Differences between Plants and Animals
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Movement in Plants and Animals
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore how plants and animals differ in their movement. Can anyone tell me how humans, as animals, are capable of movement?

Humans can walk, run, and even swim! We can move around freely.

That's right! Now, how about plants? What movement do we observe in them?

Plants don't move from place to place, but they can grow toward sunlight!

Exactly! This is called phototropism. Remember, plants are generally **immobile**; they depend on their roots for anchorage. To help remember, think of the acronym 'M' for Movement - 'M' for **Mobile** in animals and 'I' for **Immobile** in plants.

That's a helpful way to remember!

Great! So, we can summarize this point by saying animals show free locomotion while plants show directed growth. Remember this key difference!
Nutritional Modes of Plants and Animals
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's move on to how these organisms get their food. Can anyone describe how plants obtain nutrients?

They make their food through photosynthesis using sunlight.

Correct! Plants are **autotrophic**. What about animals? How do they get their food?

Animals are **heterotrophic** - they eat plants or other animals.

Yes! So remember, 'A for Autotrophic' for plants and 'H for Heterotrophic' for animals, which can be summarized as 'A+H.' Now, why do you think these differences exist?

It seems like it helps them survive in their environments.

Exactly! These adaptations are crucial for their survival. Excellent discussion!
Growth Patterns in Plants and Animals
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's discuss growth. What can you tell me about how plants grow?

Plants keep growing as long as they live, but only in certain areas like tips.

Exactly! This is called localized growth. And what about animals?

Animals grow uniformly until they reach a certain size.

Correct! Remember to differentiate - you might think of 'L for Localized' growth in plants and 'U for Uniform' growth in animals. Let's summarize that plants grow in particular areas while animals grow consistently across their body. Who has thoughts on the importance of these growth patterns?

So plants can adapt to their environment as they grow!

Yes! Great connection!
Response to Stimuli in Plants and Animals
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s discuss response times! Who can tell me how quickly plants react to their environment?

They react slowly, like how they turn towards light.

That's correct! Plants respond to stimuli, but their response is much slower compared to animals. What can anyone tell me about animals?

Animals can respond quickly, like when we pull our hands back from something hot.

Exactly! Remember: 'S for Slow' for plants and 'Q for Quick' for animals! Let's summarize: Plants may be slow to respond, whereas animals are quick, which aids their survival.
Cell Structure Differences
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let's talk about the cell structure. How many of you know about the differences in cell walls?

Plants have cell walls, but animals don’t!

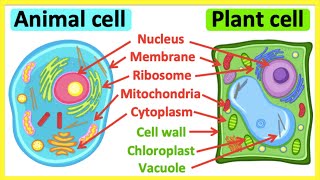
Right! Plants are surrounded by a rigid **cell wall**, which provides stability. Comparatively, animal cells only have a cell membrane. Remember this difference! We can summarize that plants’ structure supports their stationary lifestyle while animals' flexible structure supports their mobility.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Plants and animals have various differences, including their methods of movement, nutrition, growth patterns, responsiveness to stimuli, and cellular structures, which are crucial for understanding their biological roles and adaptations.
Detailed
Differences between Plants and Animals
This section delves into the key characteristics that distinguish plants from animals. Plants are primarily immobile, relying on their roots for support, whereas animals exhibit locomotion, allowing them to move freely. The method of obtaining food is another significant difference; plants are autotrophic, capable of photosynthesis to create their food, while animals are heterotrophic, consuming other organisms for energy.
In terms of growth, plants exhibit localized growth, meaning that only certain areas, such as tips and meristems, grow, whereas animal growth is uniform and continuous throughout their lifecycle until they reach maturity. When it comes to responsiveness, plants respond slowly to stimuli compared to animals, which can respond quickly and adapt to their environment. A notable structural difference is that plants possess a cell wall, while animal cells do not have this rigid structure. Understanding these differences enhances our knowledge of biological diversity and the roles of each group within ecosystems.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Movement
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Movement
Plants are generally immobile while animals show locomotion.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk discusses how plants and animals differ in terms of movement. Plants are fixed in one place and do not move from their position, whereas animals are capable of movement. This capability of animals is crucial for their survival, as it allows them to escape predators, find food, and move to different environments. In contrast, plants may move in a limited sense, such as bending towards sunlight (a process known as phototropism), but they do not relocate.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a plant in your garden standing still, soaking up sunlight, while a dog runs around the yard, chasing after a ball. The dog's ability to run and change direction represents the mobility found in animals, contrasting with the planted, stationary nature of the flower.
Nutrition
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Nutrition
Plants are autotrophic, meaning they produce their own food through photosynthesis, while animals are heterotrophic, relying on consuming other organisms for their nutrients.
Detailed Explanation
In this section, we learn about how plants and animals obtain their nutrients. Plants are autotrophs, which means they create their own food using sunlight, carbon dioxide from the air, and water. This process is called photosynthesis. On the other hand, animals cannot produce their own food; they are heterotrophs that must eat plants or other animals to obtain the nutrients and energy they require to survive.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a chef (the plant) who can prepare an endless supply of food using ingredients from the garden (the sun, water, and air) versus a customer (the animal) who needs to purchase a meal from the chef. The chef creates the meal independently, while the customer depends on the chef to satisfy hunger.
Growth Patterns
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Growth
Plants exhibit localized growth, while animals have uniform and continuous growth.
Detailed Explanation
This part highlights the differences in growth between plants and animals. Plants grow at specific points called meristems, typically found at the tips of roots and stems, which leads to localized growth. This means that new cells are produced at these points, resulting in branches or roots extending outward. In contrast, animals grow in a more uniform manner, where growth is continuous over the entire body rather than at specific locations.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a tree that grows taller as new shoots emerge from its top and branches, similar to how someone might add layers to a cake, only adding frosting at certain areas. On the other hand, a puppy grows proportionally as a whole, becoming a larger version of itself—like inflating a balloon evenly all around.
Response to Stimuli
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Response to Stimuli
Plants respond slowly to stimuli, while animals respond quickly.
Detailed Explanation
Here, we see how living organisms react to their environment. Plants have a slower response to external stimuli, such as light or touch, leading to gradual changes like growth direction. Animals, due to their nervous systems and muscles, can react quickly to stimuli, enabling fast responses that are essential for survival, such as fleeing from danger or seeking food.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a plant growing toward a window to seek sunlight slowly over days, while a rabbit bolting away from a sudden loud noise just one leap after it occurs represents the quick reaction of animals. The rabbit’s ability to swiftly respond helps it avoid predators.
Cell Structure
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Cell Structure
Plants have a cell wall, while animals do not.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk explains a fundamental difference in cellular structure between plants and animals. Plant cells contain a rigid cell wall made of cellulose, which provides additional support and protection. Animal cells, on the other hand, do not have a cell wall; instead, they are surrounded by a flexible cell membrane. This structural difference impacts how plants and animals grow and interact with their environments.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of the cell wall in plant cells as the sturdy walls of a house, providing structure and support, while the cell membrane in animal cells is akin to a soft curtain that allows some things to pass through while keeping others out. The house stands firm and strong, whereas the curtain is flexible and can be adjusted.
Key Concepts
-
Movement: Animals are mobile while plants are generally immobile.
-
Nutritional Modes: Plants are autotrophic and produce food through photosynthesis, whereas animals are heterotrophic and consume food from other sources.
-
Growth Patterns: Plants exhibit localized growth, while animals show uniform growth.
-
Response to Stimuli: Plants respond slowly to environmental changes, whereas animals respond quickly.
-
Cell Structure: Plants have a rigid cell wall which provides structure, while animals lack a cell wall.
Examples & Applications
An example of plant movement is the way sunflowers follow the sun during the day.
An example of animal movement is a cheetah running fast to catch prey.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Plants stay in one place, grow towards the sun with grace, Animals roam and run, chasing prey just for fun.
Stories
Once in a garden lived a plant named Sunny who always turned to face the sunlight. Nearby was a cheetah named Swift who ran fast to catch his food. Though both lived in nature, one stayed still and the other dashed around.
Memory Tools
Remember: 'A' for Autotrophic and 'H' for Heterotrophic - the food sources of plants and animals!
Acronyms
Key differences can be summed up as 'MANGERS'
Movement
Autotrophic
Nutritional modes
Growth
Excretion
Response
Structure.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Autotrophic
Organisms that produce their own food using sunlight or chemicals; primarily refers to plants.
- Heterotrophic
Organisms that obtain food by consuming other organisms; primarily refers to animals.
- Localized Growth
Growth occurring in specific regions of an organism, such as the tips of plants.
- Uniform Growth
Growth that occurs evenly across the entire body of an organism.
- Cell Wall
A rigid layer that surrounds the cells of plants, providing structure and protection.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
