Introduction to Structural Engineering Concepts
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Engineering Design Process
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we'll be exploring the engineering design process. It consists of four primary stages: conceptual, preliminary design, selection, and final design. Can anyone tell me what happens in the conceptual stage?

Isn't that when we identify what the client needs?

Exactly! We gather input from various stakeholders like clients and regulatory agencies. This stage lays the foundation for the design. Now, in the preliminary design stage, what do you think we focus on?

I think it's about coming up with creative ideas while considering how to actually build the structure.

Correct! We also consider expected loads on the structure. A mnemonic to remember the stages is 'C-P-S-F'—Conceptual, Preliminary, Selection, Final. Can someone recap the stages we discussed?

Sure! We have the conceptual, where we identify needs, preliminary for creative ideas, selection for evaluating alternatives, and final for exact calculations and specifications.

Great summary! Remember, each stage plays a crucial role in the design process.
Structural Analysis
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, we will delve into structural analysis. Can anyone explain what it is?

I think it’s about figuring out how structures respond to different loads?

Exactly! It involves determining forces and deformations in structures. Alright, can someone tell me what we base our analysis on?

It’s based on engineering mechanics theory and past experiences.

Yes! It’s vital for ensuring our designs can withstand expected loads safely. Now, how can we simplify remember this concept?

Maybe by using the phrase 'Analyze and Ensure' to remember that analysis helps ensure safety?

Exactly! That's a good memory aid. Let's summarize: structural analysis assesses responses to loads using established theories and experiences.
Structural Elements
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss structural elements. Can we start with tie rods and what their main function is?

Tie rods are used under tension, right?

Correct! And what about beams? What role do they play in a structure?

Beams resist bending moments and shear forces!

Exactly! And columns are also critical; what do they do?

Columns support vertical loads and can resist bending moments too.

Well stated! Remember: Tie rods = tension, beams = bending, columns = compression. Can we think of a way to organize this information?

We could create a chart to distinguish them based on their functions.

Great idea! Let's keep those roles clear.
Types of Structures
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's move to the types of structures. Can someone start by naming one type and discussing its features?

Trusses! They have triangular arrangements and are good for large spans.

Correct! What about cables and arches?

Cables carry tension loads while arches handle compression.

Exactly! Remember, cables = tension, arches = compression. Lastly, what about frames?

Frames consist of beams and columns, right?

Yes! They form a structural system through moment interactions. Let's summarize: Types include trusses, cables, arches, and frames, each with unique characteristics.
Codes and Loads
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's talk about codes and loads. Why are codes important?

They provide guidelines to ensure safety in designs.

Exactly! What are the two types of loads we should be aware of?

Dead loads and live loads!

Correct! Dead loads are permanent, while live loads vary. Can someone explain environmental loads?

Those are loads from natural forces like wind and snow.

Exactly! Let's remember this as a three-part classification: Dead, Live, and Environmental loads. We'll need to keep this in mind during the design phase.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section provides an overview of the engineering design process, structural analysis, types of structures, and key concepts related to structural elements. Emphasis is placed on understanding the design stages, load types, and the importance of codes in ensuring structural safety.
Detailed
Introduction to Structural Engineering Concepts
This section lays the groundwork for understanding structural engineering, highlighting the engineering design process through several stages:
Engineering Design Process
- Conceptual Stage: Engineers identify needs and objectives and collaborate with stakeholders such as clients, governmental agencies, and architects.
- Input from all parties ensures a comprehensive start.
- Preliminary Design Stage: During this phase, creative ideas emerge while considering construction aspects and expected loads. Key focuses include:
- Sizing of structural elements for safety.
- Architectural constraints and preliminary analysis theories.
- Selection Stage: Alternatives are evaluated, and the final design is chosen with input from all parties involved.
- Final Design Stage: Utilizing precise calculations, this stage details loads, structural analysis, drawings, specifications, and construction codes, ensuring safety and compliance.
Understanding these stages is crucial as it informs how structures are conceptualized and executed.
Structural Analysis
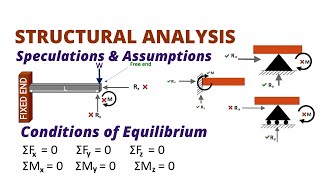
- Defined as the determination of structural response to loads and actions, relying on established theories, past experiences, and engineering judgment.
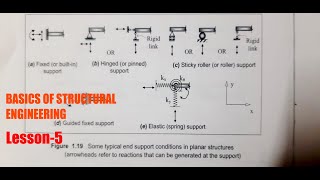
Structural Elements
- Tie Rods: Subject to tension only.
- Beams: Horizontal members that resist bending and shear.
- Columns: Vertical elements that resist compressive loads and can fail through buckling.
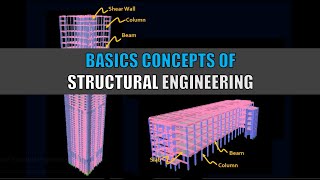
Types of Structures
A combination of elements forms structural systems, notably:
- Trusses: Large spanning structures with triangular arrangements.
- Cables and Arches: Flexible cables for tension and rigid arches for compression.
- Frames: Combinations of beams and columns prone to moment interactions.
Codes and Loads
Understanding applicable codes and various loads—dead, live, environmental—is essential for safe structure design.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Engineering Design Process Overview
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Engineering Design Process
The engineering design process consists of several stages that guide engineers in creating safe and effective structures.
Detailed Explanation
The engineering design process is a structured method that engineers follow to meet specific needs. It typically involves multiple stages, starting from understanding the client's requirements to finalizing the design specifications. This process ensures that all aspects are considered, ensuring the end structure is both functional and safe.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the engineering design process like planning a family vacation. You start by determining where you want to go (identify needs), gather ideas on how to get there and what to do (conceptual stage), decide on the best travel options (selection stage), and finally, you make bookings and finalize the itinerary (final design stage).
The Conceptual Stage
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Conceptual Stage:
- Needs are identified then objectives are expressed to meet these needs.
- Input from:
- Clients
- Governmental regulatory agencies
- Architects, planners, and engineers
Detailed Explanation
In the conceptual stage, engineers and stakeholders come together to outline what the project should achieve. This involves gathering input from various parties, including clients, regulatory bodies, and design professionals. The goal is to clearly define the needs of the project and establish objectives that ensure those needs are met.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine planning a school event. You would talk to teachers, students, and parents to understand what they need and expect from the event – like activities, food, and safety measures. This input helps you set clear goals for what the event should achieve.
The Preliminary Design Stage
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Preliminary Design Stage:
- Creative ideas by the engineers.
- Keep in mind construction aspects.
- Thorough consideration of expected loads on the structure at all construction stages and during occupancy of the finished structure.
- Sizing of structural elements for safety and serviceability.
Detailed Explanation
During the preliminary design stage, engineers begin to brainstorm and develop creative solutions for the project. They account for practical aspects such as construction methods and material choices, while also considering the loads the structure will need to support throughout its life, from construction to final occupancy. This is critical for ensuring that the structure remains safe and functional.
Examples & Analogies
This stage is like deciding on the menu and shopping list for a dinner party. You not only need to come up with tasty dishes (creative ideas), but also consider how long each dish will take to prepare, what ingredients you need to buy, and how you will set up the dining area (construction aspects).
The Selection Stage
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Selection Stage:
- At this stage, all alternatives are presented and all parties involved participate in the selection stage so the final design stage can begin.
Detailed Explanation
The selection stage involves evaluating the options generated during the preliminary design stage. All stakeholders participate in discussing the various alternatives, allowing them to understand the pros and cons of each. This collaborative effort is essential for making informed decisions about which design to move forward with into the final design stage.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a group of friends choosing a movie to watch. Each person might suggest their favorite films, and then they discuss what everyone wants to see until they agree on one movie that everyone is excited about. This consensus is critical for ensuring everyone enjoys the experience.
The Final Design Stage
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Final Design Stage:
- Loads are determined in greater accuracy than the preliminary stage.
- All loading combinations are examined in this stage.
- Structural analysis is carried with greater accuracy than the preliminary stage with the elimination of all approximations.
Detailed Explanation
In the final design stage, engineers refine their calculations about loads, ensuring a high level of accuracy. This involves a detailed analysis of different combinations of loads that the structure will experience, eliminating any rough estimates made in earlier stages. The results of this stage are compiled into detailed drawings and specifications, which guide the construction process.
Examples & Analogies
This is similar to finalizing a recipe before cooking. You double-check the ingredient amounts, review the cooking times, and ensure that you have everything ready for the big dinner. This preparation guarantees that the meal turns out perfectly when you start cooking.
Key Concepts
-
Engineering Design Process: A systematic approach to designing a structure encompassing several stages.
-
Structural Analysis: The method of determining how structures respond to loads.
-
Structural Elements: Basic components such as beams, columns, and tie rods that constitute the structure.
-
Types of Structures: Classification based on structural elements and behavior under loads, including trusses and frames.
Examples & Applications
A building designed using the engineering design process beginning with surveying stakeholder needs.
A bridge utilizing trusses to span a long gap, demonstrating effective weight distribution.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the design process there’s a sequence true, Conceptual, Preliminary, Selection, Final too.
Stories
Imagine a bridge built with creativity—first, the needs are defined, then ideas flow freely, later designs are selected, ensuring all is right—the structure’s strong, able to withstand nature’s might.
Memory Tools
For Loads, remember D.L.L.E: Dead Load, Live Load, Environmental Load.
Acronyms
C-P-S-F for Conceptual, Preliminary, Selection, Final in the design process.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Structural Engineering
Branch of engineering dealing with the design and analysis of structures.
- Load
Forces or weights applied to a structure.
- Tie Rod
A slender structural component subjected to tensile forces.
- Beam
A horizontal structural element that resists bending and shear forces.
- Column
Vertical structural element that carries loads primarily in compression.
- Truss
A framework of beams arranged in a triangular shape to span distances.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
