Introduction to Highway Engineering
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Overview of Highway Engineering and Ancient Roads
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome everyone! Today, we will explore highway engineering, starting from ancient roads. Can anyone tell me what highway engineering involves?

Isn't it about designing and maintaining roads?

Exactly! Highway engineering is centered on creating efficient and safe transportation routes. Historically, humans began with footpaths and then progressed to roads for animal transport. This evolution started our need for engineered pathways. What do you think led to the development of hardened roads?

Was it the invention of the wheel?

Right! The wheel's invention in Mesopotamia set the stage for the construction of sturdy roads to accommodate heavier loads. Let's remember that: W for Wheel = Roads became Real!
Roman Roads and Their Significance
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s dive into Roman roads. Why do you think the Romans are often credited with major road construction innovations?

They built a lot of roads across Europe, right?

Correct! They recognized the importance of good drainage and materials. Their roads, some still in use today, emphasized durability. Can anyone recall the features that made Roman roads stand out?

They had proper drainage and were built straight, right?

Yes! They incorporated strong foundation stones and used a mix of lime and volcanic materials to create resilient structures. Always focus on the three key factors: Drainage, Durability, and Design!
Highway Development in India
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s look at highway development in India. Can anyone identify significant historical periods that contributed to road construction?

The Mauryan period had good roads, right?

Yes! The Mauryan kings established extensive road networks. Additionally, what was the impact of British rule on road development?

They built the Grand Trunk Road.

Exactly! The British improved many existing roads and introduced structured road development plans like the Jayakar Committee, focusing on national interest. Remember: 'J for Jayakar = Just Roads for India!'
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section traces the evolution of highway engineering starting from the ancient roads created for basic transportation needs, advancing through significant civilizations such as the Romans, French, and British, to modern road construction technologies and the importance of highway planning in India.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Overview
Highway engineering is a fundamental aspect of civil engineering focused on the design, construction, and maintenance of roads. It has a rich history influenced by various civilizations that improved transportation infrastructure over the centuries.
History and Development
Ancient Roads
- The origins of transport began with foot traffic followed by animal-drawn vehicles which necessitated the construction of hardened road surfaces.
- Roads from as early as 3500 BC were discovered, with documented evidence from the Assyrian empire around 1900 BC.
Roman Roads
- The Romans significantly advanced road construction techniques, creating an extensive network for efficient travel and trade, characterized by durability and proper drainage features.
- Roman innovations included the use of concrete and a focus on alignment and grading for better functionality.
French Roads
- In the Napoleonic era, improvements in road construction techniques were made by Tresaguet, emphasizing drainage and the need for organized maintenance.
British Roads
- John Macadam introduced the first scientific approach to road construction which involved empirical observations and the effective use of compacted stone layers.
Modern Roads
- Present-day methods build on Macadam's principles, employing bituminous and cement concretes, alongside advanced construction technologies adapted to increasing transportation demands.
Highway Planning in India
- India's road development dates back to the Indus Valley civilization, and continued through various historical periods, heavily influenced by the British.
- Key developments notably include the Jayakar Committee’s recommendations and later plans that established structured road classifications from national to village roads.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Highway Engineering
Chapter 1 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
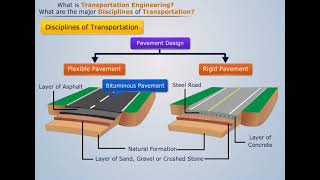
Highway engineering deals with the planning, design, construction, and maintenance of highways and road networks. It involves various aspects including traffic management, pavement design, and road safety.
Detailed Explanation
Highway engineering is a specialized branch of civil engineering focused on creating road networks that facilitate efficient transportation. It involves understanding traffic flow, designing safe pavements, and maintaining infrastructure to ensure roads are safe and efficient for vehicle traffic. Key elements include choosing materials suitable for different traffic conditions and environmental factors.
Examples & Analogies
Think of highway engineering like planning a community park. Just as a park needs walking paths, benches, and careful landscaping to ensure visitors enjoy their time safely and comfortably, highways require careful design to support the movement of vehicles and ensure driver and pedestrian safety.
History of Highway Engineering
Chapter 2 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The evolution of highway engineering dates back to ancient civilizations, where pathways were first developed for trade and travel. Significant advancements occurred through various eras, leading to modern road construction practices we see today.
Detailed Explanation
Highway engineering has roots in early human activity where paths were formed out of necessity for walking and transporting goods. Over time, with the advent of the wheel and animal-drawn vehicles, the need for more durable road surfaces arose. The Romans are credited with pioneering road construction techniques, developing extensive road systems that highlighted principles of drainage, material use, and construction standards that are foundational today. This history shows how road construction evolved from simple paths to complex networks designed for high-capacity traffic.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine how a simple dirt road in a rural area transforms into a highway over time as more vehicles start using it. Just like a trail that starts as a footpath can grow into a well-maintained trail for bikes and cars, highways have evolved from basic paths into structured roads providing connectivity and efficiency.
Roman Roads: A Milestone in Road Construction
Chapter 3 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The Romans constructed a vast network of roads that were crucial for connecting their empire. They introduced advanced techniques such as proper drainage and durable materials to ensure longevity.
Detailed Explanation
Roman roads were engineered for durability and efficiency. They included layers of materials for better drainage and sturdiness, allowing them to withstand heavy loads. The roads were constructed straight regardless of the gradient, ensuring direct routes for efficient travel. Their innovative use of lime mortar and well-sized stones set a precedent for modern road construction techniques, emphasizing the importance of good materials and maintenance.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how modern highways often use reinforced concrete for strength. Similar to how Romans built roads to last against heavy wear, highways today are made with advanced materials to support large volumes of traffic, just as a solidly built bridge can withstand heavy traffic flow over many years.
Advancements in Road Construction: French and British Contributions
Chapter 4 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Innovation continued in road construction with contributions from France and Britain. The French incorporated systematic drainage while the British refined road materials for greater efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Detailed Explanation
The French developed methods that improved drainage on their roads to prevent water damage, which can weaken road structures. The British, particularly John Macadam, revolutionized road construction by creating a method that utilized compacted stones, significantly reducing costs while enhancing durability. These advancements marked the progression from simply maintaining roads to developing scientifically-backed methods of construction.
Examples & Analogies
Much like how a gardener uses better soil and drainage systems to help plants thrive, highway engineers use modern materials and drainage techniques to ensure roads can last longer and perform better under various conditions. This is crucial, especially in areas with heavy rainfall.
Modern Road Construction Innovations
Chapter 5 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Today, highway engineering has integrated modern materials such as bituminous and cement concrete, with a focus on sustainable and cost-effective constructions.
Detailed Explanation
Modern road construction employs advanced materials like asphalt and concrete, designed for strength and reduced maintenance needs. Innovations in construction technology and equipment have also allowed for faster project completion. The focus has shifted towards sustainability, looking to use locally sourced materials and environmentally friendly techniques.
Examples & Analogies
Just like how smartphone technology improves over time, allowing for more features and better performance, modern highway construction reflects similar advancements—utilizing the latest materials and methods to meet increasing demands for traffic and environmental protection.
Highway Planning and Classification in India
Chapter 6 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Highway planning in India has evolved, from ancient routes used in the Indus Valley civilization to detailed classifications like National and State Highways.
Detailed Explanation
The planning of highways in India has a rich historical context, stemming from ancient civilizations, and has adapted to modern requirements. The classification of roads—ranging from National Highways that link states and capitals to Village Roads that serve rural regions—highlights the importance of connectivity in facilitating trade, travel, and transportation.
Examples & Analogies
Think of highway classification as organizing a library. Just as libraries have sections for different genres (like fiction, non-fiction, and reference) to help readers find what they need, highways are organized into categories that cater to specific transport functions, making navigation easier and more efficient.
Challenges in Modern Highway Infrastructure
Chapter 7 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Increasing traffic demand and changes in lifestyle have led to challenges in managing highway infrastructure effectively.
Detailed Explanation
As populations grow and lifestyles evolve, the demand for road space increases, often outpacing infrastructure development. This leads to traffic congestion, higher accident rates, and a need for more efficient traffic management strategies, such as signals and controlled access points, essential for maintaining flow and safety.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how a small café might struggle to serve customers effectively as demand grows. Just like the café must adapt to serve its increasing clientele, highway systems must evolve to manage the rising number of vehicles effectively, implementing measures to optimize road use and safety.
Key Concepts
-
Road Construction: The process of building roads, influenced by historical and modern engineering methods.
-
Drainage Importance: Essential for the longevity of roads and preventing water damage.
-
Modern Technologies: Incorporation of advanced materials and techniques for more efficient road construction.
Examples & Applications
Roman roads are an example of early engineered paths that significantly improved connectivity across regions.
The introduction of macadamization by John Macadam revolutionized the methods used for paving modern roads.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Roads so strong, built to last, Romans paved their way so fast.
Stories
Imagine a traveler in ancient Rome, taking a smooth, straight road built with precision. This traveler could easily connect to distant lands thanks to the Romans' drainage techniques!
Memory Tools
DRD: Drainage, Robustness, Design - Remember these factors for effective road construction!
Acronyms
RDS
Romans
Durability
Systems - Key contributors to effective highway engineering.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Highway Engineering
The branch of civil engineering that involves the planning, design, construction, and maintenance of road systems.
- Drainage
The system designed to remove excess rainwater or groundwater from the road surface.
- Aggregate
A material or mixture of materials such as sand, gravel, or crushed stone used in construction.
- Alignment
The layout or configuration of the highway, determining its paths, including horizontal and vertical aspects.
- Subgrade
The layer of native material beneath a road's foundation, important for overall road stability.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
