Collection Hierarchy Recap
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Collection Hierarchy
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are recapping the collection hierarchy in Java. Who can tell me some of the main types of collections we have?

I believe there are Lists, Sets, and Maps!

Great! Those are correct. What is one of the characteristics that make Lists stand out?

Lists allow duplicates and maintain order!

Exactly! Lists like `ArrayList` and `LinkedList` allow you to store elements in a specific sequence. Now, can someone explain how Sets differ?

Sets do not allow duplicates, and they usually don't maintain order, right?

Yes! Sets provide unique storage. Remember the acronym 'DNU' to recall: Duplicates Not Allowed for Sets! Now, what about Queues?

Queues follow a FIFO order, so the first element added is the first one out!

A perfect explanation! Let's summarize: Lists hold ordered data with duplicates, Sets ensure uniqueness, and Queues manage data flow with FIFO.
Diving Deeper into Maps
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's focus on Maps. Can anyone give me examples of Map implementations?

I know of HashMap and TreeMap!

Correct! HashMap accesses keys using a hash function, while TreeMap maintains a sorted order based on keys. Why would we choose TreeMap over HashMap?

Because TreeMap keeps the keys sorted, which might be important for certain operations.

Exactly! To remember this, think of 'Security in Sorting' for TreeMap. Lastly, what about ConcurrentHashMap?

It is used in multi-threaded environments because it allows multiple threads to read and write concurrently!

Bravo! By understanding the hierarchy and uses of these collections, we can utilize them more effectively in our applications.
Overview and Recap
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up, let’s summarize what we have learned today. What are the four main categories of collections?

Lists, Sets, Queues, and Maps!

Good! And what is the main purpose of using collections?

To efficiently manage and manipulate groups of objects.

Fantastic! Always remember the core functionalities of each collection type: DNU for Sets, FIFO for Queues, and key-value pairs for Maps. This understanding is crucial for your future development tasks.

Thank you! This summary really helps clarify things!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
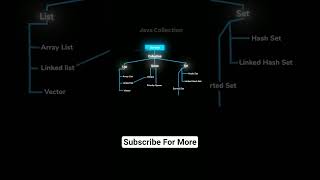
The Java Collections Framework is divided into primary components: Lists (like ArrayList and LinkedList), Sets (including HashSet and TreeSet), Queues/Deques (such as PriorityQueue), and Maps (like HashMap, TreeMap). Each of these categories provides unique functionalities suited for different caching and performance needs.
Detailed
Collection Hierarchy Recap
The Java Collections Framework (JCF) is a powerful structure that categorizes various data handling classes essential for Java programming. In this section, we recap the major categories of collections:
- Lists: This category includes implementations like
ArrayList,LinkedList, andVector, focused on storing ordered collections of elements allowing duplicates. - Sets: Includes specialized implementations such as
HashSet,LinkedHashSet, andTreeSet, aimed at preventing duplicate entries and maintaining unique elements in various ways. - Queues/Deques: Queues like
PriorityQueueandArrayDequeenable managing elements in a first-in, first-out (FIFO) manner or allow double-ended entries. - Maps: Represents a collection of key-value pairs, with implementations like
HashMap,TreeMap, andConcurrentHashMap, providing different ways of handling and accessing elements based on keys.
Each of these collections implements the core interfaces of either Collection or Map, forming the backbone of the Java Collections Framework and enabling developers to create efficient and effective data structures. Understanding this hierarchy is vital for utilizing the advanced features of JCF in real-world applications.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Java Collections
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Each of these implements either Collection or Map interface.
Detailed Explanation
In Java, all the collections mentioned above interface with two significant hierarchies: Collection and Map.
-
Collection Interface: This is the root of the collection hierarchy. It provides methods for adding and removing elements, checking if the collection is empty, and obtaining the size of the collection. All the collection types like
List,Set, andQueuederive from this interface. -
Map Interface: This interface represents a collection of key-value pairs and is not a true collection like the others. Instead of storing single objects, it maps unique keys to values. Classes that implement the
Mapinterface includeHashMap,TreeMap,LinkedHashMap, andConcurrentHashMap.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the Collection interface as the big umbrella under which all types of storage methods fall—different sections of the umbrella feature a List, a Set, and a Queue. Each section serves a unique purpose but functions under the collective aim of organizing and managing data. On the other hand, the Map interface resembles a library catalog: each book (value) is situated at a unique location (key), ensuring you can always find what you need quickly.
Key Concepts
-
Java Collections Framework: A set of classes and interfaces for managing groups of objects.
-
List: A type of collection that maintains order and allows duplicates.
-
Set: A collection that prevents duplication of elements.
-
Queue: A data structure that processes elements in a FIFO manner.
-
Map: A collection that associates unique keys with specific values.
Examples & Applications
Example of List: An ArrayList can store multiple user names where duplicates are acceptable and order is necessary.
Example of Set: A HashSet can store unique email addresses without duplication, ensuring each address appears once.
Example of Map: A HashMap can be used to store user IDs as keys and user details as values for quick lookups.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a List, order is key, duplicates roam free, a Set keeps them away, unique they will stay!
Stories
Imagine a library (List) where each book (duplicate) can be present multiple times. Now, think of a unique club (Set) where each member (unique entry) can enter only once. Then, there’s a relay race (Queue) where the first runner (first entry) goes first. Finally, picture a directory (Map) where each name (key) maps to specific details (value).
Memory Tools
LSSM: Lists, Sets, Queues, and Maps help you remember Java's collection hierarchy.
Acronyms
DNU
Duplicates Not Allowed (for Sets).
Flash Cards
Glossary
- List
An ordered collection that can contain duplicate elements, such as ArrayList, LinkedList, and Vector.
- Set
A collection that does not allow duplicate elements, including implementations like HashSet and TreeSet.
- Queue
A collection designed to hold elements prior to processing, typically in a FIFO (first-in, first-out) manner.
- Map
A collection of key-value pairs that associates keys with their corresponding values, such as HashMap and TreeMap.
- HashMap
A Map implementation that uses hashing to store key-value pairs efficiently.
- TreeMap
A sorted Map implementation that stores keys in a sorted order using a Red-Black Tree.
- ConcurrentHashMap
A thread-safe implementation of Map that allows concurrent read and write operations.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
