Trip Generation - 7
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Trip Generation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will discuss trip generation, the first stage in demand modeling. Can anyone tell me what trip generation aims to predict?

It predicts how many trips are generated in each zone?

Exactly! It looks at how many trips originate from each zone based on household and socio-economic data. Why do you think this is important?

It helps in planning transportation and understanding traffic flow!

Correct! Understanding traffic patterns is essential for city planning.
Types of Trips
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's talk about the types of trips. Who can define what home-based trips are?

Those are trips where one of the locations is home.

Correct! And what about non-home-based trips?

Those do not involve home as either the origin or destination?

Right! This classification helps us understand travel behavior. Can you remember what factors can influence trip generation?

Income and vehicle ownership?

Exactly! Let's dive deeper into these factors in our next session.
Factors Affecting Trip Generation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now we will explore the factors that affect trip generation. Can anyone list the factors affecting personal trip production?

Income, vehicle ownership, and household structure!

Great! And for trip attraction?

Employment opportunities and accessibility?

Exactly! These factors play a significant role in trip generation, especially when planning urban areas.
Growth Factor and Regression Models
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's review the modeling techniques used in trip generation. Who can explain growth factor modeling?

It’s a linear function predicting future trips based on current trips and growth factors!

Yes! And what are some variables affecting these growth factors?

Population, income, and vehicle ownership!

Correct! Now, how about regression methods?

They use multiple variables to determine trip rates, right?

Exactly! Understanding these methods is critical for accurate trip generation modeling.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
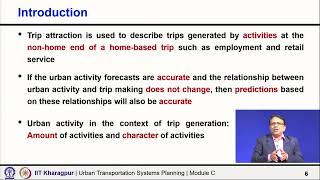
The trip generation section explains how transportation models estimate the total trips based on socio-economic characteristics of the zones. It introduces concepts like home-based and non-home-based trips, and outlines key determinants of trip production and attraction, along with two predominant modeling approaches: growth factor modeling and regression modeling.
Detailed
Trip Generation
Overview
Trip generation is the first stage in the classical aggregated demand models, focusing on predicting the number of trips generated and attracted to different zones. It uses household and socio-economic data to determine how many trips originate from each zone. This section elaborates on basic definitions, determining factors, and two main modeling techniques: growth factor modeling and regression modeling.
Types of Trips
Key definitions, such as journey, home-based trips, non-home-based trips, trip production, and trip attraction, are discussed.
1. Journey - An outwards movement from an origin to a destination.
2. Trip - An outward and return journey.
3. Home-based trips - Trips where either the origin or destination is the home of the trip maker.
4. Non-home-based trips - Trips with no association to the home.
Trips are also classified by:
- Purpose: Work, education, shopping, recreation, etc. (Mandatory vs. discretionary trips)
- Time of day: Peak vs. off-peak trips
- Traveler's profile: Influenced by socio-economic factors (income, vehicle ownership, household size).
Factors Affecting Trip Generation
Key factors include:
- Personal trip production - Income, vehicle ownership, household structure, family size.
- Trip attraction - Employment zones, accessibility, space for commercial services.
Freight trips also factor into models but constitute about 20% of total trips.
Modeling Approaches
- Growth Factor Modeling: Predicts trip numbers based on a linear function of explanatory variables, e.g., population, household income, vehicle ownership.
- Regression Methods: Usually a multiple linear regression model to relate trip rates to variables such as household size.
Understanding these aspects of trip generation is crucial as they form the foundational elements upon which transportation planning and policy are built.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Trip Generation
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Trip generation is the first stage of the classical first generation aggregate demand models. The trip generation aims at predicting the total number of trips generated and attracted to each zone of the study area. In other words, this stage answers the questions to how many trips originate at each zone, from the data on household and socioeconomic attributes.
Detailed Explanation
Trip generation is a crucial concept in understanding transportation planning. It seeks to estimate the number of trips that start or end in different areas, known as 'zones'. This estimation is based on various factors, including household characteristics and socioeconomic conditions. By accurately predicting trip generation, urban planners can better understand traffic demands and enhance urban infrastructure to accommodate these needs.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a busy shopping mall. Understanding how many shoppers come from surrounding neighborhoods (zones) can help the mall management decide how many parking spaces to provide and when to schedule security staff. Trip generation helps predict these patterns.
Types of Trips
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Some basic definitions are appropriate before we address the classification of trips in detail. We will attempt to clarify the meaning of journey, home-based trip, non-home-based trip, trip production, trip attraction and trip generation. Journey is an out way movement from a point of origin to a point of destination, whereas the word trip denotes an outward and return journey.
Detailed Explanation
To understand trip generation, it's essential to categorize different types of trips. A 'journey' refers to the movement from one location to another, while a 'trip' involves the round journey from the original point to a destination and back. Home-based trips are defined as those where either the starting point or endpoint is the traveler’s home. Conversely, non-home-based trips do not involve the home. Recognizing these categories can help in analyzing travel patterns more effectively.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a person commuting to work and returning home - that's a home-based trip. If they go directly from work to a grocery store instead of home, that's a non-home-based trip. Understanding these distinctions helps in planning services and infrastructure.
Classification of Trips by Purpose
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Trips can be classified by trip purpose, trip time of the day, and by person type. Trip generation models are found to be accurate if separate models are used based on trip purpose. The trips can be classified based on the purpose of the journey as trips for work, trips for education, trips for shopping, trips for recreation and other trips.
Detailed Explanation
Trip classification by purpose is vital for trip generation models. Common purposes include work, education, shopping, and recreation. These can be further categorized into mandatory trips (such as work and education) and discretionary trips (like shopping or leisure). By recognizing the purpose behind trips, models can be fine-tuned for accuracy in predicting travel patterns.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a family planning their week. They might have mandatory trips like going to work or school but also discretionary trips for going to the movies or shopping. By seeing how many of each type of trip they take, planners can improve transport systems to accommodate these patterns.
Factors Affecting Trip Generation
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The main factors affecting personal trip production include income, vehicle ownership, household structure and family size. In addition, factors like value of land, residential density and accessibility are also considered for modeling at zonal levels.
Detailed Explanation
Several factors influence how many trips individuals or households will produce. Income level can determine how often people travel, as higher income may lead to more discretionary trips. Vehicle ownership impacts the capacity for making trips, while household structure and family size play a role in how many members are contributing to trips. Understanding these factors helps in creating a comprehensive model for trip generation.
Examples & Analogies
Think about families with two working parents - they might make more trips than a single-parent household. Additionally, families in higher-income brackets may travel more for leisure compared to lower-income brackets whose trips might be more work or necessity-driven.
Modeling Approaches: Growth Factor and Regression
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In trip generation modeling, in addition to personal trips, freight trips are also of interest. Although the latter comprises about 20 percent of trips, their contribution to the congestion is significant. Freight trips are influenced by the number of employees, number of sales and area of commercial firms.
Detailed Explanation
In modeling trip generation, we must consider both personal and freight trips. While personal trips are numerous, freight trips, despite being fewer, can have a disproportionate impact on traffic congestion. Models need to account for various economic indicators such as the number of employees in a business or sales volume to estimate how many freight trips will be generated.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a grocery delivery service. While the number of personal trips for shopping might be high, the trucks making deliveries (freight trips) also deserve attention because they can cause traffic jams, especially during peak hours. Understanding both types of trips is essential for effective transportation management.
Key Concepts
-
Trip Generation: It predicts trips based on socio-economic data.
-
Home-Based vs. Non-Home-Based Trips: Differentiates trips based on home involvement.
-
Factors Influencing Trip Production: Includes income, vehicle ownership, etc.
-
Growth Factor Modeling: A method to predict future trips based on current conditions.
-
Regression Methods: Statistical techniques used to relate variables and trip generation.
Examples & Applications
An example of trip production is predicting trips from a zone based on average household size and socio-economic indicators.
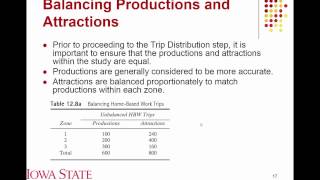
The growth factor modeling example illustrates how to calculate future trip generation rates based on current household data.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Home or not, trips we trot, for work, for play, in zones, they'll stay!
Stories
Imagine a bustling town where each family leaves home for work, school, and shopping. Every person’s movement is a trip, generated from their home, contributing to traffic patterns!
Memory Tools
Remember T - Trip, P - Production, A - Attraction: 'T-P-A' for remembering Types of trips!
Acronyms
GFR - Growth Factor Regression
Remember how to model trips using GFR techniques!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Trip Generation
The process of predicting the total number of trips originating and attracted to a particular zone.
- HomeBased Trip
Trips where either the origin or destination is the trip maker's home.
- NonHomeBased Trip
Trips where neither the origin nor the destination involves the trip maker's home.
- Trip Production
The total number of trips originating from a specific area.
- Trip Attraction
The total number of trips ending in a specific area.
- Growth Factor Modeling
A method of predicting future trips based on current trips using explanatory variables.
- Regression Methods
Statistical techniques used to estimate the relationship between variables and trip rates.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
