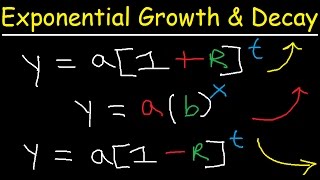
Today, we'll explore exponential functions, which have a specific form denoted as \( y = a \cdot b^x \). Has anyone encountered this form before?

I've seen it in my previous class, but I'm not sure exactly what it means.

That's okay! Let's break it down. Here, \( a \) represents the initial value when \( x = 0 \), and \( b \) is the growth or decay factor. Can anyone tell me what happens if \( b > 1 \)?

It means the function is growing!

Correct! Now, if \( 0 < b < 1 \), what would that indicate?

It would indicate decay.

Exactly! We will delve deeper into both growth and decay.
Exponential Growth
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss exponential growth. The formula for it is \( y = a(1 + r)^t \). Can someone explain what \( r \) stands for?

Isn't \( r \) the growth rate in decimal form?

Correct! Great job! Now, consider this example: if a population of 500 bacteria doubles every 3 hours, what can we calculate after 9 hours?

We can find out how many doubling periods are in 9 hours!

That's 3 periods, right?

Yes, so we calculate \( y = 500 \cdot 2^3 = 4000 \) bacteria. Excellent!
Exponential Decay
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Switching gears, let's look at exponential decay, represented by \( y = a(1 - r)^t \). Who can remind me what this formula calculates?

It calculates how much a quantity decreases by a certain rate over time.

Absolutely! Let's think about a car worth $20,000 that depreciates at 15% each year. Can someone use the formula to find its value after 5 years?

I think \( a = 20000, r = 0.15, t = 5 \). So, \( y = 20000(0.85)^5 \).

Great! And what do you get when you calculate that?

About $8,874!
Graphical Representation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, how do we graph exponential functions? What does the graph look like?

It’s a curve that never touches the x-axis!

Right! It approaches the x-axis but never crosses it. This characteristic is crucial for understanding limits in functions.

So, no matter how long we wait, it never actually reaches zero?

Exactly! Whether it’s growth or decay, the behavior of the graph remains significant.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Exponential Change
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Many real-world processes grow or decline at rates proportional to their current value. This kind of change is called exponential. Unlike linear change, where a quantity increases or decreases by the same amount, exponential change involves a constant percentage increase or decrease.
Detailed Explanation
Exponential change refers to growth or decay that occurs at a rate proportional to the current value. In contrast to linear change, where the change is constant, exponential change means the quantity changes by a consistent percentage. For example, if a population grows exponentially, it doesn't just add the same number of individuals each year; it adds a percentage of the current population, which itself is growing.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a savings account with compound interest. If you earn interest on the total amount in your account rather than on just your initial deposit, your balance increases faster over time, exemplifying exponential growth.
Key Concepts
-
Exponential Function: A function of the form \( y = a \cdot b^x \).
-
Growth and Decay: Exponential growth occurs when \( b > 1 \), while decay occurs when \( 0 < b < 1 \).
Examples & Applications
Example of growth: A population of bacteria starts at 500 and doubles every 3 hours. After 9 hours, it grows to 4000.
Example of decay: A car worth $20,000 depreciates at 15% per year, and its value after 5 years is approximately $8,874.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When bacteria grow, they double so fast, exponential growth is quite a blast!
Stories
Once, a town's population doubled every year; it grew so high, what a sight to cheer!
Memory Tools
Remember G = Growth, D = Decline in exponential equations, just think of time!
Acronyms
GROW
= Growth
= Rate
= Original amount
= Wait (time).
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Exponential Growth
A process where a quantity increases by a fixed percentage over regular intervals.
- Exponential Decay
A process where a quantity decreases by a fixed percentage over time.
- Initial Value (a)
The quantity's starting amount when the time is zero.
- Growth Rate (r)
The rate at which a quantity increases, expressed as a decimal.
- Decay Rate (r)
The rate at which a quantity decreases, also expressed as a decimal.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
