Introduction
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Average Rate of Change
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss the Average Rate of Change or AROC. It represents how much a function changes on average over a specific interval. Can anyone tell me how we can mathematically express AROC?

Is it like the slope between two points on a graph?

Exactly! It's computed as the change in the function values divided by the change in x between two points. For example, if we have a function f(x) and two points a and b, the formula looks like this: (f(b) - f(a)) / (b - a).

Okay, can you give an example?

Sure! If f(x) = x^2, what would be the AROC from x = 1 to x = 3?

We'd calculate it as (9 - 1) / (3 - 1), which equals 4, right?

Correct! This indicates the function increases, on average, by 4 units for each unit increase in x over that interval. Remember, AROC is about averages over an interval.

So, does it always mean there’s a constant rate of change?

Great question! AROC can represent an average, but the actual rate can vary at different points, which brings us to Instantaneous Rate of Change. Let's explore that next!
Instantaneous Rate of Change
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s dive into Instantaneous Rate of Change or IROC. This tells us how fast a function is changing at a particular point.

How do we calculate IROC?

Great question! The IROC is determined using the derivative of the function at a specific point. The formula is essentially a limit as we approach that point. For example, if we have f(x) = x^2, we use the definition of the derivative.

I remember that we compute the limit as h approaches 0, right?

Exactly! The formula is: f'(a) = lim (h→0) [(f(a+h) - f(a))/h]. Can anyone give me the IROC at x = 2 for our f(x) = x^2?

After performing the limit operations, we find it equals 4!

Correct! This means at x = 2, the function is changing at a rate of 4 units per unit change in x. Just like measuring the speed of a car at an instant with a speedometer.

That makes sense. The instantaneous rate feels much like being at a specific moment rather than an average.

Exactly! Now, let's connect these concepts graphically.
Graphical Interpretation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

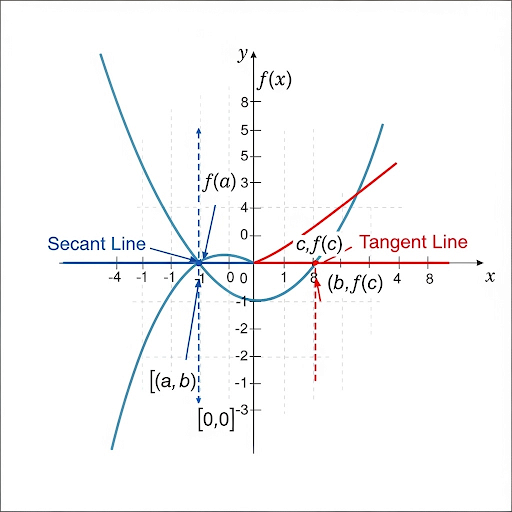
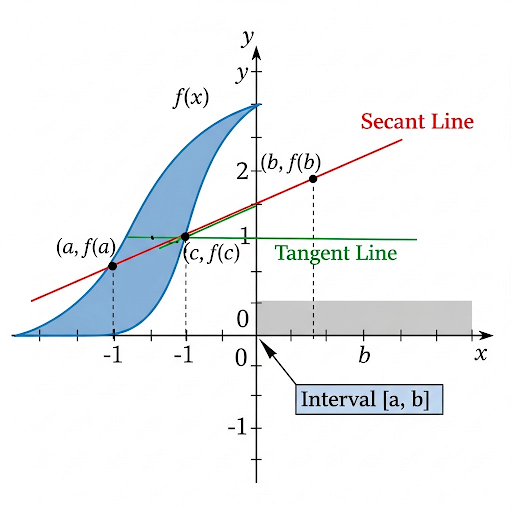
When we visualize these rates of change, we can start with Average Rate of Change represented as a secant line between two points on the graph.

So, that’s like drawing a line connecting two points on the curve?

Precisely! And the slope of that secant line gives us the AROC. Now, what about the IROC?

The slope of the tangent line at a single point, right?

Yes! The tangent line touches the curve at just one point, and its slope represents the IROC at that point. Think about driving—your average speed over a trip versus your instantaneous speed at a moment.

That analogy really helps! The speedometer shows my speed at an instant.

Fantastic! Now before we move on to applications, let’s recap these foundational points.

Average Rate of Change gives us an overall trend, while Instantaneous Rate of Change gives us a momentary insight into the process. This distinction is crucial in many fields such as physics and economics.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The introduction lays out the importance of understanding rates of change by relating them to real-world scenarios such as motion, growth, and economic changes. It emphasizes the significance of both average and instantaneous rates of change in calculus, which are critical for studying various fields, including physics and biology.
Detailed
In this introduction to rates of change, we explore how rate changes are integral to understanding variations in quantities over time or space. From cars accelerating on the roads to populations growing in nature, these dynamics are encapsulated in the mathematical frameworks of calculus. The concepts of Average Rate of Change (AROC) and Instantaneous Rate of Change (IROC) form the backbone of calculus and offer critical insights into studies across physics, biology, economics, and engineering. As we delve further, we will examine how these rates can be graphically interpreted through slopes of lines (tangent and secant) and the applications that stem from understanding these rates.
Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
The Concept of Change in the Real World
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In the real world, things are always changing — cars accelerate, water flows, and populations grow.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk introduces the idea that change is a constant in our environments. In mathematics and specifically calculus, understanding how things change is fundamental. For instance, a car’s speed varies as it accelerates or decelerates. Recognizing that objects and phenomena are not static but rather dynamic is the core focus of this section.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're riding a bicycle. Sometimes you pedal harder and go faster (accelerating), while other times you may slow down to take a turn (decelerating). This constant change in speed is similar to what we study in calculus.
Introduction to Rates of Change
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Calculus helps us understand how these changes happen and at what rate. One of the foundational concepts in calculus is the Rate of Change, which allows us to describe how one quantity changes in relation to another.
Detailed Explanation
Rates of Change in calculus quantify how a particular quantity changes with respect to another variable. For example, if we know how far a car has traveled over time, we can calculate its speed. This concept is crucial for analyzing various processes in mathematics and the sciences.
Examples & Analogies
Think of cooking. When you boil water, if you know the time it takes to reach a certain temperature, you can understand the rate at which the water is heating up. If we graph the temperature over time, the slope of that graph gives us the rate of change in temperature.
Average and Instantaneous Rates of Change
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
This chapter introduces the concept of rates of change, focusing on both average and instantaneous rates. These ideas are the basis for further study in calculus and are critical for understanding motion, growth, and change in physics, biology, economics, and engineering.
Detailed Explanation
Average rate of change measures how much a quantity changes over a specified interval, while instantaneous rate of change looks at how a quantity changes at a specific moment. For example, if you're studying the height of a plant, the average rate can tell you how much it grew over a week, whereas the instantaneous rate can tell you how fast it is growing at a particular time.
Examples & Analogies
If you track your savings, the average rate of change might represent how much your savings grow per month, while the instantaneous rate could describe the exact amount your savings grow on a day you receive a paycheck.
Importance of Rates of Change Across Disciplines
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
These ideas are the basis for further study in calculus and are critical for understanding motion, growth, and change in physics, biology, economics, and engineering.
Detailed Explanation
The concept of rates of change is not only vital in mathematics but also plays a crucial role in various fields. In physics, it is used to calculate velocity and acceleration. In biology, it helps in studying population dynamics. This section emphasizes that understanding rates of change can enhance learning across multiple scientific disciplines.
Examples & Analogies
For instance, consider how engineers design bridges. They must understand how weight (load) affects the structure (change) to ensure it is safe. By applying rates of change principles, they are able to predict how different forces will impact the integrity of the bridge.
Key Concepts
-
Average Rate of Change: Represents the average change over an interval.
-
Instantaneous Rate of Change: Measures change at a particular moment.
-
Secant Line: A line connecting two points, representing AROC.
-
Tangent Line: A line at a single point on a curve, representing IROC.
Examples & Applications
Finding AROC from f(x) = 3x^2 - 2x over x = 1 to x = 4 involves calculating the slope between the two points.
The IROC at a specific point can be calculated as the derivative of the function evaluated at that point.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Average rate high, instantaneous rate low, find the slope, and now you know!
Stories
Imagine a car on a road, averaging speed over a trip versus checking speed on the go!
Memory Tools
A for Average and I for Instantaneous, use Rate of Change to solve your calculus fame!
Acronyms
A ROC
Average Rate of Change; I ROC
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Average Rate of Change (AROC)
The change in the value of a function divided by the change in the independent variable over an interval.
- Instantaneous Rate of Change (IROC)
The rate at which a function is changing at a specific point, represented by the derivative.
- Derivative
A function that quantifies the rate of change of another function.
- Secant Line
A line that connects two points on a graph, representing the average rate of change.
- Tangent Line
A straight line that touches a curve at a single point, representing the instantaneous rate of change.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
