What is a Geometric Sequence?
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Geometric Sequences
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into an essential part of mathematics called geometric sequences. Can anyone tell me what a geometric sequence is?

Is it a sequence where you keep adding a number to each term?

Good guess, but it's actually where each term is found by multiplying the previous term by a common ratio, denoted by r. If we were to look at the sequence 2, 6, 18, 54, what's the common ratio?

I think it's 3 because if you multiply 2 by 3, you get 6.

Exactly! The common ratio is 3. Remember, geometric sequences involve multiplication, not addition. Let's remember this with the mnemonic 'Multiply to Grow'.
Formula for the n-th Term
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's learn how to find any term in a geometric sequence. We use the formula T = ar^(n−1). Can anyone explain what each part stands for?

I think a is the first term, and n is the term's position.

Correct! And r is the common ratio. Let’s find the 5th term in our sequence from before, where a = 2 and r = 3.

So, T = 2 * 3^(5−1)? That would equal 2 * 81, which is 162!

Great job! Keep in mind: 'First times Ratio for the nth Term'.
Sum of Finite Geometric Series
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s explore how to calculate the sum of the first n terms, known as a finite geometric series. Does anyone remember the formula?

Is it S = a * (1 − r^n) / (1 − r)?

Exactly right! Let's use this formula to find the sum of the first 5 terms where a = 2 and r = 3.

So, S = 2 * (1 - 3^5) / (1 - 3) = 2 * (-242)/(-2) = 242!

Well done! Always visualize it as 'Sum is a Multiplier' to remember the steps.
Infinite Geometric Series
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, who can tell me what happens with an infinite geometric series?

I think those are sequences that go on forever, right?

Exactly! However, it only converges to a finite sum if the absolute value of r is less than 1. How do we calculate the sum of an infinite series?

I believe the formula is S = a / (1 − r) for |r| < 1?

That's correct! Remember 'Infinite Sum is Limited'. Let’s apply that to find the sum of the series 5 + 2.5 + 1.25 + ... .
Real-World Applications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s look at how we can apply geometric sequences in real life, like in finance, through compound interest. Who knows the formula for total amount A after n years?

Is it A = a * (1 + r)^n?

Yes! If you invested $1,000 at 5% interest compounded annually for 3 years, how much will you have?

A = 1000 * (1 + 0.05)^3 equals approximately $1157.63!

Fantastic! Remember 'A is Amount After Interest', a great way to visualize financial growth!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of a Geometric Sequence
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
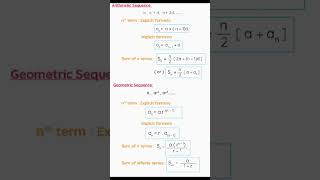
A geometric sequence is a list of numbers where each term is obtained by multiplying the previous term by the same constant. This constant is called the common ratio, denoted by 𝑟.
Detailed Explanation
A geometric sequence is defined as a sequence of numbers formed by multiplying each term by a consistent value known as the common ratio. This means if you start with a number (the first term) and repeatedly multiply it by a specific number, you will generate the sequence. For example, if your first term is 2 and your common ratio is 3, the sequence will be 2, 6, 18, 54, etc.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a plant that grows by doubling its height every week. If it starts at 1 inch, after one week it will be 2 inches, after two weeks it will be 4 inches, and so forth. Each week, the height is multiplied by the same factor, illustrating a geometric sequence in action.
Key Concepts
-
Geometric Sequence: A sequence generated by multiplying the previous term by a constant ratio.
-
Common Ratio: A fixed number used to multiply each term in a geometric sequence to obtain the next term.
-
n-th Term Formula: T = ar^(n−1) provides a method to find any specific term in the sequence.
-
Sum of a Finite Series: The total of a defined number of terms in a geometric sequence can be calculated with S = a(1 - r^n) / (1 - r).
-
Infinite Series: An infinite geometric series converges to a finite sum if |r| < 1, calculated with S = a / (1 - r).
Examples & Applications
Example of a geometric sequence: Starting with 2 and a common ratio of 3, the sequence is 2, 6, 18, 54.
To find the 4th term where a = 4 and r = 2: T = 4 * 2^(4−1) = 4 * 8 = 32.
A geometric series example: Calculate the sum of the first 5 terms for 4, 8, 16, 32, 64.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a geometric race, you multiply in each space.
Stories
Imagine a tree that grows taller every year by a certain factor. Its height in each year represents a term in a geometric sequence.
Memory Tools
First times Ratio for the n-th Term.
Acronyms
SIMPLE
Sum of Infinite Multiples is Limited Entries.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Geometric Sequence
A sequence of numbers where each term after the first is obtained by multiplying the previous term by a constant called the common ratio.
- Common Ratio (r)
The constant factor between consecutive terms in a geometric sequence, derived by dividing any term by its preceding term.
- nth Term
The term at position n in a sequence, found using the formula T = ar^(n−1).
- Finite Geometric Series
The sum of a specific number of terms of a geometric sequence.
- Infinite Geometric Series
An infinite geometric sequence that can have a finite sum only when |r| < 1.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
