PERCEPTUAL CONSTANCIES
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Perceptual Constancies
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will discuss perceptual constancies. Can anyone guess what that might mean?

Is it about how we see things differently based on the light?

Great insight! Perceptual constancies actually refer to our ability to perceive objects as stable despite changing conditions. For example, brightness constancy allows us to see an object as the same color regardless of lighting.

So, if I see a white paper in a dark room and bright sunlight, I'm still going to think it's white?

Exactly! That's brightness constancy. Memory aid: think of 'B for Brightness equals Best seen'.

What about size? How does it work?

That's size constancy! Regardless of distance, we perceive an object as its true size. If you're approaching someone, they seem bigger, but you know they haven't grown.

That helps me understand better!

To summarize, perceptual constancies allow us to maintain a stable understanding of objects. Remember the acronym BSS: Brightness, Size, Shape.
Brightness Constancy
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's delve deeper into brightness constancy. What do you think makes an object appear to have constant brightness?

Is it about how much light is reflecting off of it?

Spot on! No matter how much light is reflecting, our brains adjust to perceive it the same. For instance, a coal looks black whether in sunlight or shade.

Why do we need this ability?

It helps us function in varied environments, making our perception reliable. A good memory aid for brightness is 'Bright stays Bright!'

This makes sense! It’s like taking a picture without considering the shadows.

Exactly! To conclude, brightness constancy is crucial in maintaining visual stability.
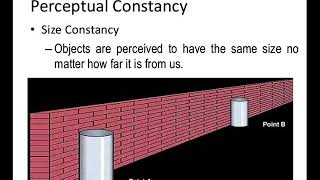
Size Constancy
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, who can tell me about size constancy?

It means we recognize objects as their true size even if they're far away?

Correct! Think about how we perceive a tree as the same size whether we’re near or far. Memory aid: 'Size Stays the Same, no matter the Space.'

What happens with objects that are very far away? Can we still tell their size?

Good question! We use contextual cues to help us gauge size, even at a distance. It’s about our brain making adjustments based on experience.

So it's not just about what we see but also about what we know?

Exactly right! To sum up, size constancy plays a vital role in our visual perception.
Shape Constancy
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s talk about shape constancy. Who knows what that is?

It’s seeing the same shape even when it looks different?

Precisely! Like how a dinner plate looks round, even when viewed from an angle. Memory aid: 'Shape Shifts but stays the Same.'

So it’s all about perspective?

Exactly! Our brain compensates for the angle of viewing. This is crucial for interpreting objects in our environment effectively.

That sounds super important for navigating spaces!

Right! Shape constancy is essential for recognizing objects accurately.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section explores how perceptual constancies, including brightness, size, and shape constancies, enable us to perceive objects as unchanging despite variations in light, distance, and angle. These constancies are critical for our understanding and interaction with the world around us.
Detailed
Perceptual Constancies
Perceptual constancies refer to the phenomena where perceived attributes of objects (like brightness, size, and shape) remain consistent even as sensory information changes. This stability in perception enables us to recognize and identify objects reliably, regardless of varying lighting, distances, or orientations.
Key Types of Perceptual Constancies:
- Brightness Constancy: This type refers to the perception that objects maintain the same level of brightness despite changes in illumination. For instance, a white piece of paper looks white whether in sunlight or dim indoor light.
- Size Constancy: Size constancy is our perception that an object’s size remains constant, even when its distance from us changes and thus its retinal image size varies. For example, when approaching a friend, their image on our retina grows larger, yet we perceive their size as unchanged.
- Shape Constancy: Shape constancy allows us to perceive shapes as constant even when the angle of view changes, thus altering the shape on the retina. For instance, a round dinner plate appears circular from various angles, whether viewed directly or at an angle.
These constancies are significant as they allow for a coherent understanding of the environment, making it easier to navigate and interact with it effectively.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Brightness Constancy
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Visual objects not only appear constant in their shape and size, they also appear constant in their degree of whiteness, greyness, or blackness even though the amount of physical energy reflected from them changes considerably. In other words, our experience of brightness does not change in spite of the changes in the amount of reflected light reaching our eyes. The tendency to maintain apparent brightness constant under different amounts of illumination is called brightness constancy. For example, surface of a paper which appears white in the sunlight, is still perceived as white in the room light. Similarly, coal that looks black in the sun also looks black in room light.
Detailed Explanation
Brightness constancy is a perceptual phenomenon where we perceive the brightness of an object to remain constant despite changes in lighting conditions. This means that if you see a white paper in bright sunlight, it appears white, and if you see the same paper in dim room light, it still appears white. This occurs because our brain is capable of maintaining the perception of brightness based on the context and conditions in which we view the object. So, even though the amount of light hitting the paper changes, our perception stabilizes its appearance, showing how our brain compensates for varying light conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Think of how we perceive colors when we are in different lighting situations. Imagine you are outside on a bright sunny day and see a white shirt. You then go indoors where the light is dimmer, but the shirt still looks white. This happens because your brain 'remembers' that the shirt was white when you first saw it and adjusts your perception accordingly, keeping your experience consistent.
Size Constancy
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The size of an image on our retina changes with the change in the distance of the object from the eye. The further away it is, the smaller is the image. On the other hand, our experience shows that within limits the object appears to be about the same size irrespective of its distance. For example, when you approach your friend from a distance, your perception of the friend’s size does not change much despite the fact that the retinal image (image on retina) becomes larger. This tendency for the perceived size of objects to remain relatively unchanged with changes in their distance from the observer and the size of the retinal image is called size constancy.
Detailed Explanation
Size constancy means that we perceive an object as having a constant size, even when its distance from us changes. For instance, as you walk towards a friend, the size of their image on your retina gets larger, but you know they don’t actually grow in size. Your brain adjusts your perception to maintain the understanding that they remain the same size, highlighting how our perceptions adapt to maintain stable experiences despite variable sensory information.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine seeing a car down the street; it looks small, but as you get closer, it appears larger. Yet, you logically understand the car itself is not changing size. Similarly, if you spot a plane in the sky, it appears tiny, but as it lands closer to you, you perceive its actual size correctly, illustrating how our minds account for distance in our perception.
Shape Constancy
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In our perceptions the shapes of familiar objects remain unchanged despite changes in the pattern of retinal image resulting from differences in their orientation. For example, a dinner plate looks the same shape whether the image that it casts on the retina is a circle, or an ellipse, or roughly a short line (if the plate is viewed from the edge). It is also called form constancy.
Detailed Explanation
Shape constancy refers to our ability to perceive the shape of an object as constant, even when the angle of view changes, thereby altering the retinal image. For example, when you look at a dinner plate from the front, it appears round, but if you see it from the side, it looks like an ellipse. Nevertheless, you still recognize it as a dinner plate, thanks to your brain’s ability to adjust perception based on prior knowledge and experience about the object.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a smartphone: when seen from the front, it looks rectangular. If you tilt it sideways, it might appear more like a trapezoid. However, because of shape constancy, you still recognize it as a smartphone. This is similar to how we can identify people from various angles; we recognize our friends regardless of whether we see them from the front or the side, thanks to our cognitive understanding of their shapes.
Key Concepts
-
Perceptual Constancies: Stability in perception of objects despite changes.
-
Brightness Constancy: Perceived brightness remains the same under different lighting.
-
Size Constancy: The perceived size of an object stays the same despite distance.
-
Shape Constancy: The perceived shape stays constant despite orientation changes.
Examples & Applications
A white paper appearing white in both sunlight and shade illustrates brightness constancy.
A person approaching a friend perceives them as the same size even as the image of them on the retina grows larger, showcasing size constancy.
A circular dinner plate appearing round, regardless of whether it is viewed directly or from an angle, exemplifies shape constancy.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Bright and bright, day or night, colors shine, they’re always right.
Stories
A painter ensured their art maintained consistent colors under all lights, if a blue seemed gray in shadow, they knew adjustments would keep it vivid and right.
Memory Tools
Remember BSS: Brightness, Size, Shape for how we see stable perceptions!
Acronyms
BSS - Brightness, Size, Shape Constancies are key concepts.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Brightness Constancy
The tendency to perceive an object's brightness as constant despite changes in the light conditions.
- Size Constancy
The perception of an object’s size remains constant even when its distance from the viewer changes.
- Shape Constancy
The understanding that an object's shape remains constant despite changes in orientation or angle.
- Perceptual Constancies
The ability to perceive objects as stable despite changes in sensory input.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
