Types of Soil in India
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Alluvial Soil
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to start with Alluvial Soil. Can anyone tell me what makes Alluvial Soil so important in India?

Is it because it's very fertile?

Exactly! Alluvial Soil is known for its fertility and is rich in potash, making it ideal for agriculture, especially in the Indo-Gangetic plains.

What crops are commonly grown in this type of soil?

Crops like rice, wheat, and sugarcane thrive here due to the soil's rich nutrient content. Remember the acronym 'FIVE': Fertile, Ideal for Vegetables, and easy.

Got it! Fertile and Ideal for Vegetables!

Great! Now, let's move on to the next type of soil.
Black Soil
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss Black Soil. Can anyone describe its characteristics?

I think it retains moisture well?

Yes! It's rich in clay and minerals, making it great for moisture retention. This helps farmers grow crops like cotton.

Where can we find Black Soil in India?

Black Soil is primarily found in the Deccan Plateau, particularly in states like Maharashtra and Gujarat. Remember 'C.R.C.' for Cotton, Retains moisture, and Clay!

That helps me remember!

Great! Let's keep going.
Red Soil
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's talk about Red Soil next. What do you guys know about it?

I think it’s less fertile and needs fertilizers?

Correct! Red Soil is less fertile than Alluvial and Black Soil, and it usually needs fertilizers to enhance productivity.

Which regions predominantly have Red Soil?

It's mainly found in states like Tamil Nadu and Karnataka. Think 'M.R.': Must be Fertilized Red soil.

That makes it easier to remember!

Excellent! Now let's recap before we proceed.
Laterite and Desert Soil
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next on the list are Laterite and Desert Soil. What sets Laterite Soil apart?

It’s rich in iron but low in fertility, right?

Exactly right! Laterite Soil is often found in regions with heavy rainfall and is less fertile.

And Desert Soil?

Desert Soil has sandy texture and is characterized by low moisture and fertility. It’s predominantly found in Rajasthan. Use 'S.L.L.': Sandy, Low moisture, Low fertility!

That really helps!

Let’s summarize what we’ve learned before moving on to the last type.
Mountain Soil
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s discuss Mountain Soil. Can someone describe its characteristics?

I know it's thin and often acidic!

Exactly! This soil supports various forests and is primarily found in the Himalayan region.

What are its uses?

Mountain Soil is vital for supporting forest ecosystems and biodiversity. Keep in mind 'A.F.S.': Acidic, Forests, Supports biodiversity!

Thanks! That's really clear now.

Let’s recap all the soil types we learned about today!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore the major types of soil in India, including Alluvial, Black, Red, Laterite, Desert, and Mountain soils, highlighting their unique properties and geographic distribution. Each type contributes differently to agriculture and ecosystem sustainability.
Detailed
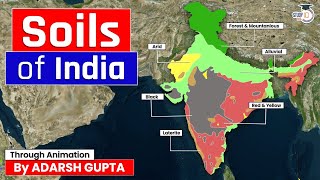
Types of Soil in India
India is characterized by a diverse range of soil types, each distinguished by its unique properties and the specific agricultural or ecological functions it supports.
Types of Soil and Their Characteristics:
- Alluvial Soil:
- Characteristics: This soil is known for its fertility, rich potash content, and an excellent capacity to support agriculture.
- Regions Found: Predominantly in the Indo-Gangetic plains, it supports a significant percentage of India’s agricultural output.
- Black Soil:
- Characteristics: Rich in clay and minerals, this soil is known for its moisture-retention capacity, making it suitable for crops like cotton.
- Regions Found: Mainly found in the Deccan Plateau, including states like Maharashtra and Gujarat.
- Red Soil:
- Characteristics: Less fertile than other soils, red soil requires fertilizers for agricultural productivity.
- Regions Found: Found mainly in Tamil Nadu and Karnataka.
- Laterite Soil:
- Characteristics: Rich in iron but poor in fertility, this soil is often found in regions with high rainfall.
- Regions Found: Prominently located in the Western Ghats and Meghalaya.
- Desert Soil:
- Characteristics: Characterized by sandy texture, low moisture, and low fertility, desert soil is challenging for agriculture.
- Regions Found: Predominantly found in Rajasthan.
- Mountain Soil:
- Characteristics: Thin and often acidic, this soil supports forests and a varied ecosystem.
- Regions Found: Common in the Himalayan region.
Understanding the types of soil in India is crucial for managing agriculture effectively and ensuring the sustainability of our ecological systems.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Alluvial Soil
Chapter 1 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Alluvial Soil: Fertile, rich in potash, best for agriculture
Regions Found: Indo-Gangetic plains
Detailed Explanation
Alluvial soil is primarily composed of fine particles that have been deposited by rivers over time. It is highly fertile, meaning it supports a lot of plant growth, especially in agriculture. The term 'rich in potash' means that this soil contains a significant amount of potassium – a nutrient critical for plant health. The regions where this soil is predominantly found are the Indo-Gangetic plains, which stretch across northern India, including states like Punjab and Uttar Pradesh.
Examples & Analogies
Think of alluvial soil like a natural fertilizer created by rivers. Just as a gardener enriches soil with compost to grow healthy plants, rivers deposit nutrient-rich sediments that make the land along their banks very fertile. Hence, farmers in the Indo-Gangetic plains can grow plenty of crops like rice and wheat.
Black Soil
Chapter 2 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Black Soil: Rich in clay and minerals, retains moisture
Regions Found: Deccan Plateau (Maharashtra, Gujarat)
Detailed Explanation
Black soil, also known as regur soil, has a unique composition rich in clay and minerals like calcium, magnesium, and iron. This type of soil has excellent water-retaining capacity, making it ideal for crops that need consistent moisture, such as cotton. It is mainly found in the Deccan Plateau region, covering areas in Maharashtra and Gujarat.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of black soil like a sponge – it has a high moisture content, which allows it to absorb and hold water well. Just like you wouldn't want to use a dry sponge for cleaning, farmers grow specific crops like cotton in this rich soil because it helps retain water during dry spells.
Red Soil
Chapter 3 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Red Soil: Less fertile, needs fertilizers
Regions Found: Tamil Nadu, Karnataka
Detailed Explanation
Red soil is characterized by its reddish color, which comes from iron oxide. Although it is less fertile compared to alluvial and black soil, it can still support vegetation. However, due to its lower nutrient content, crops grown in red soil often require fertilizers to enhance their growth. This soil type is common in southern states like Tamil Nadu and Karnataka.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine red soil as a basic lunchbox with just a sandwich – it may fill you up, but you might need some snacks (like fertilizers) for extra energy. Similarly, while red soil can sustain some plants, additional nutrients are often needed to encourage stronger and healthier crops.
Laterite Soil
Chapter 4 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Laterite Soil: Rich in iron, poor fertility
Regions Found: Western Ghats, Meghalaya
Detailed Explanation
Laterite soil is formed in tropical regions under conditions of heavy rainfall. It is characterized by a high concentration of iron and aluminum oxides, which give it a reddish color. Unfortunately, laterite soil often lacks essential nutrients, making it less fertile for agriculture. It is commonly found in regions like the Western Ghats and Meghalaya.
Examples & Analogies
Consider laterite soil similar to a rusty metal surface – it may look striking, but it might not be very useful for growing food without proper care. Just as someone might need to treat rust for functionality, farmers need to amend laterite soil with compost or fertilizers to enhance its fertility.
Desert Soil
Chapter 5 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Desert Soil: Sandy, low moisture and fertility
Regions Found: Rajasthan
Detailed Explanation
Desert soil is characterized by sandy texture, which typically drains quickly and has limited moisture retention. This type of soil is found in arid regions like Rajasthan, where water scarcity is a significant challenge for agriculture. Because of low nutrient levels, this soil is often unsuitable for most crops without significant irrigation.
Examples & Analogies
Think of desert soil like a dry sponge that has been left out in the sun; it can't hold onto water very well, making it hard for plants to thrive. Consequently, farmers in desert areas must find innovative ways, such as irrigation, to successfully cultivate crops despite the tough conditions.
Mountain Soil
Chapter 6 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Mountain Soil: Thin, acidic, supports forests
Regions Found: Himalayan region
Detailed Explanation
Mountain soil is usually thin, highly acidic, and has a limited layer of topsoil due to erosion and rugged terrain. This type of soil supports forest growth but tends to have limited agricultural potential. It is commonly found in the Himalayan region, where the slopes create challenging conditions for farming.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine mountain soil like a steep hill where you can hardly set up a picnic – it might be beautiful to look at, but doing anything productive, like growing crops, is tough. The steep slopes and thin soil make it suitable mainly for forests, which naturally thrive in such an environment.
Key Concepts
-
Alluvial Soil: Fertile, ideal for agriculture.
-
Black Soil: Moisture-retentive, found in Deccan Plateau.
-
Red Soil: Requires fertilizers, found in Tamil Nadu and Karnataka.
-
Laterite Soil: Rich in iron, low in fertility.
-
Desert Soil: Sandy texture, low moisture and fertility.
-
Mountain Soil: Thin, supports forests.
Examples & Applications
Alluvial Soil is primarily used for growing crops like rice and wheat.
Desert Soil poses challenges for agricultural use but supports unique desert flora.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Alluvial's low and black soil's wet, Red needs help, it's quite a bet.
Stories
A farmer uses Alluvial Soil for lush crops, while across the desert, another struggles in sandy stops.
Memory Tools
Remember the acronym 'A B R L D M' for Alluvial, Black, Red, Laterite, Desert, and Mountain soils.
Acronyms
Use 'F.I.C.S.' to remember
Fertile
Iron-rich
Clayey
Sandy for Alluvial
Laterite
Black
and Desert respectively.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Alluvial Soil
Fertile soil rich in potash, typically found in river plains.
- Black Soil
Soil rich in clay and minerals, capable of moisture retention, found in the Deccan Plateau.
- Red Soil
Less fertile soil mainly found in Tamil Nadu and Karnataka, requiring fertilizers.
- Laterite Soil
Soil rich in iron, but low in fertility, typically found in wet regions.
- Desert Soil
Sandy soil with low moisture and fertility, primarily found in Rajasthan.
- Mountain Soil
Thin, often acidic soil that supports forests and is found in mountainous regions.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
