DIMENSIONAL FORMULAE AND DIMENSIONAL EQUATIONS
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Dimensional Formulas
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will discuss dimensional formulas. These represent how physical quantities are related to base quantities like mass, length, and time. Can anyone tell me what a dimensional formula is?

Is it how we represent different properties like volume and speed using basic dimensions?

Exactly! For instance, the dimensional formula for volume is [M⁰ L³ T⁰]. Can anyone figure out what this means?

It means volume doesn't depend on mass or time, just on length because it has three dimensions of length.

Great understanding! Remember the acronym 'V= Length³' as a memory aid for volume. Let's move on to other quantities.
Dimensional Equations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s talk about dimensional equations. A dimensional equation equates a physical quantity to its dimensional formula. For example, what do we represent speed as?

Speed is represented as [v] = [M⁰ L T⁻¹].

Correct! Can anyone explain what that signifies?

It shows speed is based on length and time but not on mass.

Well done! Let's remember 'Speed = Distance/Time' as a concept to visualize. Now, can someone summarize what we just discussed?

We learned that dimensional equations help relate physical quantities to their dimensions.
Examples of Dimensional Formulas
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up, let’s look at some examples. We have force, represented as [F] = [M L T⁻²]. What does this tell us?

It indicates force depends on mass and acceleration, which is length per time squared.

Exactly! And how about mass density, represented as [ρ] = [M L⁻³ T⁰]?

It shows mass density is dependent on mass and inversely proportional to volume.

Yes! Let's remember the phrase 'Density = Mass/Volume' as a memory aid. Can someone summarize the importance of understanding these formulas?

Understanding these formulas helps us better analyze and relate physical quantities in different contexts.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, the idea of dimensional formulas is introduced, along with examples of key physical quantities like volume, speed, and acceleration. The relationship between physical quantities and their respective dimensional formulas is described, culminating in the explanation of dimensional equations.
Detailed
Dimensional Formulae and Dimensional Equations
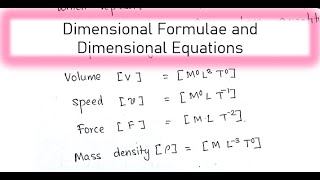
Dimensional formulas are expressions that represent how base quantities correspond to physical quantities. For example, the dimensional formula of volume is represented as [M⁰ L³ T⁰] and for speed as [M⁰ L T⁻¹]. Additionally, acceleration's dimensional formula is [M L⁻¹ T⁻²], and mass density's is [M L⁻³ T⁰].
A dimensional equation equates a physical quantity with its dimensional formula, providing a mathematical representation of the dimensions involved in that quantity. For instance:
- Volume: [V] = [M⁰ L³ T⁰]
- Speed: [v] = [M⁰ L T⁻¹]
- Force: [F] = [M L T⁻²]
- Mass Density: [ρ] = [M L⁻³ T⁰]
This section emphasizes the significance of understanding dimensional formulas and equations as they pertain to the relationships between different physical quantities, with a set of examples provided in Appendix 9 for further reference.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding Dimensional Formulae
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The expression which shows how and which of the base quantities represent the dimensions of a physical quantity is called the dimensional formula of the given physical quantity. For example, the dimensional formula of the volume is [M° L3 T°], and that of speed or velocity is [M° L T-1]. Similarly, [M° L T–2] is the dimensional formula of acceleration and [M L–3 T°] that of mass density.
Detailed Explanation
A dimensional formula represents a physical quantity in terms of its fundamental dimensions based on the seven base units: length ([L]), mass ([M]), time ([T]), electric current ([A]), thermodynamic temperature ([K]), luminous intensity ([cd]), and amount of substance ([mol]). For instance, the volume of an object can be expressed in terms of length alone because it is calculated as length cubed. Thus, its dimensional formula is [L^3]. Similarly, speed (distance over time) has the formula [L T^{-1}], indicating that it involves length and time.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a building architect who needs to understand how much space is available in a room. Just as the architect uses length measurements in different dimensions to describe the space, scientists use dimensional formulas to categorize and relate physical quantities. For example, just like saying a room is 20 feet long but also relating that to its speed of air circulation during heating or cooling—using formulas allows for identical comparisons.
Dimensional Equations
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
An equation obtained by equating a physical quantity with its dimensional formula is called the dimensional equation of the physical quantity. Thus, the dimensional equations are the equations, which represent the dimensions of a physical quantity in terms of the base quantities. For example, the dimensional equations of volume [V], speed [v], force [F] and mass density [ρ] may be expressed as [V] = [M0 L3 T0], [v] = [M0 L T–1], [F] = [M L T–2], [ρ] = [M L–3 T0].
Detailed Explanation
A dimensional equation relates a specific quantity to its dimensional formula by creating an equation where both sides represent the same physical dimensions. For instance, for speed, we write an equation that shows speed ([v]) equal to its dimensional formula ([M° L T^{-1}]). These equations are useful for establishing the relationships between physical quantities and ensuring they are consistent with dimensional analysis.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are baking. You know that for every cup of flour (the physical quantity), you also need a specific volume of water. Just like a recipe creates a relationship between quantities, dimensional equations form a bridge to understand how different physical quantities relate to one another through their dimensions, ensuring every measurement fits 'the recipe' of properties in physics.
Extracting Dimensional Formulas
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The dimensional equation can be obtained from the equation representing the relations between the physical quantities. The dimensional formulae of a large number and wide variety of physical quantities, derived from the equations representing the relationships among other physical quantities and expressed in terms of base quantities are given in Appendix 9 for your guidance and ready reference.
Detailed Explanation
To derive a dimensional formula from physical quantities, one typically starts with known equations relating those quantities. For example, force is defined as mass times acceleration (F = m * a). By substituting the dimensional formulas of mass and acceleration into this equation, we can derive the dimensional formula for force: [F] = [M L T^{-2}]. Appendix resources often summarize these relationships for various physical constants and quantities, aiding in quick reference.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it as a detective unraveling clues. Each equation that describes a relationship serves as a clue. By putting these clues together about different physical movement—like how a car accelerates and the forces involved—you can paint the full picture of how dimensions interact in physics.
Key Concepts
-
Dimensional formulas represent how physical quantities are expressed in terms of base quantities.
-
The importance of dimensional equations in relating physical quantities.
-
Examples of dimensional formulas for volume, speed, force, and mass density.
Examples & Applications
Example of Volume: The dimensional formula is [M⁰ L³ T⁰].
Example of Speed: The dimensional formula is [M⁰ L T⁻¹].
Example of Force: The dimensional formula is [M L T⁻²].
Example of Mass Density: The dimensional formula is [M L⁻³ T⁰].
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Volume's space, length cubed on display; speed's distance o'er time, fast as a ray.
Stories
Once in a classroom, a curious student named Max explored the dimensions of space, realizing that his giant cube's volume depended only on its length—unrelated to weight or time!
Memory Tools
Remember 'F=Ma' to recall force relies on mass and acceleration—dimensions matter!
Acronyms
Use the acronym 'V.S.F.M' to remember Volume, Speed, Force and Mass Density.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Dimensional Formula
An expression that represents how base quantities correspond to a physical quantity.
- Dimensional Equation
An equation obtained by equating a physical quantity with its dimensional formula.
- Base Quantities
Fundamental quantities such as mass, length, time, etc., on which other physical quantities are based.
- Physical Quantity
A quantity that can be measured and expressed in terms of base quantities.
- Volume
A measure of the space occupied by an object.
- Speed
The distance covered per unit time.
- Force
An interaction that causes a change in an object's motion or shape.
- Mass Density
The mass of an object divided by its volume.
- Acceleration
The rate of change of velocity per unit time.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
