CE 261 - Theory of Structures - College of Department of Civil Technological Studies Engineering Technology
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Statics
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome, class! Today, we're diving into the basics of statics, which is foundational for understanding structures. Who can tell me what statics involves?

Is it about objects at rest, like structures that don’t move?

Exactly! Statics is the study of forces in systems that are at rest or in equilibrium. Can someone explain what equilibrium means?

It means that all forces acting on an object are balanced, right?

Right again! Remember the phrase 'Balanced Forces' - it helps to visualize how forces interact in a static system. Let's explore some key terms frequently encountered in statics.

What are some examples of those terms?

Great question! Terms like 'force,' 'load,' and 'moment' are critical. Also, don't forget our memory aid, 'FLM' for Forces, Loads, and Moments. Can you tell me why understanding these is important?

Because they’re the building blocks of structural analysis!

Exactly! So, let's summarize: Statics deals with balance and equilibrium through terminology that forms the base of further learning.
Terminology in Structural Analysis
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, shifting gears, let’s discuss structural analysis terminology. Why do we need a glossary?

To ensure we understand the basic concepts as we progress!

Exactly! Understanding terms like 'beam,' 'cantilever,' and 'load types' will help us later in practical applications. Can someone define a beam?

A beam is a structural element that primarily resists bending!

Correct! And for our memory aid, think of 'Bend Like a Beam' when you picture what a beam does. What about 'cantilever'?

That’s a beam fixed only at one end. Right?

Spot on! Remember the 'One End' concept for cantilevers. Lastly, can someone explain why we need to understand loading types?

Different loads affect structures in various ways, right?

Absolutely! We're building a comprehensive understanding here. Let’s recap: Beam, Cantilever, and Loading Types are key terms that aid our learning.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
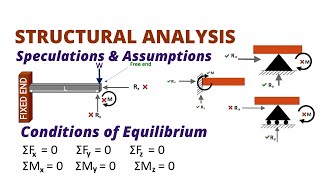
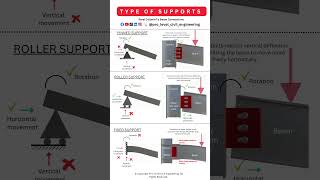
The section provides a glossary of fundamental terms related to statics and structural analysis. Understanding these terms is crucial for students in the field of civil engineering technology, as they serve as the foundation for more complex concepts in structural analysis.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
This section serves as a crucial foundation for students in the course CE 261 - Theory of Structures. It consists of a glossary designed to familiarize learners with the most commonly used terms in the context of statics and structural analysis. Mastering these terminologies is essential not only for comprehension but also for effective communication within the discipline. By engaging with this glossary, students will enhance their ability to discuss and analyze structural principles, laying the groundwork for future studies in civil engineering technology. This section highlights the necessity of familiarity with terms such as 'force,' 'beam,' 'stress,' and 'strain,' which are pivotal in later stages of structural engineering coursework.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Glossary Overview
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Here is a simple glossary of some of the most used terminology in statics and structural analysis courses.
Detailed Explanation
In this section, we introduce a glossary that contains essential terms used in the field of structural analysis and statics. Statics is the branch of mechanics that deals with objects at rest, and understanding the vocabulary is crucial for effectively learning and applying these concepts.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the glossary as a map for a traveler. Just as a map helps navigate unfamiliar terrain, this glossary helps students find their way through the technical language of structural engineering.
A - Abrupt to Accurate
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Abrupt (cid:6457) (cid:6374) (cid:6397)ﺎﻔﻣ
- Absolute ﻖﻠﻄﻣ
- Absolute Value ﺔﻘﻠﻄﻤﻟا ﺔﻤ(cid:5782)ﻘﻟا
- Absolute system of units ﺔﻘﻠﻄﻤﻟا تاﺪﺣﻮﻟا مﺎﻈﻧ
- Acceleration عرﺎﺴ(cid:5796) ّ
- Accuracy ﺔﻗد
- Accurate ﻖﻴﻗد
- Action ﻞﻌﻓ / ﻞﻤﻋ
- Active force ﺔﻃﺷ(cid:5865)ﻟا ةﻮﻘﻟا (cid:877) ﺔﻟﺎﻌﻔﻟا ةﻮﻘﻟا
- Actual (cid:6475)ﻌﻓ
- Addition ﻊﻤﺟ (cid:877) ﺔﻓﺎﺿإ
- Addition of forces ىﻮﻘﻟا ﻊﻤﺟ
- Addition of vectors تﺎﻬﺟﺘﻤﻟا ﻊﻤﺟ
- Adjacent vectors ةروﺎﺠﻤﻟا تﺎﻬﺟﺘﻤﻟا
- Advantage ﺔ(cid:5782)ﻠﻀﻓأ
- Aerostatics تازﺎﻐﻟا و ءاﻮﻬﻟا نزاﻮﺗ ﻢﻠﻋ (cid:877) ﺲﻜ(cid:5782)ﺗﺎﺘﺳوﺮﻳﻹا
- Algebra (cid:6443)(cid:6397)ﺠﻟا ﻢﻠﻋ
- Algebraic ي(cid:6443)(cid:6397)ﺟ
- Algebraic expression ي(cid:6443)(cid:6397)ﺟ (cid:6443)(cid:6398)ﺒﻌﺗ
- Algebraic sum ي(cid:6443)(cid:6397)ﺟ ﻊﻤﺟ
- Allow ﺢﻤﺴ(cid:5947)
Detailed Explanation
Here, we delve into the defined terms starting with the letter 'A'. These terms form the fundamental language of structural engineering. Each word or phrase is a building block that helps students understand more complex concepts. For example, 'Acceleration' refers to the change in velocity and is crucial for understanding dynamic loads.
Examples & Analogies
Consider this section of the glossary as learning the vocabulary of a new language. Just as knowing basic words in a language allows you to form sentences, understanding these essential terms enables students to grasp advanced engineering principles.
Additional Terms Definitions
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Analysis ﻞ(cid:5782)ﻠﺤﺗ
- Analytical ﺔ(cid:5782)ﻠ(cid:5782)ﻠﺤﺗ
- Analyze ﻞ(cid:5782)ﻠﺤﺗ
- Anchor bolts (cid:6465)
- Anemometers ﺢــــ(cid:5716)(cid:5610)ﻟا ةﺪﺷ سﺎ(cid:5782)ﻗ زﺎﻬﺟ (cid:877) (cid:6443)ﻴﻣﻮﻤ(cid:5782)ﻧأ
- Angle ﺔ(cid:5716)واز
- Angular ﺔ(cid:5716)واﺶﻝﺎ(cid:5728) ﺔﻗﻼﻋ وذ (cid:877) يواز
- Answer ﺔ(cid:5728)ﺎﺟإ
- Apex ةورذ
- Application ﻖﻴﺒﻄﺗ
- Applied force ﺔﻘ(cid:5761)ﻄﻤﻟا ةﻮﻘﻟا
Detailed Explanation
This section continues the glossary with more terms beginning with the letter 'A'. 'Analysis' is the systematic examination of a structure's components and their behavior under various conditions. It is central to understanding how different elements in a structure interact when loads are applied.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a mechanic analyzing a car's components to diagnose a problem. Similarly, engineers analyze structures to predict their behavior under stress and ensure they are safe and durable.
Key Concepts
-
Statics: Study of forces acting on bodies at rest.
-
Equilibrium: Condition where all forces are balanced.
-
Force: Influence that can change an object's state of motion.
-
Beam: Structural element resisting bending.
-
Cantilever: A beam anchored at one end only.
-
Load: External force applied to a structure.
-
Moment: Tendency of a force to cause rotation about a point.
Examples & Applications
A bridge is an example of a structure that relies on beams to support loads.
In an overhang, the cantilever concept is applied where one end is supported while the other extends freely.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Stay still, balance the will, forces in line, won't cross the line.
Stories
Once there was a bridge supported firmly at both ends, able to withstand any load placed upon it, teaching future engineers the importance of stability.
Memory Tools
Remember FLM for Forces, Loads, and Moments.
Acronyms
Use the acronym BEAM for Beam, Equilibrium, Action, and Moment.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Statics
The branch of mechanics dealing with bodies at rest and forces in equilibrium.
- Equilibrium
A state where all the forces acting on a body are balanced.
- Force
A push or pull exerted on an object resulting in an acceleration.
- Beam
A structural element that primarily resists bending.
- Cantilever
A beam supported at one end and free at the other.
- Load
The weight or force applied to a structure.
- Moment
The measure of the tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
