Materials, & Geometry
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Material Selection
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to explore the materials used for the Eiffel Tower. What material do you think was used, and why?

I think it was steel because it's strong.

That's a good guess! However, the Eiffel Tower was primarily constructed using wrought iron. Can anyone tell me why wrought iron was chosen over steel?

Maybe because it's cheaper?

Exactly, wrought iron was less expensive than steel, and Gustave Eiffel had more experience working with it. This combination of factors significantly influenced the design.

What’s so special about wrought iron?

Wrought iron is known for its malleability and durability, making it ideal for intricate designs. It’s also more resistant to corrosion than other materials, which is important for a structure exposed to the elements.

So, does that mean it contributed to the tower's longevity?

Absolutely! The choice of materials directly impacts the structure's lifespan.

In summary, the selection of wrought iron for the Eiffel Tower was based on cost-effectiveness, availability of expertise, and beneficial properties of the material.
Geometric Design
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s dive into the geometric aspects of the Eiffel Tower. What kind of support system does the tower use?

I think it has four supports, right?

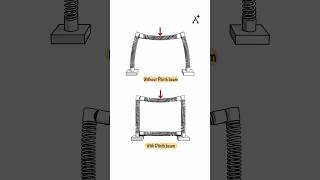
That's correct! The Eiffel Tower stands on four inclined supports. This unique design helps distribute weight effectively. Can anyone describe why this is important?

It helps balance the tower and keeps it from falling.

Great point! The geometric arrangement ensures that loads are shared evenly, preventing stress on any single point.

Does the shape of the supports matter?

Definitely! The cross-sectional area of each support is designed to handle specific loads while minimizing material use, making it both efficient and strong.

In summary, the geometric structure of the Eiffel Tower, particularly its four inclined supports, is essential for its stability and effectiveness in load distribution.
Load Considerations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Last session, we talked about the geometry of the Eiffel Tower. Now, let's discuss the loads that the structure needs to support. How heavy do you think the Eiffel Tower is?

Is it over 10,000 kilograms?

It's actually about 18,800 kilograms! This weight isn't distributed evenly. What do you think that means for the design?

They probably had to design it carefully to handle the uneven weight.

Exactly! The design must account for this uneven distribution of weight to ensure safety and integrity. Can anyone tell me how they might approximate the load distribution?

They might use calculations or diagrams?

Correct! Engineers use idealized models to calculate the loads acting on different sections of the tower, commanding the necessary structural responses.

In summary, understanding load distribution is crucial for designing a safe and stable structure like the Eiffel Tower.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, the significance of using wrought iron for the Eiffel Tower is explored, including its cost-effectiveness and suitability given Gustave Eiffel’s experience with the material. Key geometrical aspects and the structuring of supports are briefly outlined.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
The Eiffel Tower is an impressive feat of engineering, primarily constructed from wrought iron rather than steel. Wrought iron was chosen largely due to its lower cost and Gustave Eiffel’s familiarity with the material. The structural design of the Eiffel Tower incorporates four inclined supports, which are critical to its stability and load distribution. The idealization of the supporting structure is presented, alongside key dimensional specifications, emphasizing how geometry and material selection play a pivotal role in the tower's integrity and architectural beauty.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Material Used for the Tower
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The tower was built out of wrought iron, less expensive than steel, and Eiffel had more experience with this material.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk discusses the primary material used in constructing the Eiffel Tower, which is wrought iron. Wrought iron is known for its ductility and resistance to corrosion, making it a suitable choice for creating large structures. Compared to steel, wrought iron was not only more affordable, but also a material that Gustave Eiffel was more familiar with due to his previous work experience.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine building a treehouse: if you have more experience working with wood rather than metal, you might choose to use wood instead, even if metal may be stronger. Just like in treehouse construction, Eiffel chose the material he felt most confident working with.
Cost Considerations
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Less expensive than steel.
Detailed Explanation
Using wrought iron was a cost-effective decision in the construction of the Eiffel Tower. Budget constraints are always a significant factor in engineering projects. By choosing a material that was less expensive, Eiffel could allocate funds to other important aspects of the tower's design and construction.
Examples & Analogies
Consider when students have a budget for a school project and must choose materials wisely; selecting a cheaper option can free up resources for additional features or enhancements, similar to how Eiffel handled his budget.
Experience with Wrought Iron
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Eiffel had more experience with this material.
Detailed Explanation
The expert knowledge Eiffel had with wrought iron provided him with the skills needed to work effectively with this material. Experience is crucial in engineering, as it helps engineers understand the properties and behaviors of materials under various conditions. Eiffel's familiarity allowed him to innovate in the design and engineering of the Eiffel Tower.
Examples & Analogies
Think of an artist who has painted extensively with watercolors; they can create more intricate works compared to someone who is just starting. Similarly, Eiffel’s experience with wrought iron made him more adept at using it for the complexities of the tower's design.
Key Concepts
-
Material - Wrought iron was chosen for its cost-effectiveness and durability.
-
Structural Design - Four inclined supports distribute loads effectively.
-
Load Distribution - The weight of the tower is unevenly distributed, necessitating careful engineering considerations.
Examples & Applications
The use of wrought iron allowed for the intricate lattice design of the Eiffel Tower, while also contributing to cost savings.
The design's geometric structure with inclined supports allows the tower to withstand high winds and hold considerable weight.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Iron wrought, the tower caught, strong and light, in every fight.
Stories
Imagine Gustave Eiffel holding iron beams, dreaming of a tower that defies gravity - he chose wrought iron, strong and beaming.
Memory Tools
Use 'WISS' to remember: Wrought Iron, Inclined Supports, Stability.
Acronyms
Remember 'WISP' for Wrought Iron, Supports, and Load distribution Precision.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Wrought Iron
A type of iron that is worked with tools, making it malleable and pliable; chosen for its strength and durability.
- Inclined Supports
Slanting structural elements that bear loads and provide stability to the tower.
- Load Distribution
The way in which weight is spread over the structure of an object, especially in terms of engineering design.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
