Atmosphere and Climate
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to the Atmosphere
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to learn about the atmosphere, which is the blanket of gases surrounding the Earth.

Why is it important for our planet?

Great question! The atmosphere plays a vital role in regulating temperature, supporting life, and influencing weather and climate.

Can you explain what climate means?

Certainly! Climate refers to long-term patterns of temperature, humidity, wind, and precipitation in a region. Think of weather as the daily mood and climate as the overall personality!

That’s a nice way to put it!

Exactly! Understanding climate helps us prepare for what might happen in a region over time.
Structure of the Atmosphere
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

The atmosphere is divided into five main layers. Can anyone name one of the layers?

Is the Troposphere one of them?

Exactly! The Troposphere is where we experience the weather, and it stretches from 0 to 12 km. Temperature decreases with altitude here.

What about the other layers?

After the Troposphere, we have the Stratosphere, which contains the ozone layer. Then comes the Mesosphere, which is the coldest, followed by the Thermosphere and finally the Exosphere.

That sounds fascinating! What happens in the Thermosphere?

In the Thermosphere, temperatures can be extremely high, and you might see auroras and space shuttles!

Wow, that’s amazing!
Weather vs. Climate
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s clarify the difference between weather and climate. Can anyone tell me how they differ?

Weather is what happens daily, right?

Exactly! Weather is the short-term atmospheric condition, and it changes all the time!

And climate is the average of those conditions over a long time?

Correct! Climate is measured over 30 years or more and defines regions like deserts or tundras.

What about temperature and rainfall?

Good point! Both are key components of weather and climate.

Thanks for clarifying that!
Factors Influencing Climate
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s talk about the factors that influence climate. Who can name one?

Latitude!

Excellent! Latitude affects how much sunlight different areas receive, impacting temperature.

What about altitude?

Yes, higher altitudes are generally cooler. Remember, the temperature decreases with elevation!

What else?

Distance from the sea, ocean currents, and winds also play crucial roles in determining climate!
Greenhouse Effect and Climate Change
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Who knows what the greenhouse effect is?

Is it about gases trapping heat?

Spot on! The greenhouse effect is essential for life, trapping heat from the sun, but too much of it leads to global warming.

What causes global warming?

Great question! Causes include excess greenhouse gases from burning fossil fuels and deforestation.

And what are its effects?

Effects include melting polar ice, rising sea levels, and changing weather patterns.

That sounds serious. What can we do to help?

We can use renewable energy, practice conservation, and support reforestation efforts!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses the composition and structure of the atmosphere, differentiates between weather and climate, highlights factors influencing climate, explains the greenhouse effect, and addresses global warming's causes and effects as well as human contributions and solutions to mitigate climate change.
Detailed
Atmosphere and Climate
The atmosphere, comprising a protective blanket of gases surrounding Earth, plays a crucial role in regulating the planet's temperature and supporting life. Climate represents long-term patterns of temperature, humidity, wind, and precipitation in various regions.
Structure of the Atmosphere
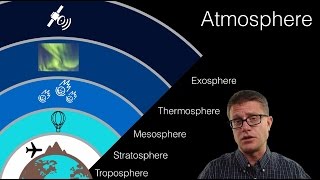
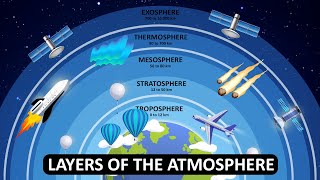
The atmosphere is sectioned into five layers:
1. Troposphere (0–12 km): Weather occurs here, with temperatures decreasing with altitude.
2. Stratosphere (12–50 km): Contains the ozone layer; temperatures rise with altitude.
3. Mesosphere (50–80 km): This is the coldest layer where meteors burn up.
4. Thermosphere (80–500 km): Characterized by high temperatures and phenomena like auroras and space shuttle activities.
5. Exosphere (above 500 km): The outermost layer that gradually merges with space.
Composition of the Atmosphere
The atmosphere consists mainly of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%), with trace amounts of argon, carbon dioxide, and varying levels of water vapor and dust.
Weather vs. Climate
- Weather is the short-term atmospheric condition that can change daily, including elements like temperature and rainfall.
- Climate represents long-term averages of these weather patterns over decades, aiding in defining different regions like deserts and tundras.
Factors Influencing Climate
Several key factors influence climate:
- Latitude: Affects sunlight intensity and temperature.
- Altitude: Higher locations generally experience cooler temperatures.
- Distance from the sea: Coastal areas usually have moderate climates.
- Ocean currents: Influence temperature and precipitation patterns.
- Winds and air masses: Affect overall weather conditions.
The Greenhouse Effect
The greenhouse effect is essential for life, caused by gases like CO₂ and CH₄ trapping heat, but excessive levels can lead to global warming.
Global Warming and Climate Change
Global warming refers to the rising average surface temperature of Earth due to increased greenhouse gases, deforestation, and industrial activities. Its consequences include melting ice caps, rising sea levels, altered rainfall patterns, and an increase in extreme weather events.
Human Role in Climate Change
Human activities contributing to climate change include fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, pollution, and waste generation.
Measures to Mitigate Climate Change
Numerous strategies exist to combat climate change, such as:
- Utilizing renewable energy sources
- Promoting afforestation and reforestation
- Enhancing energy conservation
- Advancing eco-friendly transport
- Cooperating on global agreements like the Paris Agreement.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to the Atmosphere
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The atmosphere is the blanket of gases surrounding the Earth. It plays a vital role in regulating temperature, supporting life, and influencing weather and climate. Climate refers to the long-term patterns of temperature, humidity, wind, and precipitation in a region.
Detailed Explanation
The atmosphere is the layer of gases that envelops our planet. It is crucial because it keeps the Earth warm, allows water and air to support various forms of life, and affects weather patterns. Climate, on the other hand, is a broader term that encompasses the average weather conditions (like temperature and rainfall) in a particular area over a long period, usually measured over 30 years or more.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the atmosphere like a giant blanket that keeps you warm on a cold night. Just as a blanket helps prevent body heat from escaping, the atmosphere helps retain heat from the sun, making our planet suitable for life.
Structure of the Atmosphere
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The atmosphere is divided into five main layers:
| Layer | Altitude Range | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Troposphere | 0–12 km | Weather occurs here; temperature decreases with altitude |
| Stratosphere | 12–50 km | Contains the ozone layer; temperature increases with altitude |
| Mesosphere | 50–80 km | Coldest layer; meteors burn here |
| Thermosphere | 80–500 km | Very hot; auroras and space shuttles present |
| Exosphere | 500 km and above | Outermost layer; merges into outer space |
Detailed Explanation
The atmosphere is organized into five distinct layers, each characterized by different temperatures and phenomena. The Troposphere is where we live and experience weather, and its temperature decreases as you go higher. The Stratosphere contains the ozone layer, which protects us from the sun's harmful radiation and gets warmer as altitude increases. The Mesosphere is the coldest layer, where meteors burn up upon entering. In the Thermosphere, temperatures soar, and phenomena like auroras occur. Finally, the Exosphere is the thinnest layer that transitions into outer space.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine stacking layers of different materials on top of each other. Just like how a cake or a lasagna has various layers that can have different ingredients and textures, the atmosphere has layers that have distinct characteristics and roles, contributing to the weather and climate we experience.
Composition of the Atmosphere
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
| Constituent | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N₂) | 78% |
| Oxygen (O₂) | 21% |
| Argon, Carbon Dioxide | ~1% |
| Water Vapour, Dust, etc. | Variable amounts |
Detailed Explanation
The atmosphere is primarily made up of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%), which are essential for life. Other gases like argon and carbon dioxide make up a small fraction, around 1%. Water vapor and dust particles also vary in amount depending on the location and current weather conditions. Each component plays a vital role; for example, oxygen is crucial for breathing, while carbon dioxide is used by plants for photosynthesis.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the atmosphere as a smoothie. The nitrogen and oxygen are like the main fruits that make up the bulk of the drink, while carbon dioxide and argon are like the small bits of flavoring that enhance the taste. Just as a good smoothie relies on a balanced mix of ingredients, our atmosphere functions effectively due to its diverse composition.
Difference Between Weather and Climate
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
| Weather | Climate |
|---|---|
| Short-term atmospheric condition | Long-term average weather patterns |
| Changes daily | Measured over 30+ years |
| Includes temperature, rainfall | Defines regions like desert or tundra |
Detailed Explanation
Weather refers to the day-to-day state of the atmosphere, like if it's sunny, rainy, or windy. It can change rapidly and is short-term. Climate, however, is about the long-term patterns we see over years, defining what kind of weather a region typically experiences. For example, a desert has a hot climate, whereas an Arctic region has a cold climate.
Examples & Analogies
Think of weather as a snapshot while climate is like a photo album. The snapshot shows you what’s happening in a moment (like rain today), while the photo album shows the bigger picture over many years (like how it usually rains in your area from June to September).
Factors Influencing Climate
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Latitude – Distance from the equator affects sunlight and temperature
● Altitude – Higher altitudes are cooler
● Distance from sea – Coastal areas have moderate climates
● Ocean currents – Warm and cold currents influence coastal climate
● Winds and air masses – Affect temperature and precipitation
Detailed Explanation
Various factors influence a region's climate. Latitude determines how much sunlight an area receives; regions near the equator are warmer than those closer to the poles. Altitude also plays a role; higher elevations typically mean cooler temperatures. Coastal areas benefit from moderate climates due to their proximity to water, which loses and gains heat slowly. Ocean currents can either warm or cool coastal areas, and the movement of air masses can bring different weather conditions, impacting temperature and precipitation.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of climate like a recipe, where different ingredients (factors) come together to create a unique dish (the climate). Just as varying amounts of salt, spices, and herbs can change the flavor of a meal, factors like latitude, altitude, and proximity to seas can significantly alter the climate of a place.
Key Concepts
-
Atmosphere: The gas layer surrounding Earth, vital for life and climate regulation.
-
Weather vs. Climate: Weather is the short-term state of the atmosphere; climate is the long-term average.
-
Greenhouse Effect: Essential for storing heat on Earth, but excess leads to global warming.
-
Climate Change: Long-term changes in temperature and weather patterns due to human and natural activities.
Examples & Applications
An example of weather: A sunny day followed by a rainy day. This change occurs rapidly and frequently.
An example of climate: The climate of a desert region is classified as arid due to low precipitation over many years.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Atmosphere holds the gas we need, for life to grow, it takes the lead.
Stories
Once upon a time in the sky, gases danced and never ran dry. They cooled, warmed, kept life around, in layers vast, they could be found.
Memory Tools
TRS ME! - To remember the layers: Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, Thermosphere, Exosphere.
Acronyms
WEATHER - Weather's Easy To Observe, Temperature Helps Everyone Report.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Atmosphere
The layer of gases surrounding the Earth, essential for supporting life and regulating temperature.
- Climate
The long-term average of weather conditions in a specific region.
- Troposphere
The lowest layer of the atmosphere where weather occurs, extending from 0 to 12 km.
- Stratosphere
The layer of the atmosphere above the troposphere, containing the ozone layer and extending from 12 to 50 km.
- Greenhouse Effect
The warming of Earth's surface due to greenhouse gases trapping heat.
- Global Warming
The increase in Earth's average surface temperature due to human activities and excess greenhouse gases.
- Deforestation
The clearing of forests, contributing to increased carbon levels in the atmosphere.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
