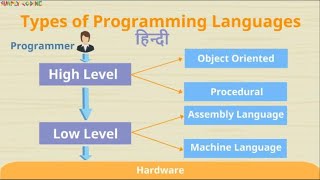
Comparison with Low-Level Languages
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Readability of Languages
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

One of the key features that differentiate high-level languages from low-level languages is readability. Can anyone explain how this might impact a programmer's ability to develop software?

High-level languages are easier to understand, which helps when debugging.

Exactly! When code is more readable, it allows for better collaboration among developers. Now, why do you think low-level languages have lower readability?

They use a lot of complex commands and don’t resemble human languages.

Right! Let's use the mnemonic 'CODES'—Clarity, Organization, Debugging, Ease of understanding, Syntax—to remember the importance of readability in coding!

That’s a helpful trick!

To summarize, high readability in HLLs fosters easier maintenance and collaboration, while low readability in low-level languages can be a barrier.
Performance Differences
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive into performance. Why do you think low-level languages usually perform better than high-level languages?

Perhaps they are more efficient because they interact directly with the hardware?

That's correct! Low-level languages like Assembly are optimized for the machine's architecture. In contrast, HLLs add layers that can slow things down. Remember the acronym 'SPEED' to recall why low-level languages are better for performance: Simplicity in deployment, Processing directly, Efficiency, Direct access.

How does that impact what kind of projects each is best suited for?

Great question! High-level languages are ideal for applications where development speed is prioritized, while low-level languages excel in systems programming where performance is critical. Let’s summarize: HLLs improve development speed, while LLs are faster in execution.
Debugging and Error Management
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

When developing software, debugging is crucial. How does debugging in HLLs compare to LLs?

It's usually easier in high-level languages since they have more advanced tools and clearer error messages.

Exactly! The error handling in HLLs often abstracts away a lot of complexity making it more manageable. Use the mnemonic 'CLEAR'—Clarify, Locate, Examine, Adjust, Review—to remember the key steps in debugging!

That's helpful! So LLs require more understanding of the machine?

Yes, well said! In conclusion, while HLLs offer easier debugging paths, LLs demand a deeper understanding of the hardware for effective debugging.
Portability of Languages
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s discuss portability. Why are high-level languages typically more portable than low-level ones?

HLLs can run on different platforms without major changes?

Absolutely! This portability allows developers to create applications that can reach wider audiences and platforms. To memorize this, think of the acronym 'EASE'—Ease of deployment, Adaptability, Software reuse, Execution across platforms.

This is important for applications that need to be accessible widely and easily.

Correct! HLL portability is beneficial for developers looking to maximize their software's reach. Remember, high portability enhances flexibility in programming.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
High-level programming languages (HLLs) offer advantages such as better readability and portability compared to low-level languages like Assembly and Machine Code. The text discusses various features including debugging ease, performance comparison, and hardware control, emphasizing the usability of HLLs in modern programming.
Detailed
Comparison with Low-Level Languages
In this section, we compare high-level programming languages (HLLs) with low-level languages, primarily focusing on the following aspects:
Readability
- High-Level Languages: These languages, such as Python and Java, are designed to be human-readable, making them easier to write and understand.
- Low-Level Languages: In contrast, languages like Assembly and Machine Code have a syntax that is more complex and less readable for humans.
Hardware Control
- High-Level Languages: These languages provide limited direct control over hardware components, abstracting many hardware details for ease of use.
- Low-Level Languages: They allow for complete and fine-grained control over hardware, which is essential for system-level programming.
Performance
- High-Level Languages: Typically, these languages are slower in execution compared to low-level ones due to the layers of abstraction.
- Low-Level Languages: They are more efficient and faster as they interact more closely with the hardware.
Debugging
- High-Level Languages: Errors and bugs are easier to identify and fix due to their readable syntax and robust debugging tools.
- Low-Level Languages: Debugging is more challenging, often requiring in-depth knowledge of both the language and the hardware.
Portability
- High-Level Languages: They can operate on multiple platforms with little modification, making them highly portable.
- Low-Level Languages: They are generally platform-specific, thus less portable which can hinder code reuse.
The comparison outlines that while HLLs simplify modern software development, low-level languages remain valuable for specific, performance-oriented tasks.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Readability
Chapter 1 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Feature: Readability
- High-Level Language: High
- Low-Level Language: Low
Detailed Explanation
Readability refers to how easy it is for humans to read and understand the code. High-level languages have a simple, human-like syntax that makes them more understandable. Low-level languages, in contrast, use a syntax that is more closely tied to machine code, which can be cryptic and challenging to read. This difference means that developers can write and maintain high-level code more easily than low-level code.
Examples & Analogies
Think of high-level languages as a novel written in your native language, while low-level languages are like ancient hieroglyphics. The novel is easy to read and understand, while the hieroglyphics require special knowledge to interpret.
Hardware Control
Chapter 2 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Feature: Hardware Control
- High-Level Language: Limited
- Low-Level Language: Full
Detailed Explanation
Hardware control refers to how closely a programming language can interact with the physical components of a computer. Low-level languages provide full control over hardware, allowing programmers to manipulate memory and CPU operations directly. High-level languages, however, abstract these details, providing limited control, which makes them safer and easier to use, but less flexible for tasks requiring direct hardware manipulation.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine building a house. Using high-level languages is like having a contractor who manages the work for you; you focus on design without worrying about the details of construction. Low-level programming is like being the architect and builder, needing to understand every nail and beam in the house.
Performance
Chapter 3 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Feature: Performance
- High-Level Language: Slower
- Low-Level Language: Faster
Detailed Explanation
Performance refers to how quickly a program runs and how efficiently it uses system resources. High-level languages typically have more abstraction layers, which can slow down execution compared to low-level languages that are more closely optimized for hardware performance. This means that while high-level languages are easier to work with, they may not be as fast or resource-efficient as low-level languages.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a fast sports car versus a family minivan. The sports car (low-level language) is built for speed and nimbleness but requires a skilled driver, while the minivan (high-level language) is spacious and easy to drive but isn't designed for racing.
Debugging
Chapter 4 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Feature: Debugging
- High-Level Language: Easier
- Low-Level Language: Difficult
Detailed Explanation
Debugging is the process of finding and fixing errors in code. High-level languages usually include more powerful debugging tools and produce more readable error messages, making it easier for developers to troubleshoot problems. Low-level languages often provide less information during errors, which can lead to more complicated debugging processes.
Examples & Analogies
Think of debugging high-level languages like using a user-friendly map app that indicates where you went wrong and how to get back on track, while debugging low-level languages feels like using an outdated paper map with vague instructions that may not accurately show your current location.
Portability
Chapter 5 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Feature: Portability
- High-Level Language: High
- Low-Level Language: Low
Detailed Explanation
Portability refers to a program's ability to run on different hardware platforms without requiring significant changes. High-level languages are usually designed to be portable, meaning code written in one can often run on various systems with minimal modification. Low-level languages, however, are highly dependent on specific hardware, making them less adaptable across different environments.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a video game developed for multiple consoles. If it's written in a high-level language, it can easily be adapted for different systems (like PlayStation and Xbox). But a game programmed in a low-level language might only work on one specific console, similar to a key that only fits one lock.
Examples
Chapter 6 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Example:
- High-Level Languages: Python, Java
- Low-Level Languages: Assembly, Machine Code
Detailed Explanation
This part summarizes some examples of each type of language. High-level languages like Python and Java are widely used for applications, web development, and data analysis due to their ease of use and readability. Low-level languages like Assembly and Machine Code are used for tasks requiring precise control and high performance, often in system programming or embedded systems.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine baking a cake (high-level programming) where you follow a straightforward recipe, using common ingredients. In contrast, low-level programming is like crafting a traditional dish that requires specific, hard-to-find ingredients and precise techniques. While the cake is easier to make and serve (like high-level languages), the traditional dish can be crafted to perfection (like low-level languages).
Key Concepts
-
Readability: The clarity and simplicity of the programming language syntax.
-
Hardware Control: The degree of direct manipulation a programming language allows over hardware components.
-
Performance: The efficiency of executing code, usually favoring low-level languages.
-
Debugging: The process of identifying and fixing code errors, often easier in high-level languages.
-
Portability: The ability of code to run across different systems without modification, which is generally higher in high-level languages.
Examples & Applications
Python is an example of a high-level language that prioritizes readability and ease of use.
Assembly is an example of a low-level language that allows precise control over hardware but is complex and less readable.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
High-level's easy, from code to read, / While low-level's tricky, for high-speed deed.
Stories
Imagine a chef in a restaurant versus a home cook; the chef uses sophisticated tools (high-level languages) to create complex dishes quickly, while the home cook (low-level language) knows each knife and fire settings intricately but moves slower overall.
Memory Tools
Remember 'RHPD': Readability, Hardware control, Performance, Debugging for comparing HLLs and LLLs.
Acronyms
Use 'HARD' for High-level Abstraction, Readability, Debugging — the strengths of high-level languages.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- HighLevel Language
A programming language that provides abstraction from hardware, making it more readable and easier to use.
- LowLevel Language
A programming language that provides little abstraction from the computer's hardware, offering fine-grained control but is more challenging to read.
- Readability
The ease with which code can be read and understood by humans.
- Performance
A measure of how efficiently a language executes commands and processes data.
- Debugging
The process of identifying and resolving errors or bugs in computer code.
- Portability
The ability of software to run on different operating systems or environments with little or no modification.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
