Basidiomycetes
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Basidiomycetes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into the fascinating world of Basidiomycetes. Can anyone tell me what they think Basidiomycetes are?

Aren't they the mushrooms we see in the woods?

Exactly! Basidiomycetes, commonly known as mushrooms, include many familiar fungi. They have an important role as decomposers in ecosystems. Remember this acronym 'MUSH' for Mushrooms, decomposers, Umbrella-shaped, and Symbiotic.

So they help break down dead plants and animals?

Correct! By decomposing organic matter, they recycle nutrients back into the soil.
Structure of Basidiomycetes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss what Basidiomycetes look like on the inside. Who knows about their mycelium?

Is it made of hyphae?

Yes! Their mycelium is formed from branched and septate hyphae. This structure is essential for nutrient absorption. A quick memory aid: 'My-Cellium' for Mycelium's role in cells absorption.

What about their reproductive structures?

Great question! They're known for basidia - the fruity bodies where basidiospores are produced. This is key in their sexual reproduction cycle.
Reproduction in Basidiomycetes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Moving on to reproduction! Basidiomycetes are unique because they primarily reproduce sexually. Can anyone tell me how?

Is it through spores?

Yes! Specifically through basidiospores formed in basidia. There's an important dikaryotic phase, which is when two different mating types come together before forming a diploid cell. Remember 'Dika = Double' to recall the dikaryotic phase characteristics.

What happens during this dikaryotic stage?

Good question! In the dikaryotic phase, the two nuclei coexist without fusing immediately. This stage is crucial before the formation of the basidium, where karyogamy occurs!
Ecological Roles of Basidiomycetes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's look at their ecological roles. How do Basidiomycetes contribute to their environments?

They help decompose matter. I remember because of their mushroom shape!

Exactly! They're vital as decomposers and can interact in symbiotic relationships with plants. Remember 'Myco' from Mycorrhiza to understand their association in nutrient exchange with plant roots.

Do they also affect plant health negatively?

Yes, they can act as pathogens as well, causing diseases in plants. Understanding both these roles helps us appreciate their complexity in ecosystems.
Review of Basidiomycetes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Before we conclude, let's recap what we learned about Basidiomycetes. Who can summarize their structure and key features?

They have a branched mycelium and reproduce mainly through basidiospores.

And they have a dikaryotic phase before becoming diploid!

Excellent! And what about their roles in the ecosystem?

They're important decomposers and can also be parasites.

Yes! You've all grasped the essential points about Basidiomycetes, their structure, reproduction, and ecological significance.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Basidiomycetes, commonly known as mushrooms, bracket fungi, and puffballs, exhibit a diverse range of forms and habitats. The section details their structure, reproductive methods, and ecological roles, highlighting their dikaryotic phase and the formation of basidia in fruiting bodies.
Detailed
Basidiomycetes Overview
Basidiomycetes are a significant class within the kingdom Fungi, encompassing a variety of familiar fungi such as mushrooms, puffballs, and bracket fungi. They play crucial ecological roles as decomposers, symbionts, and parasites.
Structure and Characteristics
- Mycelium: Their mycelium is branched and septate, allowing for greater nutrient absorption and growth.
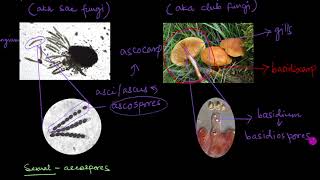
- Reproduction: Unlike other fungi, asexual reproduction is not common in Basidiomycetes. They primarily reproduce sexually through the formation of specialized structures called basidia, where karyogamy occurs leading to the production of basidiospores.
- Dikaryotic Phase: Notably, Basidiomycetes undergo a dikaryotic stage (n + n) before forming diploid cells, which is a key aspect of their life cycle.
Ecological Impact
Basidiomycetes contribute to nutrient cycling within ecosystems and engage in important relationships with plants, either as decomposers breaking down organic matter or as parasites affecting plant health. Understanding their life processes and ecological roles is vital to appreciating their importance in biodiversity.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Basidiomycetes
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Commonly known forms of basidiomycetes are mushrooms, bracket fungi or puffballs. They grow in soil, on logs and tree stumps and in living plant bodies as parasites, e.g., rusts and smuts.
Detailed Explanation
Basidiomycetes represent a significant group of fungi that are easily recognized by their common forms, which include mushrooms, puffballs, and bracket fungi. These fungi can flourish in various habitats - most notably in soil, as well as on decaying logs and tree stumps. In addition to these growth forms, some basidiomycetes are known to be parasitic, meaning they live on or inside other living plants, often causing diseases such as rusts on crops. Understanding where they grow helps in identifying and utilizing them in ecological research and agriculture.
Examples & Analogies
Think of basidiomycetes as nature's recyclers. Just as some people make compost from old food to enrich the soil for better plant growth, basidiomycetes break down dead organic matter, like fallen leaves and logs, helping to return nutrients back to the earth.
Mycelium Characteristics
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The mycelium is branched and septate. The asexual spores are generally not found, but vegetative reproduction by fragmentation is common.
Detailed Explanation
The structure of basidiomycetes includes a complex network known as mycelium, which is characterized by being branched and septate. This septate design means that the hyphae (the filament-like structures that make up fungi) have divisions or cross-walls, which can help in compartmentalizing the fungi's structure and functions. Unlike some other fungi, basidiomycetes do not often reproduce using asexual spores. Instead, they commonly reproduce vegetatively, meaning they can spread and grow by fragments of their mycelium breaking off and forming new fungal structures.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a sprawling city where buildings (hyphae) are connected by streets (mycelium). Instead of creating new buildings (spores), if part of a building collapses (fragmentation), it can still provide shelter and resources for another building nearby to stand intact and thrive.
Reproductive Structure and Process
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The sex organs are absent, but plasmogamy is brought about by fusion of two vegetative or somatic cells of different strains or genotypes.
Detailed Explanation
In basidiomycetes, traditional sex organs are not present as we might find in many plants and animals. Instead, these fungi reproduce sexually through a process called plasmogamy, where two different vegetative cells (which are the main cells that make up the fungus) fuse together. This merging forms a dikaryotic cell, where two separate nuclei from the parent cells coexist, setting the stage for further development into reproductive structures.
Examples & Analogies
Think of plasmogamy as a collaborative art project where two artists (the vegetative cells) come together, merging their works into a single masterpiece. Even though both artists (nuclei) maintain their styles, together they create something new that can evolve and change, leading to the eventual production of art (basidiospores) that can be showcased.
Formation of Basidiospores
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The resultant structure is dikaryotic which ultimately gives rise to basidium. Karyogamy and meiosis take place in the basidium producing four basidiospores.
Detailed Explanation
Once the dikaryotic cell forms after plasmogamy, it eventually leads to the creation of a specialized structure called basidium. Within this basidium, karyogamy occurs, which is the fusion of the two nuclei, leading to the formation of a diploid nucleus. Following this, meiosis (a type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number) takes place, resulting in the production of four haploid basidiospores. These spores are crucial for the life cycle of basidiomycetes as they are responsible for spreading and starting new fungal colonies.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the dikaryotic structure as a small factory that, after gathering all necessary materials (nuclei), undergoes a transformation. Once the final product is manufactured (basidiospores), those products are distributed to new locations, each carrying the potential to start a new factory of its own.
Fruiting Bodies
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The basidia are arranged in fruiting bodies called basidiocarps. Some common members are Agaricus (mushroom), Ustilago (smut) and Puccinia (rust fungus).
Detailed Explanation
The basidia, which produce the basidiospores, are grouped together to form fruiting bodies known as basidiocarps. These structures can be seen as the reproductive phase of basidiomycetes, and they are often what we recognize as mushrooms or puffballs. Examples of significant members of this group include Agaricus, which is commonly seen as edible mushrooms; Ustilago, a smut fungus that affects cereal crops; and Puccinia, notorious for causing rust diseases in plants.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a basidiocarp as a farmer's market. Just like farmers showcase their produce (basidiospores) to the public, basidiocarps serve as the visible fruit of a fungus's lifecycle, spreading their spores to grow new fungal colonies in nearby environments.
Key Concepts
-
Basidiomycetes: A class of fungi that includes mushrooms and bracket fungi.
-
Mycelium: The branched structure helping in nutrient absorption.
-
Basidia: The reproductive structure where basidiospores are produced.
-
Dikaryotic Phase: A unique stage in Basidiomycetes before diploid formation.
Examples & Applications
Mushrooms, such as Agaricus, are common edible fungi belonging to the Basidiomycetes.
Brackets fungi, commonly found on tree trunks, are also part of this group.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Mushrooms grow, Decompose and flow, Basidia in the show!
Stories
Once upon a time in a damp forest, mushrooms grew on fallen trees, helping to decay the dead wood while secretly forming basidia to release spores into the wind.
Memory Tools
D.B.C - D for Dikaryotic phase, B for Basidia, C for Colorful mushrooms!
Acronyms
MUSH - Mushrooms, Under umbrella-shaped, Symbiotic, Heterotrophic.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Basidiomycetes
A class of fungi that includes mushrooms, bracket fungi, and puffballs that reproduce through basidiospores.
- Mycelium
A network of branching, interconnecting hyphae of a fungus.
- Basidia
Specialized reproductive structures in Basidiomycetes where karyogamy and meiosis take place to produce basidiospores.
- Dikaryotic Phase
A stage in the life cycle of some fungi, including Basidiomycetes, characterized by the coexistence of two different nuclei.
- Basidiospores
Spores produced by Basidia during sexual reproduction in Basidiomycetes.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
