Diurnal tide
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Tides
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Greetings, everyone! Today, we're going to explore tides, specifically focusing on diurnal tides. Can anyone tell me what a tide is?

Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels, right?

Exactly! Tides result from the gravitational forces of the moon and sun acting on Earth's water. Now, what about the term 'diurnal'?

Doesn't it mean something happens once a day?

Correct! Diurnal tides occur once each lunar day, meaning one high and one low tide. Let's remember this with the acronym 'H-L' for High-Low. Why might that be useful?

So we can easily remember that there's one high and one low tide each day?

Exactly! Great connection. Now, can anyone think about why the height of tides can vary?

Maybe because of the moon’s position relative to the Earth?

Yes, well done! The gravitational pull changes based on the distance of the moon. Remember, 'closer = higher'.
Factors Affecting Tide Heights
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In our last discussion, we talked about diurnal tides. Now, let's dive into the factors that affect tide heights. What are some geographic features that might impact this?

Bays and estuaries could change how severe the tides are.

Right! The shape of the coastline can indeed amplify or reduce tide heights; this is known as 'funneling' effect.

So, areas like the Bay of Fundy experience higher tides because of their shape?

Correct again! The Bay of Fundy is famous for this effect, experiencing the highest tidal ranges in the world. Let’s remember this with the phrase 'Fundy = High Tide!'

That sounds easy to recall!

It is! Additionally, the gravitational pull of the moon and sun also fluctuates based on their positioning. Can anyone identify why?

It must be due to their respective distances during orbits!

Absolutely right! The closer they are, the stronger the pull – making for higher tides. Remember, distance equals influence!
Predictability and Importance of Tides
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss why understanding tides, particularly diurnal tides, is important. What are some benefits of knowing tide patterns?

Fishermen can plan their fishing trips around tides.

Exactly! Tides influence fish behavior and feeding habits. Fishermen can optimize their catch by aligning with high tides. Anyone else?

Navigators need to know when to enter or leave harbors!

Spot on! Accurate tidal predictions ensure safe navigation and prevent groundings. Let’s highlight this with the mnemonic 'Safe Sailors Use Tides' (SSUT).

That’s a helpful way to remember it!

Glad you think so! Predictability also aids in combating coastal erosion and managing waterfront environments effectively. Why might that be?

Knowledge of tides can help implement better coastal defenses!

Exactly! Also, certain renewable energy sources can exploit tidal movements for power generation. Great insights today, everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The diurnal tide is characterized by the occurrence of one high tide and one low tide each lunar day. This tidal cycle is significantly influenced by the gravitational pull of the moon and is understood in contrast to semi-diurnal and mixed tides. Various factors such as geography and coastline shape can affect tide heights and patterns.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Diurnal tides represent a unique tidal pattern featuring one high tide and one low tide within each lunar day, typically lasting about 24 hours. The primary driving forces behind these tidal movements are the gravitational attractions of the moon, which create bulges in the ocean water, leading to these distinct rises and falls in sea level. In regions experiencing diurnal tides, the successive high and low tides are approximately equal in height.
Global patterns of tides can be classified into three major types: semi-diurnal, diurnal, and mixed tides, with diurnal tides being most common in specific regions like parts of the Gulf of Mexico. The variation in tide heights primarily occurs due to gravitational influences and local geographical features such as bays and coastal shapes. Moreover, diurnal tides are predictable, allowing for safe navigation and activities like fishing, as tidal patterns can be anticipated based on the moon’s position.
Youtube Videos









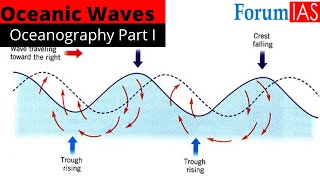
Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Diurnal Tide
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Diurnal tide: There is only one high tide and one low tide during each day. The successive high and low tides are approximately of the same height.
Detailed Explanation
A diurnal tide is a specific type of tidal pattern where there is only one high tide and one low tide each day. This means that unlike some coastal areas that experience two high and two low tides daily, locations experiencing diurnal tides go through their tidal cycle once every 24 hours. The heights of these tides (the high and the low) are usually similar and consistent from day to day.
Examples & Analogies
Think of diurnal tides like a daily schedule where you have only one meal in the morning and one at night. Just as you get used to this routine, the ocean in areas with diurnal tides follows a similar pattern, rising and falling in the water level just once each day.
Comparing Tidal Patterns
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Types of Tides: Tides vary in their frequency, direction and movement from place to place and also from time to time.
Detailed Explanation
Tides can be categorized based on how often they occur. For example, diurnal tides feature one cycle of high tide and low tide daily, in contrast to semi-diurnal tides which have two cycles within the same timeframe. Understanding the differences in tidal patterns across various locations can help in maritime navigation and predicting coastal conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a public transportation schedule. In a city with a bus that comes every hour, that would be similar to a diurnal tide, whereas a city with buses arriving every 30 minutes would resemble semi-diurnal tides. Knowing the different schedules helps passengers plan their trips better.
Importance of Understanding Diurnal Tides
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The height of rising water (high tide) varies appreciably depending upon the position of sun and moon with respect to the earth.
Detailed Explanation
Understanding diurnal tides is important not just for coastal navigation, but also for ecological reasons. The interaction between the gravitational pull of the moon and the sun causes the heights of these tides to vary, impacting marine life and coastal ecosystems. Being aware of these changes helps fishermen and boaters plan their activities according to tidal patterns.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a time you need to catch a specific bus at its highest point. The timing of your arrival must account for the bus’s schedule (high tide), which may change based on the day. If the bus runs on a tight schedule influenced by unexpected traffic (like changing tide heights), you can only successfully catch it by being observant and preparing in advance!
Key Concepts
-
One high tide and one low tide occur per day in diurnal tides.
-
Gravitational pull of the moon is the primary cause of tides.
-
Tide heights can vary greatly depending on geographical features.
-
Predictability of tides is vital for navigation and coastal management.
Examples & Applications
Port of San Diego experiences diurnal tides.
The Gulf of Mexico typically has diurnal tides.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Tides rise and fall, one high, one small, let’s all stand tall and heed their call.
Stories
Once there was a fisherman who always planned his day by the tides; he learned the dance of the moon and how it pulled the ocean each day just once.
Memory Tools
Remember the acronym 'HL' for High-Low to recall that diurnal tides have one high and one low tide.
Acronyms
SST
'Safe Sailors Use Tides' helps remember the importance of predicting tides for navigation.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Tide
The periodic rise and fall of sea levels caused primarily by the gravitational pull of the moon and sun.
- Diurnal
Referring to or occurring every day; specifically linked to tides that happen once each day.
- Gravitational Pull
The attraction between two masses, primarily affecting the tides due to the moon and sun.
- Funneling Effect
The phenomenon where tidal heights are amplified due to the shape of the coastal geography.
- Tidal Range
The vertical difference in height between consecutive high and low tides.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
