3D MEMS and Advanced Packaging Techniques
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to 3D MEMS
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we’ll explore 3D MEMS and why they are important in modern technology. 3D MEMS refer to the ability to stack micro components vertically to save space. Can someone tell me why saving space is significant?

It makes devices smaller and more portable, like smartphones!

Exactly! Efficiency is key in design. These compact designs can also lead to improved performance. Can anyone think of an example where compact design is crucial?

Wearable devices! They have to be small enough to be comfortable.

Great example! Now, let’s talk about the technologies that enable this vertical stacking—Through-Silicon Vias, or TSVs.

What exactly are TSVs?

TSVs are tiny vertical interconnections that allow electrical signals to pass through silicon layers. Think of them like highways connecting cities in a region.

So, they help in making connections between stacked components more efficient?

That’s right! And this also brings us to another essential aspect—improved electrical performance. When components are close together, the signal loss can be minimized. Let’s summarize what we’ve learned.

1. 3D MEMS save space. 2. They improve electrical performance. 3. TSVs help achieve this integration. Excellent participation today!
Benefits of Advanced Packaging
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Continuing our discussion, let’s explore the benefits of advanced packaging techniques in detail. What general advantages do you think integrating components in 3D provides?

It likely allows for multifunctional systems!

Exactly! By stacking, you can create devices that serve multiple functions. Can anyone give an example of a multifunctional device?

Smartwatches that track health, play music, and alert you!

Perfect example! Now, let’s discuss space-saving designs. Why is this critical in technology today?

Because technology is everywhere, and we need it to fit in our daily lives without being bulky.

Correct! A compact design enhances usability. Lastly, improved electrical performance ensures our devices function optimally. Let’s summarize this session.

1. 3D MEMS create multifunctional systems. 2. They offer space-saving solutions. 3. Enhanced electrical performance is fundamental for functionality.
Real-World Application of 3D MEMS
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s take a look at a real-world application of 3D MEMS technology: stacked MEMS microphones. Who can describe how this technology might work?

I think they combine MEMS microphones with audio processors!

Great insight! This combination can enhance audio quality in devices like smartphones and voice assistants. Why do you think this integration is beneficial?

It improves the sound processing capabilities and saves space at the same time!

Exactly! This is a perfect example of multifunctionality and space-saving working together. Can anyone think of other devices that could benefit from similar technology?

Maybe cameras? They need small but powerful sensors.

That's correct! Compact sensors are crucial. To summarize this session: 1. The stacked MEMS microphones integrate sound processing. 2. They improve audio quality. 3. Such technology could revolutionize multiple devices.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section covers advanced packaging techniques such as Through-Silicon Vias (TSVs) and wafer-level packaging, focusing on the benefits of vertical integration, space-saving designs, and improved electric performance. It highlights how these advancements lead to multifunctional systems, providing specific examples like stacked MEMS microphones.
Detailed
3D MEMS and Advanced Packaging Techniques
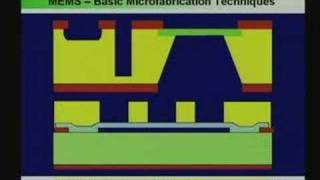
This section delves into the emerging field of 3D MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) and their corresponding advanced packaging strategies. As the demand for compact and efficient microsystems increases, packaging technologies such as Through-Silicon Vias (TSVs) and wafer-level packaging are gaining traction. These technologies enable the vertical stacking of components, allowing for denser integration and improved functionality.
Key Benefits
- Space-Saving Designs: By stacking components, 3D MEMS can contribute to more compact devices, ideal for applications where space is a premium.
- Improved Electrical Performance: The close proximity of components can minimize the length of interconnections, potentially enhancing the electrical performance of the devices.
- Multifunctional Systems: 3D packaging allows for integrating various functionalities into a single system, reducing the need for multiple separate devices.
Example Application
- Stacked MEMS Microphones: This example illustrates how 3D integration can combine MEMS microphones with audio processors, enhancing the performance and capability of audio devices.
These advanced packaging methods signify a vital step forward in making MEMS technology more versatile and effective in various applications, solidifying its role in the advancement of microelectronics.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to 3D MEMS Packaging
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
New packaging strategies are enabling vertical stacking and higher density integration.
Detailed Explanation
In this chunk, we learn about the concept of 3D MEMS packaging, which refers to new methods of arranging micro-electromechanical systems vertically instead of horizontally. This is particularly important as it allows for higher density integration, meaning more components can fit into a smaller space. Vertical stacking can lead to smaller devices that maintain or even improve performance while saving space.
Examples & Analogies
Think of 3D MEMS packaging like stacking containers in a warehouse. Instead of spreading everything out across a large area, stacking containers allows us to use the vertical space efficiently. Just as this method saves floor space in a warehouse, 3D MEMS packaging saves space in electronic devices, leading to more compact and powerful gadgets.
Technologies Behind 3D MEMS
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Technologies: Through-Silicon Vias (TSVs), wafer-level packaging, 3D heterogeneous integration
Detailed Explanation
This chunk describes specific technologies used in 3D MEMS packaging. Through-Silicon Vias (TSVs) are tiny vertical channels that allow electrical connections to pass through silicon wafers, which is essential for integrating multiple chips. Wafer-level packaging involves packaging techniques applied to entire wafers before they are diced into individual chips, ensuring that each chip is properly protected and connected. Lastly, 3D heterogeneous integration means combining different types of chips (which may have various functions) into a single compact package. Together, these technologies enhance the performance and functionality of MEMS devices.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine building a complex Lego structure where different types of Lego blocks represent various components—some are sensors, some are processors, and some are memory. Through-Silicon Vias (TSVs) are like the bridges you build between different layers, allowing each part to communicate. Wafer-level packaging makes sure all blocks are snugly fit before final assembly, ensuring that the whole structure is stable and efficient. 3D heterogeneous integration is like combining these different Lego pieces to create a multifunctional model, fulfilling multiple roles in a compact design.
Benefits of 3D MEMS Packaging
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Benefits: Space-saving, improved electrical performance, and multifunctional systems
Detailed Explanation
This chunk outlines three key benefits of 3D MEMS packaging: it saves space, improves electrical performance, and creates multifunctional systems. By stacking components, manufacturers can design smaller devices without compromising on the features and capabilities. Improved electrical performance comes from shorter pathways for signal transmission, leading to faster processing speeds and reduced power consumption. Additionally, integrating multiple functions into a single chip reduces the number of individual components, simplifying design and enhancing reliability.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a Swiss Army knife, which combines multiple tools into one compact device. Just like the Swiss Army knife saves space while providing various functions, 3D MEMS packaging allows manufacturers to create small devices that perform multiple tasks efficiently. This efficiency not only saves physical space but also enhances how quickly and accurately the device functions.
Example of 3D MEMS Application
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Example: Stacked MEMS microphones integrated with audio processors
Detailed Explanation
This chunk gives a practical example of 3D MEMS in action—the integration of stacked MEMS microphones with audio processors. This setup allows the microphones to function more effectively by reducing space and enhancing sound quality, all while being part of a compact system. The audio processors can handle sound data more efficiently, leading to superior audio experiences in devices such as smartphones and voice-controlled gadgets.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it as having a well-organized kitchen, where all the ingredients (like different spices and tools) are easily accessible in a compact space. Just as a well-organized kitchen allows a chef to cook delicious meals efficiently, stacking MEMS microphones and processors in a compact way improves audio performance efficiently, ensuring better quality sound without taking up much space in our devices.
Key Concepts
-
3D MEMS: Vertically stacked MEMS to optimize space and performance.
-
Through-Silicon Vias (TSVs): Vertical connections for improved integration.
-
Wafer-Level Packaging: Efficient packaging allowing high-density integration.
-
Multifunctional Systems: Devices performing multiple functions through advanced integration.
Examples & Applications
Example of stacked MEMS microphones enhancing audio processing capabilities in smartphones.
Application of wafer-level packaging to reduce footprint in sensors.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
3D MEMS save the day, stacking smart in every way.
Stories
Imagine a small apartment where every room is connected through secret doors, just like TSVs connecting layers in 3D MEMS architecture.
Memory Tools
Remember the acronym SPACE for 3D MEMS: S = Space-saving, P = Performance improved, A = Advanced Integration, C = Compact Design, E = Enhanced Functionality.
Acronyms
MEMS = Miniaturized Electronic Mechanical Systems.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- 3D MEMS
Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems that are vertically stacked to enhance integration and performance.
- ThroughSilicon Vias (TSVs)
Vertical connections that allow for electrical interconnectivity between different layers of silicon.
- WaferLevel Packaging
A method of packaging semiconductors at the wafer level for high-density integration.
- Stacked MEMS Microphones
MEMS microphones integrated with audio processors in a stacked configuration for enhanced functionality.
- Multifunctional Systems
Systems designed to perform multiple functions using integrated technologies.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
