WHAT IS AN EXECUTIVE?
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding the Role of the Executive
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're discussing the executive branch of government. Can anyone tell me what they think the executive does?

I think the executive is responsible for making laws.

Not quite. The executive actually implements laws created by the legislature. It’s more about executing laws rather than making them.

So, it’s like the managers of a company who follow the rules set by the board?

Exactly! You can think of it that way. Who can tell me the difference between the political executive and the permanent executive?

Is the political executive everyone who gets elected, like ministers?

Correct! The political executive is composed of elected officials, while the permanent executive refers to civil servants who are appointed to implement policies.

To summarize, the executive is crucial for implementing laws and maintaining order, much like a manager in a company carries out board decisions.
Different Types of Executives
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s explore the different types of executives around the world. Can someone give me an example of a presidential system?

The United States has a presidential system.

Right! The president there is both the head of state and government. What about a parliamentary system?

India has a parliamentary system where the President is ceremonial, and the Prime Minister is the head of government.

Exactly! The Prime Minister leads the government while the President's powers are largely ceremonial and exercised based on the Prime Minister’s advice.

Are there countries with semi-presidential systems?

Yes! Countries like France have a semi-presidential system where both the President and Prime Minister share certain powers.

To summarize, understanding the type of executive in a government is crucial as it defines the power dynamics within that government system.
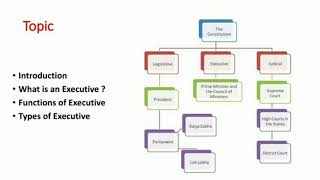
The Indian Executive
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand types of executives, let’s focus on the Indian executive. Who knows who formally holds executive power in India?

The President?

Correct! The Constitution vests executive power in the President, but that power is exercised with the advice of the Council of Ministers headed by the Prime Minister.

So, the President doesn’t make decisions alone?

Right! The President acts based on the Council's advice, showing the interconnectedness of the executive and legislature.

What happens if the President and the Prime Minister disagree?

That’s an interesting question! In practice, the Prime Minister usually has the majority support in parliament, which often guides decisions.

In summary, while the President is the nominal head, the actual power is with the Prime Minister and the Ministers.
Accountability of the Executive
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

A crucial part of governance is accountability. How is the executive held accountable?

I think the legislature can remove the Prime Minister if they lose the majority?

That’s true! The Council of Ministers is collectively responsible to the Lok Sabha, and if they lose confidence, they must resign.

What role does public opinion play?

Public opinion is vital since the executive needs to remain responsive to the people’s needs. They are elected representatives, after all.

To summarize, accountability is key to democracy, ensuring the executive remains aligned with the public's interests.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section delineates the structure and responsibilities of the executive in a government, highlighting the interdependence between the executive and legislature, the function of the President in India, and various types of executive systems worldwide.
Detailed
Overview of the Executive Branch
The executive is one of the three key organs of government, alongside the legislature and judiciary, and plays a crucial role in implementing laws and policies. In a parliamentary system, the executive and legislature are closely linked, with the legislature able to control the executive.
Key Features of the Executive:
- Definition: The executive refers to the body responsible for administering laws and implementing policies. This entails managing day-to-day affairs and making high-level decisions regarding governance.
- Functions: The primary function is law implementation, policy framing, and overseeing administrative practices.
- Types: Different countries have varying executive systems, such as presidential, parliamentary, or semi-presidential systems, each with distinct powers and structures. For example, in India, the President serves as the ceremonial head while the Prime Minister leads the government.
- Constitutional Position: The President exercises executive powers, mainly based on the advice of the Council of Ministers.
- Interdependence: Emphasizes the unique relationship between executive and legislature, where accountability and responsiveness to public needs are pivotal.
Conclusion
The section underlines the essential nature of the executive in governance, outlining its relationship with the public and legislative representatives.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Executive
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In any organisation, some office holder has to take decisions and implement those decisions. We call this activity administration or management. But administration requires a body at the top that will take policy decisions or the big decisions and supervise and coordinate the routine administrative functioning. The word executive means a body of persons that looks after the implementation of rules and regulations in actual practice.
Detailed Explanation
The executive is a crucial part of any organization or government, acting as a leader to manage and implement decisions. This body encompasses the leaders who create policies and those who ensure these policies are executed effectively. Essentially, the executive ensures that laws and policies are enacted and followed in practice, coordinating the daily operations of the organization.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a school where the principal is like the executive. The principal makes important decisions about school policies, while teachers (the administrative staff) implement these policies in the classroom. Just like in a school, the executive in government takes the big decisions that help the country run smoothly.
Functions of the Executive
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Executive is the branch of government responsible for the implementation of laws and policies adopted by the legislature. The executive is often involved in framing of policy. The official designations of the executive vary from country to country.
Detailed Explanation
The executive has the vital responsibility of implementing laws passed by the legislature. Not only does it ensure that these laws are upheld, but it also plays a key role in shaping policies. This means that the executive doesn’t just carry out laws, but also suggests or crafts new policies that guide the government's direction.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a chef in a restaurant. The legislature is like the menu, which states what dishes are available, while the chef (the executive) not only prepares these dishes but may also come up with new ones based on tastes and trends. This creative process is similar to how the executive influences policies.
Types of Executive
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Every country may not have the same type of executive. The USA has a presidential system where executive powers are in the hands of the President. Canada has a parliamentary democracy with a constitutional monarchy where Queen Elizabeth II is the formal chief of state and the prime minister is the head of government.
Detailed Explanation
There are various forms of executive depending on the country's political structure. In a presidential system like that of the USA, the president has extensive powers. In contrast, in parliamentary systems like Canada's or the UK's, the executive authority is often shared between a ceremonial head of state and a prime minister who actually runs the government. This differentiation affects how laws are enacted and how leaders are accountable.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the difference between a ship with a single captain (presidential system) and a ship with a captain and a crew of officers who help make decisions (parliamentary system). In the first case, the captain (president) has clear, sole control. In the latter, while the captain has authority, the officers (prime minister and council) play a significant role in navigating the ship (government).
Semi-Presidential Systems
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In a semi-presidential system, there is both a president and a prime minister. The president has significant powers but normally must work with the prime minister, who is responsible for everyday government operations. Countries like France and Russia exemplify this system.
Detailed Explanation
In semi-presidential systems, the power is shared between the president and the prime minister. This dual system can create a balance of power and responsibilities, meaning that while the president might have broad authority, the prime minister is tasked with daily governance. This structure can lead to complex political dynamics.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a sports team with a head coach (president) and an assistant coach (prime minister). The head coach is responsible for the overall strategy and big decisions, while the assistant coach focuses on day-to-day practices and play calls. Their roles need to be coordinated for the team's success, similar to how a semi-presidential executive operates.
The Importance of the Executive
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The executive plays a significant role in leadership and governance, acting as the point of contact between the people and the law. It holds power that directly impacts citizens' lives and ensures that service delivery is effective.
Detailed Explanation
As the main governing body, the executive's decisions can greatly influence the daily lives of citizens. The executive's role goes beyond just enforcing laws; it is responsible for ensuring that public services function effectively, facilitating programs, and addressing the needs of the populace. This direct connection to the citizens illustrates the importance of accountable and effective leadership.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a government as a large hospital. The executive is like the hospital's administration, ensuring that patients receive care smoothly. If the administration does its job well—managing staff, resources, and policies—patients (the citizens) experience a good standard of care. But if it fails, the service deteriorates, just as poor governance can impact society negatively.
Key Concepts
-
Executive Branch: Administers the government and implements laws.
-
Political Executive: Composed of elected officials, responsible for policy-making.
-
Permanent Executive: Made up of civil servants who implement policies.
-
Types of Executive Systems: Presidential, parliamentary, and semi-presidential systems.
-
Accountability: The principle that the executive must answer to the legislature and the public.
Examples & Applications
In a company, the executive board implements the regulations set by shareholders, similar to how the governmental executive implements laws.
In India, the President is the ceremonial head of state, while the Prime Minister leads the government with actual power.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the government, the executive's the heart, implementing laws, playing a vital part.
Stories
Once upon a time in a kingdom, a wise ruler created two groups: one was elected to make rules (the political executive), and the other was tasked with following those rules (the permanent executive) to ensure harmony in governance.
Memory Tools
PE - Political Executive, they’re the leaders,
Acronyms
PAR
Power
Accountability
Responsiveness - the essence of an executive.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Executive
The branch of government responsible for implementing laws and policies.
- Political Executive
Elected officials like the Prime Minister and Ministers who make policy decisions.
- Permanent Executive
Civil servants and bureaucrats responsible for day-to-day governance and administration.
- Presidential System
A system where the president is the head of state and government, holding significant powers.
- Parliamentary System
A system with a Prime Minister as the head of government and a ceremonial head of state.
- Accountability
The obligation of the executive to report, explain, and justify its actions to the legislature and public.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
