Deep Sea Plain
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Ocean Floors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll learn about ocean floors, focusing on the Deep Sea Plain. Can anyone tell me what they think the characteristics of ocean floors might be?

Are there different types of ocean floors?

Yes! Ocean floors can be divided into several types including continental shelves, slopes, deep sea plains, and oceanic deeps. Today, we will specifically focus on the Deep Sea Plain. Does anyone know where it lies?

Is it located at the bottom of the ocean?

Exactly! The Deep Sea Plain exists between ocean trenches and continental slopes. It's fascinating because it's one of the flattest regions on Earth! Remember, 'Deep Sea Plain = Depth and Flat'.
Formation of the Deep Sea Plain
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's discuss how the Deep Sea Plain is formed. What do you think influences its formation?

Could it be the tectonic activity?

Yes! Tectonic movements, along with volcanic activities and sediment deposition over thousands of years, shape the Deep Sea Plain. This illustrates how dynamic our Earth's surface is!

So it's not just flat land; it's built up over time?

Precisely! It's composed of layers of sediments. A useful mnemonic is 'SAND' for Sediment Assembling Naturally Daily!
Importance of the Deep Sea Plain
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Why do we think the Deep Sea Plain is significant? Any ideas?

It must be important for marine life?

Exactly! The Deep Sea Plain is a habitat for numerous marine species and helps in the overall health of ocean ecosystems. Additionally, it also relates to ocean currents.

Do we study these areas for climate effects too?

Absolutely! Ocean floor structures impact atmospheric conditions. Remember: 'OCEAN' - Oceans Create Ecological Awareness Notions!
Deep Sea Plain and Sediments
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive a little deeper. What can someone tell me about the sediments on the Deep Sea Plain?

I read they are mostly fine-grained like clay and silt.

Correct! These fine sediments are vital for the ecosystem. They hold nutrients and habitats for organisms. Keep those key points in mind: 'NUTRIENTS nourish life'.

So the ecosystem relies on those sediments?

Exactly! Sediments are the backbone of many forms of marine life. A mnemonic to recall this could be 'SEDIMENT = Sustaining Ecosystems Deep In Marine Environments, Naturally Together.'
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The Deep Sea Plain is a significant feature of the ocean floor, lying between ocean trenches and continental slopes, predominantly covered with fine sediments and significant in geological and ecological studies.
Detailed
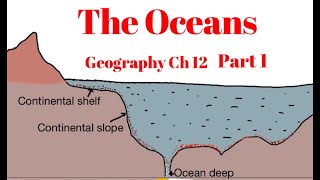
Deep Sea Plain
The Deep Sea Plain represents the broad, smooth area of the ocean floor, constituting the Earth's flattest and most extensive regions. This section details its characteristics, formation processes, and the crucial role it plays in marine ecosystems.
Key Characteristics
- Depth Range: Deep Sea Plains typically exist at depths ranging from 3,000 to 6,000 meters.
- Sediment Coverage: These plains are covered with fine-grained sediments such as clay and silt, resulting from various geological and biological processes.
- Formation: Similar to continental formations, the features of Deep Sea Plains are shaped through tectonics, volcanic activity, and sediment deposition over millennia.
- Importance: They serve as important habitats for a variety of marine life, influence oceanic currents, and play a role in the geothermal processes of the Earth.
Overall, the Deep Sea Plain is a vital component of the Earth's oceanic systems, influencing biodiversity and contributing to climatic and geological processes.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Deep Sea Plains
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Deep sea plains are gently sloping areas of the ocean basins. These are the flattest and smoothest regions of the world.
Detailed Explanation
Deep sea plains refer to large, flat areas found on the ocean floor. Unlike the ruggedness of mountain ranges or trenches, these plains are characterized by their gentle slopes and smooth surfaces. They represent a significant portion of the ocean basins and cover vast areas beneath the sea.
Examples & Analogies
Think of deep sea plains like the flat landscape of a wheat field compared to the steep hills of a mountain region. While wheat fields spread out flat and are easy to traverse, the mountains are steep, steep, and rugged. Similarly, deep sea plains are vast, flat areas beneath the ocean.
Characteristics of Deep Sea Plains
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The depths of deep sea plains vary between 3,000 and 6,000m. These plains are covered with fine-grained sediments like clay and silt.
Detailed Explanation
Deep sea plains are typically found at great depths in the ocean, ranging from 3,000 to 6,000 meters below the surface. Because of their significant depth, the environment is drastically different from shallow waters. The sediment on these plains is usually composed of fine particles such as clay and silt, which settle slowly and form a soft layer over the ocean floor.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the bottom of a tranquil, slow-moving river where fine particles settle and form a soft bed. In a similar way, the bottom of the deep sea plains is like that riverbed, but it is much deeper and covered in a layer of soft, fine sediment.
Key Concepts
-
Deep Sea Plain: The flattest regions of the ocean floor, vital for marine ecology.
-
Sediments: Fine particles that form the foundation of life on the Deep Sea Plain.
-
Tectonic Activity: Plays a significant role in shaping the ocean's floor features.
Examples & Applications
The Hudson Canyon is a well-known example of a topical feature that illustrates the geologic processes active in oceanic regions.
Seamounts and guyots are relevant features that illustrate the geological structures found in ocean basins.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Deep Sea Plain, smooth and wide, Where marine life and sediments abide.
Stories
Once, a sailor traveled to the Deep Sea Plain, where the smooth ocean floor held secrets and life, showing that beneath the waves planned incredible biodiversity.
Memory Tools
SAND - Sediment Accumulation Nourishes Deep sea.
Acronyms
SPLACE - Smooth Plains Lying At Continental Edges.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Deep Sea Plain
A flat region of the ocean floor existing at depths generally between 3,000 and 6,000 meters, covered predominantly by fine sediments.
- Sediment
Small solid particles that settle at the bottom of a liquid or are deposited by wind or water.
- Tectonic Activity
The movement of the Earth's tectonic plates, which significantly shapes continents, ocean floors, and geological features.
- Ecosystem
A community of living organisms and their interaction with the environment.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
