Electrolysis of Molten Lead Bromide (PbBr₂)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Electrolysis of Lead Bromide
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we are going to discuss the electrolysis of molten lead bromide, specifically focusing on what happens at the electrodes. Can anyone tell me what we understand by 'electrolysis'?

Isn’t it the process of breaking down a substance using electricity?

Exactly! Electrolysis involves using electrical energy to cause a chemical change. Now, when we look at lead bromide, what do you think happens when we apply electricity to it?

I think it splits into lead and bromine?

Correct! It splits into lead ions and bromide ions. The lead ions are positively charged and move towards the cathode. What happens there?

They get reduced to form lead metal?

That's right! The reaction is Pb²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Pb. At the same time, what happens at the anode?

Bromine ions are oxidized to form bromine gas!

Exactly, well done! We get Br₂ as the product at the anode.

So, to summarize: at the cathode, lead ions are reduced, and at the anode, bromide ions are oxidized. This is a fundamental example of electrolysis. Remember the acronym 'CRAMP'—C is for cathode, R is for reduction, A is for anode, M is for oxidation, and P is for products.
Detailed Reactions and Products
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive a bit deeper into the reactions. Can someone remind us of the cathode reaction during the electrolysis of PbBr₂?

It’s Pb²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Pb!

Great! And why is it important to know this reaction?

Because it shows how lead is extracted from lead bromide?

Exactly! By understanding the cathode reaction, we can comprehend how lead is deposited. Now, what about the reaction at the anode?

That’s 2Br⁻ → Br₂ + 2e⁻.

Correct! This releases bromine gas. Why is it necessary to know both reactions?

So we can understand the entire process and know the products formed!

Exactly! Understanding both allows us to appreciate the full electrolysis process. Always remember the acronym 'CRAMP' we discussed earlier for easy recollection of this process.
Practical Applications of Electrolysis in Industry
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, why do you think understanding the electrolysis of lead bromide is important in industry?

So we can extract lead for various uses?

Exactly! The lead extracted can be used in batteries and radiation shielding. What other applications can you think of that rely on electrolysis?

Electroplating, maybe?

Yes! Electrolysis is essential there as well. It’s used in electroplating metals to provide a protective layer. Always connect the dots between classroom concepts and real-world applications!

Can we apply this knowledge to other types of electrolysis?

Absolutely! The principles we’ve discussed apply to many electrolytic processes. Keep the acronym 'CRAMP' in mind—it helps make connections to more complex processes.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
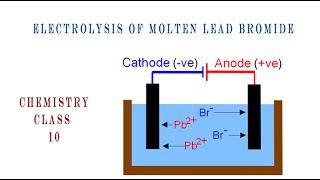
The electrolysis of molten lead bromide (PbBr₂) involves the reduction of lead ions at the cathode and the oxidation of bromide ions at the anode, yielding lead metal and bromine gas. Understanding these reactions is critical for grasping the practical applications of electrolysis in the extraction of metals.
Detailed
Electrolysis of Molten Lead Bromide (PbBr₂)
The electrolysis of molten lead bromide is a classic example that demonstrates the processes of electrolysis involving ionic compounds. When lead bromide (PbBr₂) is molten, it dissociates into its constituent ions: lead ions (Pb²⁺) and bromide ions (Br⁻).
Key Reactions:
- Cathode Reaction: At the cathode, lead ions are reduced:
- Pb²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Pb (Lead is deposited on the cathode)
- Anode Reaction: At the anode, bromide ions are oxidized:
- 2Br⁻ → Br₂ + 2e⁻ (Bromine gas is evolved)
Products:
- The products of this electrolysis are solid lead metal deposited at the cathode and bromine gas released at the anode.
Understanding these reactions is important not only for academic purposes but also for industrial applications in metal extraction and purification. This section sets the foundation for the study of other electrolysis processes and their applications in various chemical industries.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Cathode Reaction
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Cathode reaction: Pb²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Pb (lead deposited)
Detailed Explanation
At the cathode, lead ions (Pb²⁺) gain electrons (2e⁻) during the electrolysis process. This reduction reaction results in the deposition of solid lead metal (Pb) on the cathode. The process involves the transfer of electrons, which are supplied by the external circuit, facilitating the change of lead ions into lead metal.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the cathode as a sponge soaking up water. In this analogy, the lead ions are like water molecules that need to be absorbed, and the electrons are like the sponge's ability to hold the water. Just as a sponge gets heavy and fills up, the cathode accumulates lead metal as the ions are reduced.
Anode Reaction
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Anode reaction: 2Br⁻ → Br₂ + 2e⁻ (bromine gas evolved)
Detailed Explanation
At the anode, bromide ions (Br⁻) lose electrons in an oxidation reaction. Two bromide ions release a total of two electrons to form bromine gas (Br₂). This reaction is responsible for the evolution of bromine gas at the anode. The electrons generated at the anode are now available to flow back to the cathode, completing the electrical circuit.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the anode as a balloon that, instead of being filled with air, is releasing it. The bromide ions represent the air within the balloon. As bromide ions lose electrons, it's like the balloon letting out air, and in this case, they combine to form bromine gas as they escape.
Products of Electrolysis
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Products: Lead metal at cathode, bromine gas at anode.
Detailed Explanation
The products of the electrolysis of molten lead bromide are solid lead deposited at the cathode and bromine gas released at the anode. This outcome indicates that during the electrolysis, the original compound (lead bromide) has been broken down into its constituent elements: lead and bromine.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of this process like a factory that separates building materials into parts. Just like how a factory might take materials and produce bricks and cement, the electrolysis of lead bromide separates it into solid lead and bromine gas, demonstrating the effective breakdown of compounds.
Key Concepts
-
Cathode Reaction: The reduction of Pb²⁺ to lead metal.
-
Anode Reaction: The oxidation of Br⁻ to bromine gas.
-
Products of Electrolysis: Lead at the cathode and bromine at the anode.
Examples & Applications
The electrolysis of molten lead bromide produces lead metal for use in batteries and bromine gas for other chemical applications.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
At the cathode, lead will thrive,; Bromine at anode comes alive.
Stories
Imagine a factory where lead and bromine are separated by electricity. At the cathode, workers gather lead to mold into useful shapes, while at the anode, bromine escapes as gas, eagerly waiting to be reused in various products.
Memory Tools
Remember 'P-B-R' where P stands for lead produced at the cathode, and B for bromine gas at the anode.
Acronyms
CRAMP
for cathode
for reduction
for anode
for oxidation
and P for products.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Electrolysis
The chemical decomposition of an electrolyte by passing an electric current through it.
- Electrolyte
A substance that conducts electricity in molten or aqueous solution and breaks down chemically.
- Cathode
The negative electrode where reduction occurs.
- Anode
The positive electrode where oxidation occurs.
- Cation
Positively charged ions that move toward the cathode during electrolysis.
- Anion
Negatively charged ions that move toward the anode during electrolysis.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
