Conclusion
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Overview of Force
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're wrapping up our study on force. Can anyone remind us what force is?

It's a vector quantity that can change an object’s motion or shape.

Great! And what unit do we measure force in?

In Newtons, right?

Correct! Remember, 1 Newton is the force needed to accelerate a 1 kg mass at 1 m/s². Can anyone give an example of a force?

Friction between a sliding box and a surface.

Exactly! Does anyone remember how friction affects motion?

It opposes movement, making it harder for objects to slide past each other.

Exactly right! These interactions are crucial for understanding how we use forces in engineering.

Let's recap; force causes changes in motion, it’s measured in Newtons, and friction is a vital aspect to consider. Ready for the next topic?
Effects of Force
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, what are some effects that force can have on an object?

It can change its shape, like stretching a rubber band.

Or cause it to move in a different direction!

Yes! Specifically, it can lead to acceleration or even rotation under certain conditions. What do we call that rotational effect?

That's torque, right?

Correct! Torque is crucial in designs like levers. Can anyone summarize why understanding these effects is important in engineering?

We need to know how forces will act on structures or machines, so they can be safe and functional.

Excellent point! So in our conclusion, understanding the effects of force helps engineers design better systems.
Applications of Force
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s discuss the applications of force. Can someone name a few systems that use force effectively?

Like pulleys and gears!

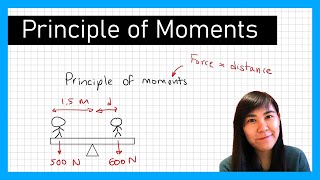
And levers, right? They use the principle of moments.

Yes, the principle of moments is essential—can someone explain how it works in a lever system?

For every distance from the pivot, the force required to lift an object can vary!

Exactly! These concepts not only help us in understanding physics but are practical in building stable structures and mechanical devices. Remember, the prowess of force goes beyond theory to real applications.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this conclusion, we revisit the importance of force in mechanics, covering its definition, effects like motion change and deformation, the role of friction, and application in mechanical systems such as levers, gears, and pulleys.
Detailed
Conclusion
In this section, we summarize the crucial aspects of force as introduced throughout the chapter. We define force as a vector quantity essential for changing an object's state of motion or its shape, with its effects manifesting in various forms including acceleration, rotation, and deformation. The role of friction is underscored as a primary resistive force that influences motion, teaching us the practical means of measuring it. Moreover, we discuss how the principle of moments is integral in the design of mechanical systems, including levers and gears, which serve to illustrate the practical applications of these concepts in real-world engineering and physics.
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Summary of Key Points
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Force is a fundamental concept in mechanics that causes an object to change its state of motion or shape. It is measured in Newtons (N).
Detailed Explanation
The conclusion summarizes the essential aspects of force in mechanics. It highlights that force is a basic principle that influences how objects move or change shape. The measurement of force is done in Newtons (N), which is a standard unit recognized in science.
Examples & Analogies
Think of force like a push or pull you apply when opening a door. If you push harder (more force), the door swings open more easily. This illustrates how changing the amount of force affects the motion of the door, just as it does for all objects.
Effects of Force
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The effects of force include changes in motion (acceleration), rotation (moments), and shape (deformation).
Detailed Explanation
This part of the conclusion reiterates the various effects that force has on objects. When force is applied, an object can accelerate, change direction (motion), rotate around a point (moments), or its shape can be altered (deformation). These effects are crucial in understanding how forces operate in our physical world.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine playing with clay. When you push or pull the clay (applying force), it changes shape (deformation). If you roll it on a table, it can move (change in motion) and may even start to spin as you shape it into a ball (rotation). This shows how force directly impacts both motion and form.
Importance of Friction
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Friction is an important resistive force that affects motion and can be measured using experiments.
Detailed Explanation
The conclusion stresses the significance of friction as a force that opposes motion. Understanding friction is crucial because it affects how easily or difficultly objects can move. It can be quantified through experimental methods to determine how much force is necessary to overcome friction between surfaces.
Examples & Analogies
Consider trying to slide a heavy box across a floor. The rough surface creates friction that makes it sluggish and hard to move. If the floor were smooth, like ice, the box would slide easily. This concept illustrates the pervasive role friction plays in everyday movements.
Applications of the Principle of Moments
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The principle of moments is used to design mechanical systems such as levers, gears, and pulleys.
Detailed Explanation
The conclusion also underlines the application of the principle of moments, which is essential in engineering and mechanics. It refers to how different types of machines utilize force and rotation to function effectively. Understanding this principle allows engineers to create devices that can lift heavy loads or change the direction of forces efficiently.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a seesaw on a playground. When one child at one end pushes down, they can lift the child at the other end up due to the lever principle. By understanding how forces interact on either side of the pivot, we see practical applications of moments in a fun and relatable setting.
Key Concepts
-
Force: A vector quantity that causes an object to change its motion or shape.
-
Effects of Force: Includes changes in motion, shape, and rotation.
-
Friction: A crucial resistive force affecting motion.
-
Torque: The rotational impact of a force computed from the force and distance from the pivot.
-
Applications: Understanding force's role in mechanical systems is vital for engineering.
Examples & Applications
Using a car's acceleration pedal to apply force, thereby changing its motion.
Stretching a rubber band demonstrates the change in shape caused by force.
Turning a doorknob applies torque to rotate the door around its hinges.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Force and motion, like the sea, changes shapes and sets us free.
Stories
Imagine you're at the park. You push a swing (force), and it starts moving (motion). If you lean back to give it more push (shape), the swing goes further—that’s how force works in our lives!
Memory Tools
Friction Stops Motion (FSM) helps remember that friction opposes movement.
Acronyms
FAM (Force, Acceleration, Motion) helps recall that force leads to acceleration which changes motion.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Force
A vector quantity that causes an object to undergo a change in its state of motion or shape.
- Newton (N)
The SI unit of force, defined as the force required to accelerate a 1 kg mass by 1 meter per second squared.
- Friction
A resistive force opposing relative motion between surfaces in contact.
- Torque
The rotational effect of a force, calculated as the product of the force and the perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation.
- Leverage
Using a lever to amplify force in lifting heavy objects.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
