What Is a Limit?
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding the Concept of a Limit
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

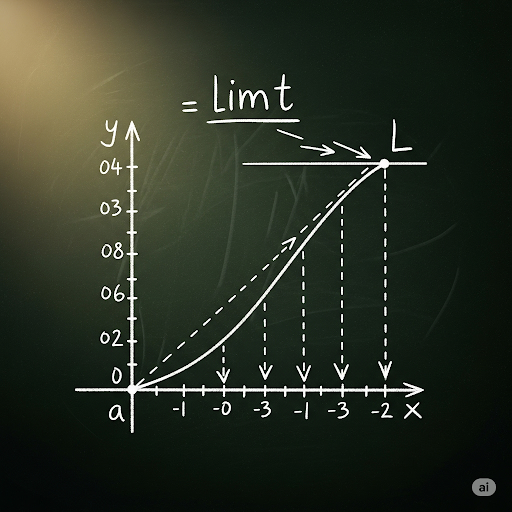
Today, we’re going to learn about limits. A limit is the value a function approaches as the input approaches a specific value. For example, if we have a function f(x) and as x gets closer to a value a, f(x) approaches a value L, we write this as lim f(x) = L as x approaches a.

So, it's about what happens to f(x) when x gets close to a?

Exactly! You can think of limits as how our input x influences the output f(x) as we creep up to a certain point.

Is that like when you try to get right to the edge of a cliff, but you never actually go over?

Great analogy! You're getting close but not actually touching it. Let's summarize: limits model behavior at specific points.
Evaluating Limits from a Table
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, we’ll figure out limits using a table. If we can't plug x = a directly, we can approximate its value. For instance, if we evaluate lim (x^2 + 3) as x approaches 2, we can create a table with values near 2.

Do we just take points smaller and larger than 2?

Exactly! You'd look at values like 1.9, 1.99, 2, 2.01, and 2.1. What do you think we’ll find?

It looks like it's getting close to 7!

Correct! So lim (x^2 + 3) as x approaches 2 equals 7. Good observation on the table results!
Evaluating Limits Graphically
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's discuss how to evaluate limits graphically. By looking at a graph, we can determine the limit by observing values from both sides as x approaches a certain point.

What if the graph shows different values from each side?

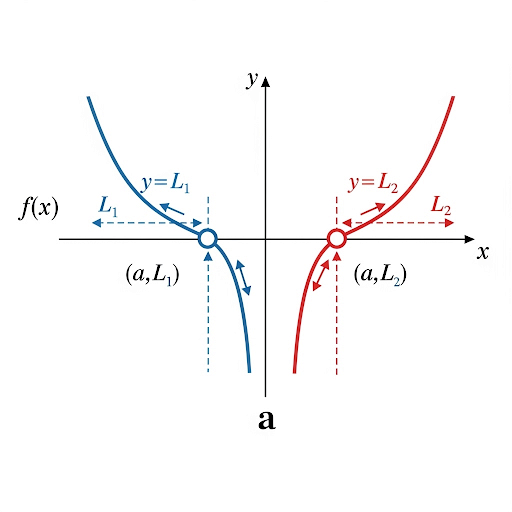
Great question! If the left side and right side converge to different values, the limit does not exist or DNE.

Can you show us an example?

Sure! If we look at a graph where f(x) approaches 5 from the left and 3 from the right as x approaches a, we say the limit as x approaches a does not exist.

Got it! So we can't say the limit is 4, since it's undefined.
Algebraic Evaluation of Limits
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s do algebraic evaluation. For simple functions, direct substitution works great. But sometimes we have indeterminate forms like 0/0. In these cases, we simplify first!

So, if we had lim (x^2 - 1)/(x - 1) as x approaches 1, we'd need to factor it first?

Right! Factor as (x - 1)(x + 1) to cancel out the (x - 1). Then you can find the limit by substituting.

That makes sense! So we can get the limit by substituting 1 into x + 1.

Exactly! It becomes 2, showing how limits can simplify complex-looking functions.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section introduces the concept of limits in calculus, explaining how to evaluate them numerically and graphically, as well as addressing one-sided and infinite limits, and situations where limits might not exist.
Detailed
In calculus, a limit defines the value a function approaches as the input approaches a particular point. This section outlines the foundational idea of limits, describing how to evaluate limits using tables and graphs. The notation used for limits is explained, as well as methods for algebraic evaluation. Students will learn about one-sided limits, infinite limits, and conditions under which limits do not exist. The understanding of limits is crucial as it forms the basis for differentiation and integration in calculus.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of a Limit
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A limit is the value that a function approaches as the input (or variable) approaches a certain value.
Detailed Explanation
In calculus, a limit refers to the behavior of a function as its input gets closer to a specific point. If we denote the function as 𝑓(𝑥) and a particular value as 𝑎, we express the limit of 𝑓(𝑥) as 𝑥 approaches 𝑎 as: lim𝑓(𝑥) = 𝐿 (𝑥→𝑎). This means that as 𝑥 gets very close to 𝑎, the values of 𝑓(𝑥) get very close to 𝐿, the limit. Understanding this concept is crucial for analyzing functions and their behaviors.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're trying to measure how close you can get to a brick wall without actually touching it. As you step closer and closer to the wall (approaching that limit), you're getting nearer to the wall's surface but never really crossing it. In calculus, we look at how functions behave as we get near a certain value without necessarily reaching it.
Key Concepts
-
A limit describes the behavior of a function as x approaches a specific value.
-
Direct substitution can evaluate many limits.
-
One-sided limits focus on the approach from one direction.
-
Infinite limits indicate that a function heads toward infinity.
-
Limits can be classified as existing or non-existing (DNE).
Examples & Applications
Evaluating lim (x^2 + 3) as x approaches 2 gives us 7.
Using a table, we found limits close to a certain point.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When limits are clear, don’t fear, just plug in, they’re near!
Stories
Imagine you are inching towards a treasure marked by x. Closer and closer you get, and even though you never step on it, you sense its value from afar.
Memory Tools
Use 'DIRE' for 'Direct substitution', 'Indeterminate forms', 'Right-hand limit', 'Evaluate from tables' when thinking about limits.
Acronyms
Remember 'LIFE'
Limit Indicates Function’s Ending.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Limit
The value that a function approaches as the input approaches a given point.
- Direct Substitution
Plugging the value directly into the function to find the limit, if defined.
- Indeterminate Form
A form that does not provide a clear limit, such as 0/0.
- OneSided Limit
The limit approached from one direction, either left or right.
- Infinite Limit
A limit where the function increases or decreases indefinitely.
- DNE (Does Not Exist)
A term used when a limit cannot be determined.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
