What is Mechatronics?
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Mechatronics
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll start by discussing what mechatronics is. Mechatronics combines four disciplines: mechanical engineering, electronics, computer systems, and control theory. Can anyone tell me how these fields might work together?

Maybe they come together to make machines that can think and act on their own?

Exactly! That's a great way to put it. They create intelligent systems. For a memory aid, just remember MECC: Mechanical, Electronics, Control, and Computer Systems. It’ll help you remember the key components of mechatronics.

So does that mean every robot uses mechatronics?

Not every robot, but most modern robots do! They rely on the integration of these disciplines to function effectively.
Key Components of Mechatronics
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's dissect what makes up mechatronics. We have sensors, actuators, controllers, and of course, the mechanical structure. Who can describe what a sensor does?

Sensors detect changes in the environment, like temperature or position!

Absolutely! Think of sensors as the sensory organs of the system. Now, who can share what an actuator does?

Actuators create movement, like turning wheels or opening doors!

Perfect! Actuators are crucial because they implement the decisions made by the controllers. Remember the acronym SCAM: Sensor, Controller, Actuator, Mechanical structure.
Examples of Electro-Mechanical Systems
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's delve into where we've seen these systems in action. For example, can you name an electro-mechanical system in cars?

Anti-lock braking system?

Exactly! Now, what about something in our homes?

How about washing machines?

Great examples! These systems showcase how mechatronics is embedded in everyday life. To help you remember, think of 'Wash Cars' to remind you of washing machines and cars!
Importance of Mechatronics
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, why is mechatronics important? Can anyone suggest a benefit?

Automation! It makes processes more efficient.

Exactly, automation improves productivity! Also, mechatronics encourages interdisciplinary thinking. Remember the acronym MAPE: Miniaturization, Automation, Precision, Interdisciplinary thinking. Can you think of a place where precision is crucial?

In medical instruments, like MRI scanners!

Right again! Well done, everyone! Remember, mechatronics is everywhere.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section introduces mechatronics as a field that combines multiple engineering disciplines to design and manufacture systems that are automated and intelligent. It explores key components, characteristics, applications, and the importance of mechatronics in modern engineering.
Detailed
What is Mechatronics?
Mechatronics is the synergistic integration of mechanical engineering, electronics, computer systems, and control theory. The objective is to design and manufacture intelligent systems capable of performing complex tasks.
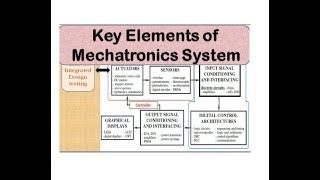
Key Components of Mechatronics
- Mechanical Engineering: The backbone that involves the design and operation of machinery.
- Electronics: Incorporation of circuits and devices that control electricity.
- Computer Systems: Utilization of software and hardware to process information and automate tasks.
- Control Theory: Methods that govern how these components interact and behave over time.
Electro-Mechanical Systems
An electro-mechanical system combines electrical and mechanical components to perform specific functions. Key components include:
- Sensors: Detect physical changes such as temperature or position.
- Actuators: Create physical motion utilizing motors and solenoids.
- Controllers: Implement decisions based on input from sensors using devices like microcontrollers and PLCs.
- Mechanical Structures: Transform or transmit motion through gears and linkages.
Characteristics of Electro-Mechanical Systems
- Integration of Hardware and Software: Necessary for seamless operation.
- Feedback Control Systems: Enables open-loop or closed-loop control mechanisms.
- Precision and Automation: Vital to achieving high performance.
- Interfacing: Necessary connections between electrical inputs and mechanical outputs.
Real-World Examples
Automobiles:
- Anti-lock Braking System (ABS)
- Electric Power Steering
- Automatic Transmission Systems
Home Appliances:
- Washing Machines
- Refrigerators
Medical Instruments:
- Surgical Robots
- MRI Scanners
Importance in Engineering
Mechatronics is crucial due to its focus on automation, precision, and interdisciplinary thinking, which enhances productivity and offers innovative solutions in engineering.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Mechatronics
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Mechatronics is the synergistic integration of:
● Mechanical engineering
● Electronics
● Computer systems
● Control theory
to design and manufacture intelligent systems and products.
Detailed Explanation
Mechatronics is a multidisciplinary field combining four major areas: mechanical engineering, electronics, computer systems, and control theory. This integration creates systems that can operate intelligently by incorporating various technologies. For example, in robotics, mechanical parts work together with software to make decisions based on input from sensors, all of which are crucial for the successful operation of complex machinery.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a modern car: the mechanical parts (like the engine and brakes), electronic components (like sensors and control systems), and the software that manages everything work together seamlessly. This collaborative approach is similar to how a well-decorated cake combines various ingredients to create a delicious final product.
Purpose of Mechatronics
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
to design and manufacture intelligent systems and products.
Detailed Explanation
The goal of mechatronics is to create intelligent machines that can perform tasks autonomously. This involves not just building machines but also ensuring they can learn from their environments, respond to changing conditions, and improve their efficiency over time. It emphasizes functionality and adaptability in various applications, from simple household devices to complex industrial robots.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a smart vacuum cleaner. Rather than just being a machine that moves around and cleans, it uses sensors to map out the room, avoids obstacles, and even returns to its charger when its battery is low. This smart behavior is a direct result of mechatronics integrating different engineering disciplines.
Key Concepts
-
Mechatronics: The integration of different engineering disciplines to create intelligent systems.
-
Electro-Mechanical Systems: Systems that fuse electrical and mechanical components.
-
Sensors: Devices that detect physical changes.
-
Actuators: Components that generate movement.
-
Controllers: Decision-making devices based on sensor input.
Examples & Applications
Anti-lock braking system (ABS) in automobiles which utilizes sensors and controllers.
Washing machines that integrate microcontrollers and actuators for automatic washing.
Surgical robots in medical instrumentation that combine precision movement with advanced sensors.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In mechatronics, we see, mechanical and electronic harmony, with controllers that decide with ease, and sensors that detect with expertise.
Stories
Imagine a car that uses a magic eye (sensor) to see obstacles, a brain (controller) that thinks fast, and legs (actuators) to move safely, all working together to drive smoothly.
Memory Tools
Remember MECC for Mechatronics: Mechanical, Electronics, Control, and Computer.
Acronyms
MAPE for Mechatronics Importance
Miniaturization
Automation
Precision
Interdisciplinary thinking.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Mechatronics
The integration of mechanical engineering, electronics, computer systems, and control theory to design intelligent systems.
- ElectroMechanical System
A system that combines electrical and mechanical components to perform a function.
- Sensor
A device that detects changes in physical quantities such as temperature or position.
- Actuator
A component that produces movement, like a motor or hydraulic cylinder.
- Controller
A device that makes decisions based on sensor input and implements actions.
- Mechanical Structure
Parts that transmit or transform motion, such as gears and linkages.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
