Using JAX-RS (Java API for RESTful Web Services)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to JAX-RS
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will be discussing JAX-RS, the standard API for creating RESTful services in Java EE. Can anyone tell me what REST stands for?

I think it stands for Representational State Transfer.

That's correct! JAX-RS facilitates the creation of REST APIs. Does anyone know why we prefer using JAX-RS?

Because it simplifies the development process?

Exactly! It allows easy management and manipulation of HTTP requests and responses. JAX-RS also helps with annotations. For example, the @Path annotation is used to specify the URI of our resources.

How does it handle different HTTP methods?

Great question! JAX-RS uses annotations like @GET, @POST, @PUT, and @DELETE to correspond with those methods. This means we can build a complete API with standard HTTP operations.

Let's summarize what we've learned. JAX-RS is essential for developing REST APIs in Java EE, and it simplifies response handling with annotations. Remember: JAX-RS + Annotations = Simplified API Development!
Setting up Dependencies
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand the basics of JAX-RS, how do we actually include it in our project?

Do we add it to the pom.xml file in Maven?

"Exactly right! Here’s what we would include in our pom.xml. Take a look at this code snippet:
Creating REST Resources
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's enhance our understanding by actually creating a REST resource for managing employee data. First off, who can remind us of the annotation to define a REST resource class?

@Path?

"That's right! Here’s an example of how we might define a class for employees:
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we delve into using JAX-RS to develop RESTful services in Java EE. We cover dependency setup using Maven, the creation of REST resources, and demonstrate essential methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE within a RESTful API framework.
Detailed
Using JAX-RS (Java API for RESTful Web Services)
JAX-RS is an important API for building RESTful services within Java EE environments. This section emphasizes its significance by explaining how to create a REST resource for managing employee entities.
Key Points Covered
- JAX-RS Overview: It is the standard Java API to develop RESTful web services, enabling easy integration within Java EE applications.
- Dependencies: Usage of Maven to manage JAX-RS dependencies, specifically the following snippet:
- Creating REST Resources: Here, we implement a simple REST resource for employees. The key methods demonstrated are:
- @GET: To retrieve the list of employees, producing JSON format:
- @POST: To add a new employee:
- @PUT: To update existing employee data:
- @DELETE: To remove an employee:
Significance
Understanding JAX-RS is vital for Java developers aiming to implement efficient RESTful APIs. It simplifies the interaction between clients and servers, ensuring smooth handling of HTTP requests and responses in a stateless manner.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to JAX-RS
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
JAX-RS is the standard API for creating RESTful services in Java EE.
Detailed Explanation
JAX-RS, which stands for Java API for RESTful Web Services, provides a set of APIs to create web services in a way that adheres to REST principles. Java EE developers commonly use this framework as it aligns well with the architecture and design of enterprise applications, allowing for the seamless development of robust RESTful services.
Examples & Analogies
Think of JAX-RS like a toolbox specifically designed for craftspersons building furniture. Just as a toolbox provides the right tools to create a chair or a table efficiently, JAX-RS provides developers with the necessary tools to build web services that are efficient and effective.
Dependencies for JAX-RS
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
javax.ws.rs javax.ws.rs-api 2.1
Detailed Explanation
To use JAX-RS in a Java EE application, you need to include the relevant dependencies in your project. This snippet specifies that you are including the JAX-RS API with version 2.1 in your Maven project. By adding this dependency to your pom.xml file, Maven will automatically download the necessary libraries, making class and method calls available for use in your code.
Examples & Analogies
Consider this step like getting the ingredients ready before baking a cake. Just as you gather flour, eggs, and sugar to prepare for baking, adding dependencies to your project ensures you have all the necessary components to build your RESTful services.
Creating a REST Resource
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
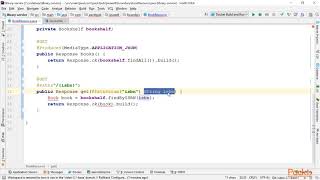
@Path("/employees")
public class EmployeeResource {
private static List employees = new ArrayList<>();
@GET
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
public List getEmployees() {
return employees;
}
@POST
@Consumes(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
public Employee addEmployee(Employee employee) {
employees.add(employee);
return employee;
}
@PUT
@Path("/{id}")
@Consumes(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
public Employee updateEmployee(@PathParam("id") int id, Employee employee) {
for (Employee e : employees) {
if (e.getId() == id) {
e.setName(employee.getName());
e.setDepartment(employee.getDepartment());
return e;
}
}
return null;
}
@DELETE
@Path("/{id}")
public String deleteEmployee(@PathParam("id") int id) {
employees.removeIf(e -> e.getId() == id);
return "Employee deleted.";
}
}
Detailed Explanation
This code snippet demonstrates how to create a REST resource for managing employee data using JAX-RS. The EmployeeResource class is annotated with @Path("/employees"), indicating that it handles requests to the /employees endpoint. The class provides methods for various HTTP methods: GET for retrieving employee data, POST for adding a new employee, PUT for updating existing employee data, and DELETE for removing an employee.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine running a library where each shelf holds different books. Just like each shelf has its own space and collection of books, each method in your REST resource acts as a specific function—helping you get, add, update, or remove a book from the library. This organization makes it easy for anyone to find the book they want!
Key Concepts
-
JAX-RS: Framework for creating RESTful services in Java EE.
-
Dependency Management: Used to manage JAX-RS libraries through Maven.
-
Annotations: Metadata added to classes or methods to specify their behavior in a RESTful context.
Examples & Applications
Creating an Employee resource with JAX-RS using @Path('/employees').
Defining GET and POST methods for handling employee data retrieval and creation.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In JAX-RS, we define our way,
Stories
Imagine a manager at a company called JAX-RS. This manager makes sure that employees can be hired, updated, or fired with specific steps: GET brings them in, POST creates happy new hires, PUT updates information, and DELETE sends them away. Each action has its method, just like a productive office.
Memory Tools
Remember: G, P, U, D for the methods in JAX-RS. G is for GET, P for POST, U for UPDATE, D for DELETE.
Acronyms
RAPI
REST API Processes Instruction - For remembering how to interact with RESTful APIs using JAX-RS.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- JAXRS
Java API for RESTful Web Services used for building RESTful applications in Java EE.
- REST Resource
An object that represents a resource in a REST API, addressing a specific data entity like an employee.
- Maven
A build automation tool used primarily for Java projects, enabling the management of project dependencies.
- Annotations
Special markers in Java code that provide metadata about the class or method they annotate.
- @Path
An annotation used in JAX-RS to define the URI path of a resource.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
