What is a System on Chip (SoC)?
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding SoC Components
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we will delve into the components of a System on Chip, or SoC. Can anyone start by telling me what they think an SoC includes?

Is it just the CPU on a chip?

Good point! The CPU is a central component, but an SoC is more than that. It includes memory, peripherals, and sometimes custom hardware too. Let's remember this as **'C-M-P-C'**: CPU, Memory, Peripherals, Custom hardware.

So, memory could be RAM or ROM, right?

Exactly! RAM is used by the CPU for temporary data storage while ROM is for permanent storage. Anyone know why we prefer SoCs for mobile devices?

I think it's because they save space and energy?

Yes, you got it! By combining everything onto one chip, we save space and also lower power consumption, which is crucial for devices like smartphones.

What about custom hardware? Does that mean special features?

Absolutely! That can be anything from a GPU for gaming to DSPs for audio processing. It's what makes these chips versatile. So, let's recap: SoCs combine CPU, memory, peripherals, and custom hardware for efficiency.
Benefits of SoCs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we know the components, let’s discuss the advantages of using an SoC. Why do you think they're important in today's devices?

They must be cheaper to produce?

Correct! Integrating everything reduces manufacturing costs and lessens the need for multiple chips on a board. Any other benefits?

I think they help with performance too, right?

Yes! Because everything is on one chip, data transfer between parts is faster, thus improving performance. Another mnemonic to remember is **'C-S-P'** which stands for Cost, Size, Performance.

Are SoCs used in IoT devices then?

Exactly! Their efficiency is why they're the backbone of many IoT devices. It helps them function effectively while maintaining low power consumption.

So, everything from smart thermostats to wearables use SoCs?

That’s right! So, remember: SoCs are essential for modern efficiency, allowing devices to be smaller, cheaper, and more capable.
Real-World Applications of SoCs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s explore how SoCs are used in real-world applications. Can anyone name a device that uses an SoC?

Smartphones! They have SoCs, right?

Exactly! Smartphones utilize SoCs for everything from processing to managing the camera. Can someone tell me another example?

What about IoT devices? They need low power, so SoCs are great for them!

Absolutely! IoT devices, like smart home gadgets, need energy-efficient solutions, and SoCs fit that demand well. Remember the acronym **'P-C-P'**: Performance, Cost, Power!

Do SoCs have any future applications?

Definitely! As technology advances, we’ll see SoCs used in even more areas, like cars for advanced driver-assistance systems. To wrap up, let’s remember the wide-ranging applications of SoCs in our daily lives, making devices smarter and more efficient.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
SoCs combine critical system elements, such as CPUs, memory, peripherals, and custom hardware, into one integrated chip. This design reduces size, cost, and power consumption, making SoCs essential in modern electronics, from smartphones to IoT devices.
Detailed
What is a System on Chip (SoC)?
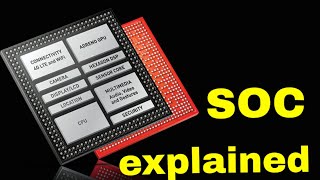
A System on Chip (SoC) is a conceptual and physical integration of various essential components of a computing system onto a single silicon chip. This technology includes the central processing unit (CPU), memory like RAM and ROM, peripherals, and specialized hardware like graphics processing units (GPUs) or digital signal processors (DSPs) that enable advanced capabilities.
Key Characteristics of SoCs
SoCs serve as the backbone for modern embedded systems and smart devices, providing reduced size, cost efficiency, and lower power consumption, which are crucial in the context of mobile and connected devices, such as smartphones and Internet of Things (IoT) gadgets. By integrating multiple components onto one chip, SoCs allow for better performance while also simplifying the design process for device manufacturers.
Typical components included in an SoC are:
- CPU: The core unit that executes instructions for operations.
- Memory: This includes volatile and non-volatile storage (e.g., RAM, ROM).
- Peripherals: Interface ports (like USB, UART, I2C) that connect the SoC to other devices.
- Custom Hardware: Ranges from GPUs to accelerators designed for specific tasks (like AI processing).
- Power Management: Features integrated to manage energy efficiency effectively across the chip.
In summary, the innovative design of an SoC exemplifies how modern computing seeks to advance efficiency and capability while addressing the constraints of size and power consumption.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of SoC
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A System on Chip (SoC) is a single-chip solution that integrates all the necessary components of a computing system, such as the central processing unit (CPU), memory, peripherals, and custom hardware, onto a single silicon chip. SoCs are the backbone of modern embedded systems, smartphones, and IoT devices.
Detailed Explanation
A System on Chip, or SoC, is essentially a complete computing system integrated into a single chip. This means that all the vital parts of a computer, like the CPU that processes information, different types of memory to store data, and interface connections to other devices, are all combined into one small piece of silicon. This is crucial in modern technology, especially in devices like smartphones and IoT gadgets, where space and efficiency are key.
Examples & Analogies
Think of an SoC like a Swiss Army knife. Just as a Swiss Army knife combines various tools into one handy device, an SoC bundles all necessary computing components into one chip, allowing devices to perform multiple functions without needing separate parts.
Components of an SoC
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
An SoC combines various essential components such as the processor, memory, input/output interfaces, and specialized peripherals into a single chip, reducing size, cost, and power consumption.
- CPU: The central processing unit that executes instructions.
- Memory: Includes RAM, ROM, and other types of storage.
- Peripherals: Hardware interfaces such as UART, SPI, I2C, USB, and more.
- Custom Hardware: Specialized blocks like GPUs, DSPs, or AI accelerators.
- Power Management: Power-efficient design features for managing the chip’s energy consumption.
Detailed Explanation
An SoC is made up of several key components that work together. Firstly, it has a CPU, which is like the brain of the system, where instructions are processed. It also includes various types of memory to store data temporarily (like RAM) and permanently (like ROM). Additionally, peripherals enable communication and interaction with other devices, using specific protocols. Custom hardware, like graphics processing units (GPUs) or digital signal processors (DSPs), allows for specialized tasks such as image processing. Lastly, SoCs integrate power management features to operate efficiently, reducing energy use. Combining these components on a single chip helps minimize the overall size and cost of electronic systems.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a small factory where each part of the production process happens in a separate room. This setup is inefficient and takes up a lot of space. An SoC is like designing that factory so that all processes occur in one room. The CPU is the manager who directs operations, memory is the storage area for raw materials and finished products, peripherals are the machines, and custom hardware are the specialized tools that speed up certain tasks. This arrangement makes everything more streamlined and efficient.
Importance of SoCs
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
SoCs are the backbone of modern embedded systems, smartphones, and IoT devices.
Detailed Explanation
The role of SoCs in technology cannot be overstated; they serve as the foundation for many modern electronic devices. Embedded systems rely on SoCs to function, which are systems integrated into larger systems, such as cars or appliances. Smartphones, which demand high functionality and compact sizes, also depend on SoCs to perform various tasks seamlessly. Additionally, Internet of Things (IoT) devices utilize SoCs to connect and communicate efficiently, enabling automation and smart technology in our daily lives.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of SoCs as the engine in a vehicle. Just as the engine drives a car, powering it and allowing it to function, SoCs enable devices like smartphones and smart appliances to perform multiple tasks efficiently. Without engines, vehicles wouldn’t be able to move, and without SoCs, our advanced smart devices wouldn't work as they do today.
Key Concepts
-
Integration of Components: SoCs integrate CPU, memory, and peripherals onto a single chip.
-
Power Efficiency: The design of SoCs leads to reduced power consumption, crucial for portable devices.
-
Cost Reduction: Producing an SoC is generally cheaper than using multiple separate chips.
Examples & Applications
Smartphones utilize SoCs to combine processing, memory, and communication interfaces.
IoT devices like smart thermostats and wearables leverage the compactness and efficiency of SoCs.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In every chip of silicon bright, CPU and memory unite, peripherals join in a close embrace, making gadgets small and a friendly space.
Stories
Once in a digital kingdom, a lonely CPU longed for friends. It met memory, who brought RAM and ROM, and then peripherals like UART joined in, creating the happiest SoC. Together, they built many devices, making them smart and efficient.
Memory Tools
Remember C-M-P-C: CPU, Memory, Peripherals, Custom hardware.
Acronyms
Use 'P-C-P' to recall
Performance
Cost
Power for the benefits of SoCs.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- System on Chip (SoC)
An integrated circuit that consolidates all components of a computer onto a single chip.
- CPU
The central processing unit, the primary component that executes instructions in computing.
- Memory
Storage components, including RAM and ROM, that hold data for processing and permanent storage.
- Peripherals
External devices connected to the SoC for input/output operations.
- Custom Hardware
Specialized components like GPUs and DSPs integrated into the SoC for specific tasks.
- Power Management
Techniques implemented on the SoC to minimize power consumption and manage energy efficiency.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
