Introduction to Advanced Topics in Optoelectronics
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Fundamentals of Optoelectronic Devices
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome everyone! Today, we will start by discussing optoelectronic devices. Can anyone tell me what these devices are?

Are they devices that combine light and electronic applications?

Exactly! Optoelectronic devices use light for various applications. Some examples include LEDs, lasers, and photodiodes. What can you tell me about their importance?

They are used in many technologies, like communication and medical devices!

Right! They play a crucial role in telecommunications, imaging, and energy generation. Remember the acronym ' L-P-S' for 'Light, Photonics, and Semiconductors' to recall key areas these devices influence.

L-P-S! Got it!

Great! Now, let's explore how advances in these devices are shaping the future.
Emerging Technologies in Optoelectronics
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand basic optoelectronic devices, let's talk about the emerging technologies shaping this field. What do you think these technologies could improve?

I think they could improve speed and efficiency in devices!

Absolutely! For instance, advancements in quantum dots allow for more efficient solar cells and displays. What are quantum dots?

Aren't they tiny semiconductor crystals that have unique optical properties?

Exactly! Their unique properties enhance color purity and energy conversion, especially in applications like QLEDs and solar cells. An easily remembered phrase is 'Small dots, big promise' to remember their potential.

That's a catchy way to remember it!

I'm glad you like it! Keep that in mind as we explore more advancements later.
Applications of Optoelectronics
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Applications of optoelectronics span various fields. Can anyone name a few?

Medical applications, like imaging and laser therapy?

Correct! Medical imaging techniques, like Optical Coherence Tomography, utilize optoelectronic components for non-invasive diagnostics. Who could tell me another application?

How about in telecommunications?

Exactly! Devices like fiber optic cables revolutionized data transmission. Remember the acronym 'T-M-E' for 'Telecommunications, Medical, Energy' to remember core applications!

T-M-E! I’ll definitely remember that!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section introduces the dynamic field of optoelectronics, highlighting the evolution and innovation of devices such as LEDs, lasers, and photodiodes. It emphasizes the significance of new materials and applications in telecommunications, biotechnology, and energy generation, setting the stage for exploring emerging trends and advanced applications in later sections.
Detailed
Introduction to Advanced Topics in Optoelectronics
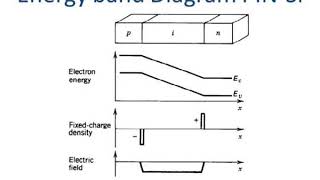
The field of optoelectronics is evolving rapidly, driven by innovative materials and technologies. Optoelectronic devices—encompassing LEDs, lasers, photodiodes, solar cells, OLEDs, and fiber optics—are being enhanced to push the boundaries of speed, efficiency, and functionality. Advances in materials science, fabrication techniques, and device integration are unlocking new applications in sectors such as telecommunications, biotechnology, quantum computing, sensing, and energy generation. This chapter aims to delve into these emerging trends and discuss the future trajectory of optoelectronics, examining both novel technologies and their potentially groundbreaking applications.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Rapid Advancements in Optoelectronics
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The field of optoelectronics is rapidly advancing with emerging technologies that are pushing the boundaries of what is possible in terms of speed, efficiency, and new applications.
Detailed Explanation
Optoelectronics combines optics and electronics, focusing on devices that source, detect, and control light. Recently, fast-paced innovations have emerged, enhancing the speed at which these devices operate and their overall efficiency. Emerging technologies are continuously pushing boundaries, creating new applications that were previously impossible, such as advanced communication systems and improved energy generation methods.
Examples & Analogies
Think of optoelectronics like upgrading a phone. Just as newer models offer faster processing speeds and more features, advancements in optoelectronics improve how devices interact with light, making them faster, more efficient, and capable of performing new tasks.
Evolving Optoelectronic Devices
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Optoelectronic devices, such as LEDs, lasers, photodiodes, solar cells, OLEDs, and fiber optics, continue to evolve with new materials, fabrication techniques, and integration methods.
Detailed Explanation
Optoelectronic devices have a wide variety of applications, from lighting (LEDs) to telecommunications (fiber optics). The evolution of these devices occurs through the introduction of new materials and methods of production. For example, advancements may introduce materials that are more efficient at generating light or allow devices to be produced in significantly cheaper and faster fashion, leading to more widespread usage and higher performance.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how smartphones have changed over time. Initially, they had basic features, but as new technologies emerged—like better cameras and faster processors—smartphones evolved into multifunctional devices. Similarly, as optoelectronic devices undergo improvements, they take on new and improved capabilities.
Groundbreaking Applications
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
These developments are enabling groundbreaking applications in fields like telecommunications, biotechnology, quantum computing, sensing, and energy generation.
Detailed Explanation
The advancements in optoelectronics are facilitating transformative applications across various sectors. In telecommunications, for instance, fiber optics allows for faster and more secure data transmission. In biotechnology, optoelectronic devices can help with medical diagnostics and therapies. Quantum computing relies on optoelectronic materials to improve data processing capabilities. Each of these applications demonstrates how optoelectronics is reshaping industries and enhancing technology.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the impact of the internet on communication—it dramatically changed how we connect with others. Similarly, advancements in optoelectronics are revolutionizing various fields, from how we transmit information to how we treat diseases, enhancing efficiencies and capabilities across the board.
Overview of the Chapter
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
This chapter explores the emerging trends in optoelectronics, focusing on novel technologies, advanced applications, and the future of the field.
Detailed Explanation
In this chapter, we will delve deeper into the emerging trends that are shaping optoelectronics today. Each aspect, from cutting-edge materials like quantum dots to innovative applications in medical and space technologies, will be discussed. Understanding these trends is crucial for grasping how optoelectronics will evolve in the future and what to expect in both academic and practical contexts.
Examples & Analogies
Think of this chapter as a roadmap that guides you through an exciting new city (the field of optoelectronics), pointing out the latest attractions (trends and technologies) and what you might encounter (future applications) as you explore its streets.
Key Concepts
-
Optoelectronics: The study of devices that detect and utilize light.
-
Quantum Dots: Nano-sized materials used for enhancing light emissions and efficiency in devices.
-
Photodiodes: Key components in detecting light and converting it into electrical signals.
-
LEDs: Essential light sources that are energy-efficient and integral to modern lighting and displays.
-
Solar Cells: Devices crucial for converting solar energy to usable electricity.
Examples & Applications
Quantum Dot Solar Cells that capture a broader light spectrum and improve efficiency.
Flexible OLED displays used in modern mobile devices by integrating organic semiconductors.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In light we trust, for devices so bright, / Optoelectronics guide us, day and night!
Stories
Imagine a tiny crystal that catches every color of light, helping devices be vivid and bright. That's the magic of quantum dots and their role in optoelectronics!
Memory Tools
Remember the phrase 'L-P-S' for Light, Photonics, and Semiconductors in optoelectronics.
Acronyms
Use 'T-M-E' to remember Telecommunications, Medical, Energy as key applications of optoelectronics.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Optoelectronics
The study and application of electronic devices that source, detect, and control light.
- Quantum Dots (QDs)
Nano-sized semiconductor particles with unique optical properties, useful in displays and solar cells.
- Photodiodes
Semiconductor devices that convert light into an electrical current.
- Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs)
Semiconductor devices that emit light when an electric current passes through.
- Solar Cells
Devices that convert sunlight directly into electricity using photovoltaic effects.
- Organic LEDs (OLEDs)
A type of LED where the emissive layer is composed of organic compounds, allowing for flexible displays.
- Fiber Optics
Technology that uses thin fibers of glass or plastic to transmit light signals.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
