Law of Conservation of Mass
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to the Law of Conservation of Mass
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Good morning, class! Today we are diving into the Law of Conservation of Mass. To start, can anyone tell me what they think this law means?

Does it mean that mass can’t disappear?

Exactly! The Law of Conservation of Mass states that mass can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. Can someone tell me how this might apply to a chemical reaction?

So if we mix substances, the total mass before should be the same as after the reaction?

Right on! This is crucial for balancing chemical equations later on. Remember this principle as we move forward.
Applications of the Law of Conservation of Mass
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand what the Law of Conservation of Mass states, let’s think about its importance in real-world scenarios. Why do you think this law is significant?

It helps in making sure reactions are balanced and we know what to expect from them!

Exactly! This law allows chemists to predict the outcomes of reactions with certainty. Anyone can give me an example of a reaction?

How about burning wood? The ashes are less than the wood?

Great thought! Actually, in that process, gaseous products like carbon dioxide are released into the atmosphere, which means that gases also contribute to the total mass. Therefore, the law holds true when you account for all reactants and products.
Experimental Proof of Conservation of Mass
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

I want to show you an experiment to see the Law of Conservation of Mass in action. We will combine vinegar and baking soda. What do you think will happen to the mass?

It should stay the same because mass is conserved!

That’s the spirit! We'll measure the reactants’ mass before we mix them, and then capture the total gas that gets generated. We will measure the mass again after the reaction. Let’s see if it adds up.

I can’t wait to see if we get the same mass!

Remember, the reaction will produce gas, which is part of the total mass we must account for!
Summary and Quiz
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up, let’s review what we covered about the Law of Conservation of Mass. It’s crucial that the total mass of reactants equals the total mass of products. Can anyone state something important we learned?

If mass seems to disappear, we need to account for all gases produced!

Spot on! Now, let’s do a quick quiz. If I mix 20 grams of chemical A with 30 grams of chemical B, how much will I have after the reaction?

Fifty grams, right? Because 20 plus 30 equals 50!

Correct! Well done, everyone. You’re all ready to apply this law in chemical equations!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
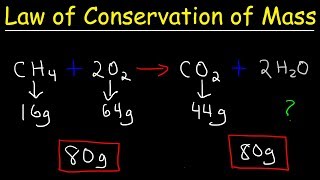
According to the Law of Conservation of Mass, in a closed system, the total mass of the reactants is equal to the total mass of the products resulting from a chemical reaction. This principle is fundamental in understanding chemical reactions and balancing chemical equations.
Detailed
Law of Conservation of Mass
The Law of Conservation of Mass is a fundamental concept in chemistry, positing that mass cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. This means that the total mass of the reactants before a reaction must equal the total mass of the products after the reaction has taken place.
This principle is essential not only for theoretical understanding but also for practical applications, such as balancing chemical equations. It emphasizes the integrity of matter and guides chemists in predicting the outcomes of chemical interactions. Mastering this concept lays the groundwork for further studies in chemistry, particularly in the understanding of chemical reactions and stoichiometry.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to the Law of Conservation of Mass
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Mass can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
Detailed Explanation
The Law of Conservation of Mass states that in any chemical reaction, the total mass of the substances involved remains constant. This means that the mass of the reactants (the starting materials) is equal to the mass of the products (the substances formed). For instance, if you start with 10 grams of reactants, you will end up with 10 grams of products, regardless of the changes that occur during the reaction.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a birthday balloon. When you inflate it, you add air into the balloon, but the total weight of the balloon plus the air stays the same. Similarly, in a chemical reaction, while the reactants may change into new products, the total mass remains unchanged.
Application of the Law in Chemical Reactions
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Total mass of reactants = Total mass of products
Detailed Explanation
This part of the law emphasizes the equality of mass between reactants and products. When a chemical reaction occurs, the mass before the reaction (total mass of reactants) will always be equal to the mass after the reaction (total mass of products). This concept helps scientists to balance chemical equations and understand the quantities needed or produced in reactions. For example, in a combustion reaction where wood burns, the mass of oxygen used and the mass of the ash produced, combined with the gases released, will equal the initial mass of the wood and oxygen before the reaction.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are baking a cake. If you use 2 cups of flour, 1 cup of sugar, and 1 cup of milk, the mass of these ingredients before baking is equal to the mass of the finished cake plus the baking time losses (like evaporation). This ensures that nothing magically appears or disappears; everything you put in is accounted for in the final product.
Key Concepts
-
Mass Conservation: Mass cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction.
-
Total Mass: The mass of the reactants is equal to the mass of the products in a chemical reaction.
Examples & Applications
Example of a balanced equation: 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O, where the mass of the hydrogen and oxygen equals the mass of the water produced.
In a closed system, when baking soda is mixed with vinegar, the total weight before the reaction equals the total weight after the gas is released.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the lab where we mix and spin, the mass stays the same, it won't thin!
Stories
Imagine a magic pot where ingredients mix; no matter how much you stir and fix, the weight stays the same, it’s a clever trick!
Memory Tools
Remember 'MCP': Mass Conservation Principle - mass is conserved in chemical reactions!
Acronyms
Use the acronym M+P=MR
Mass of Products equals Mass of Reactants.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Law of Conservation of Mass
A principle that states that in a closed system, mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
- Reactants
The initial substances that undergo a chemical reaction.
- Products
The new substances formed as a result of a chemical reaction.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
