Spring Configuration
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Spring Configuration
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to talk about Spring Configuration. Can anyone tell me what configuration means in the context of programming?

I think it's how we set up our application components!

Exactly! In Spring, we have various ways to configure our application components. Let's start with XML-based configuration. Can someone tell me what XML is?

XML stands for eXtensible Markup Language, right? It’s often used for configuration files.

Correct! And an XML Spring configuration might look like this: `<bean id="car" class="com.example.Car"/>`. What does this code do?

It defines a bean for the Car class!

Exactly! This allows Spring to manage the `Car` object's lifecycle. Now, let's move on to annotation-based configuration.
Annotation-based Configuration
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

"With annotation-based configuration, we can use annotations to define beans directly in Java classes. For example, look at this code:
Java-based Configuration
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

"In Spring Boot, we can set up our application with minimal configuration. For instance:
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Spring provides various configuration methods for developers to set up their applications. This section highlights three primary approaches: XML-based configuration, annotation-based configuration, and Java-based configuration, each designed to simplify the initialization of Spring components.
Detailed
Spring Configuration
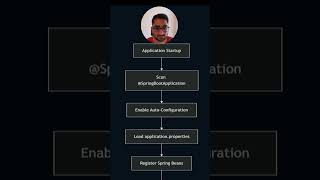
In this section, we explore the different ways to configure Spring applications, which are fundamental to the framework's flexibility and usability in developing enterprise-level applications.
XML-based Configuration
XML-based configuration is the traditional method of defining Spring beans. An example configuration could be:
This creates a Spring-managed bean for the Car class, allowing Spring to manage its lifecycle and dependencies.
Annotation-based Configuration
With the rise of annotations in Java, Spring introduced annotation-based configuration, which allows the setup to be less verbose and more readable. Here’s an example:
This configuration uses the @Configuration and @Bean annotations, defining the Car bean within a configuration class.
Java-based Configuration
Furthermore, developers can utilize Java-based configuration introduced by Spring. An example of a simple Spring Boot application setup is:
Here, the @SpringBootApplication annotation eliminates the need for extensive boilerplate code, setting up the application context in a straightforward manner.
Significance
These configuration methods are vital as they reflect the flexible yet structured nature of the Spring framework. As Spring applications often involve complex setups, having multiple ways to configure beans allows developers to choose the best approach that suits their project needs, thus simplifying development and increasing productivity.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
XML-based Configuration
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Detailed Explanation
In Spring, XML-based configuration allows developers to define beans and their properties in an XML file. The <bean> tag is used to declare a bean in Spring's context. In this example, the id attribute uniquely identifies the bean as 'car', and the class attribute specifies the Java class (com.example.Car) that this bean will instantiate. This XML configuration lets the Spring framework automatically wire the dependencies needed for the 'car' bean.
Examples & Analogies
Think of XML-based configuration like a recipe where all ingredients and their quantities are listed. Just like a chef follows a recipe to prepare a dish, the Spring framework uses the XML configuration to create and manage the components needed for the application.
Annotation-based Configuration
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public Car car() {
return new Car();
}
}
Detailed Explanation
In annotation-based configuration, Spring uses annotations to define how beans are constructed and managed. The @Configuration annotation indicates that AppConfig is a source of bean definitions. Within this class, the @Bean annotation tells Spring that the method car() instantiates a Car object. When Spring runs, it calls the car() method and registers the resulting object as a bean. This method is preferred for its conciseness and clarity compared to XML configuration.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a builder who uses blueprints instead of written instructions to construct a house. The blueprints (annotations) provide clear guidance on how to build the house (create beans) without needing a lengthy description (XML).
Java-based Configuration
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
@SpringBootApplication
public class MyApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MyApp.class, args);
}
}
Detailed Explanation
Java-based configuration uses the @SpringBootApplication annotation to indicate that the class contains configurations tailored for a Spring Boot application. The main method is the entry point of the application, where SpringApplication.run(MyApp.class, args); initializes the Spring application context. This approach simplifies the whole configuration process and sets up the server, allowing the developer to focus more on business logic instead of configurations.
Examples & Analogies
Think of starting a car: when you turn the key in the ignition, it starts the engine (initializes Spring). The @SpringBootApplication serves like the ignition key that kicks off your application smoothly, ready for driving (running your application).
Key Concepts
-
XML-based Configuration: Using XML files to manage Spring beans.
-
Annotation-based Configuration: Simplifying configuration via annotations.
-
Java-based Configuration: Configuring applications using Java code with Spring Boot.
Examples & Applications
Define a bean for a Car class using XML configuration: <bean id="car" class="com.example.Car"/>.
Use annotation configuration for a Car bean:
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public Car car() {
return new Car();
}
}
Set up a Spring Boot application:
@SpringBootApplication
public class MyApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MyApp.class, args);
}
}
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In Spring, we set the flow, with beans that steal the show. XML, Annotations too, Java’s here to help you through.
Stories
Imagine a chef who organizes their kitchen. They can either label everything (XML), use clear instructions (Annotations), or even create a blueprint (Java) to ensure all dishes are prepared perfectly.
Memory Tools
Remember 'A-JE': Annotation, Java, and XML - the trio of Spring Configuration.
Acronyms
Use 'BJA' to recall the configuration types
Beans
Java
Annotations.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- XMLbased Configuration
A traditional way of configuring Spring applications using XML files that define beans and dependencies.
- Annotationbased Configuration
Configuration method that uses Java annotations, making setup less verbose and more integrated within the code.
- Javabased Configuration
A configuration style that allows developers to set up Spring applications using standard Java code.
- Bean
An object that is instantiated, assembled, and managed by the Spring IoC container.
- Spring Boot
A Spring framework that simplifies the setup and development of new Spring applications.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
