Introduction to Vapor Absorption Systems
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to VARS
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’re delving into Vapor Absorption Refrigeration Systems, or VARS. Can anyone tell me how VARS differ from traditional vapor compression systems?

I think VARS uses heat instead of electricity to generate cooling?

Exactly! VARS are thermally-driven systems that use heat energy from sources like steam or waste heat instead of relying solely on electricity for cooling. This is a significant shift compared to vapor compression systems.

What are some advantages of using VARS?

Great question! Some key advantages include its ability to utilize low-grade thermal energy, quieter operation, and fewer moving parts which lead to lower maintenance. Remember, we call this the ‘triple advantage’ of VARS!

So they're better for remote locations?

Absolutely! VARS are ideal for industrial, remote, and even solar-powered refrigeration settings. Let's recap: VARS use heat energy, are quieter, require less maintenance, and are suitable for places where electricity is limited.
Key Components of VARS
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss the basic components of a VARS. Who can name one of the components?

Isn't there an absorber?

Correct! The absorber is one of the key components. It helps to absorb the vaporized refrigerant. Can anyone name others?

I remember the generator and the pump.

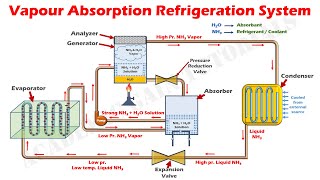
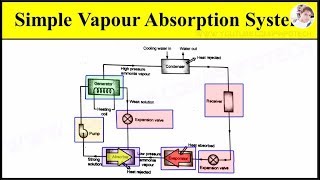
That's right! In total, we have the absorber, generator, solution pump, and a pressure-reducing valve. These components work together to circulate the refrigerant and complete the cooling cycle. Can anyone summarize their roles?

The generator uses heat to separate the vapor, and the pump moves the solution, right?

Exactly! Together, they form a cycle that allows VARS to effectively generate cooling. Remember the acronym ‘AGPS’ for Absorber, Generator, Pump, and Solution pump.
Applications of VARS
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

As we conclude, let’s explore the applications of VARS. Where might we find these systems in use?

Probably in places with a lot of waste heat?

Great thinking! They're highly effective in industrial applications where waste heat can be harnessed. What about other uses?

They could be used for air conditioning in remote areas, right?

Absolutely! VARS are suitable for remote refrigeration needs as well as solar-powered systems. Remember, their versatility is one of their greatest strengths.

So, they really can work anywhere there's heat available?

Yes, that's the essence of VARS! To summarize, VARS are efficient for industrial, remote, and environmental-friendly applications.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
VARS systems utilize low-grade thermal energy to replace mechanical compressors found in traditional refrigeration. These systems are advantageous due to their quiet operation, reduced maintenance, and suitability for various applications, including industrial and remote settings.
Detailed
Introduction to Vapor Absorption Systems
Vapor Absorption Refrigeration Systems (VARS) serve as an innovative and efficient alternative to traditional vapor compression systems. Unlike conventional systems, where a mechanical compressor is paramount, VARS operates on a thermal-based principle. It leverages heat energy—sourced from steam, waste heat, or even solar energy—to facilitate the refrigeration cycle. This approach offers several advantages, such as the ability to utilize low-grade thermal energy, a quieter operational profile, and fewer moving parts, leading to reduced maintenance demands. VARS finds applications across diverse settings, particularly in industrial, remote, and solar-powered refrigeration contexts.
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Vapor Absorption Refrigeration Systems (VARS)
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A Vapor Absorption Refrigeration System (VARS) is a thermally-driven refrigeration system that replaces the mechanical compressor in vapor compression systems with an absorption process, using heat energy (from steam, waste heat, or solar) to facilitate refrigeration.
Detailed Explanation
A Vapor Absorption Refrigeration System (VARS) uses thermal energy instead of electricity to create cooling. Unlike standard refrigeration systems that use a mechanical compressor to move refrigerants around, VARS relies on an absorption process. This means that instead of using electricity to power a compressor, it harnesses heat from sources such as steam or solar energy. This is particularly significant because it allows for the utilization of energy that is typically discarded (like waste heat) or renewable energy sources.
Examples & Analogies
Think about VARS like a sponge that soaks up water instead of a pump that pushes water. The sponge (absorbent) collects the heat, which then helps cool down your beverages inside the fridge without needing electricity to run a noisy pump.
Key Advantages of VARS
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Uses low-grade thermal energy instead of high-grade electricity.
- Quiet operation, fewer moving parts → lower maintenance.
- Suitable for industrial, remote, and solar-powered refrigeration.
Detailed Explanation
VARS has several key advantages compared to traditional refrigeration systems:
1. Energy Efficiency: It employs low-grade thermal energy, which is often more sustainable and economical than high-grade electricity.
2. Reduced Noise: Since it operates with fewer mechanical parts, VARS is generally quieter than traditional systems, leading to a more pleasant environment.
3. Versatile Applications: VARS can function effectively in various settings including industrial areas, remote locations far from electrical grids, and in applications utilizing solar energy for heating.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine having a quiet library where no noisy cooling compressor disrupts your reading. The VARS is like a stealthy air conditioner that uses natural sunlight instead of relying on a noisy generator, allowing you to focus in peace.
Key Concepts
-
Thermally-driven Systems: VARS utilize heat energy rather than electricity for refrigeration.
-
Components of VARS: Includes absorber, generator, solution pump, and pressure reducing valve.
-
Applications of VARS: Effective in industrial, remote, and solar-powered refrigeration contexts.
Examples & Applications
A VARS installed in a remote village can utilize solar heat to provide refrigeration without electricity.
In an industrial plant, waste heat from operations is harnessed to power a VARS for cooling purposes.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
VARS needs heat, not electric feet, to stay cool and keep our food neat.
Stories
Imagine a village where the sun shines bright, VARS helps keep their icy delight without any electrical might.
Memory Tools
AGPS: Absorber, Generator, Pump, and Solution pump – key components of VARS!
Acronyms
Remember ‘VARS’ for Vapor Absorption Refrigeration Systems. Each letter represents the shift towards energy-efficient refrigeration.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Vapor Absorption Refrigeration System (VARS)
A thermally-driven refrigeration system that replaces mechanical compressors with absorption processes.
- Absorber
Component in VARS that absorbs vaporized refrigerant into an absorbent solution.
- Generator
Component that applies heat to separate refrigerant vapor from the absorbent.
- Solution Pump
A pump used to circulate the absorbent-refrigerant solution in the system.
- Refrigerant
A substance used in a heat cycle that vaporizes and absorbs heat.
- Absorbent
A liquid that absorbs the refrigerant vapor in VARS.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
