Development of Sex Organs
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Sex Organ Development
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Good morning, class! Today we will talk about important changes that occur during puberty, especially regarding the development of sex organs. Can anyone tell me what puberty is?

Isn't puberty the time when kids start to change into teenagers?

Exactly! Puberty typically starts around ages 11 to 19. During this time, both boys and girls undergo physical changes including the development of their reproductive organs. In boys, this includes the testes and penis. Can anyone tell me what happens to these organs during puberty?

I think the testes start to produce sperm during puberty!

Great point! And in girls, what develops during puberty?

The ovaries enlarge and start maturing eggs.

Correct! Both sexes also develop secondary sexual characteristics, influenced by hormones. For example, boys experience facial hair growth and deeper voices due to testosterone. Let's remember the acronym 'THREE' for Testosterone, Hormones, Reproductive, Enlarge, and Eggs to recall these key concepts.

That's a helpful way to remember!

To sum up, puberty signifies the period when our reproductive organs develop and function begins. Any questions?
Role of Hormones in Development
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand what organs develop, let’s discuss hormones. Why do you think hormones are important during puberty?

I suppose they help with the body's changes, right?

Yes! Hormones are chemical messengers. In boys, testosterone is responsible for developing male characteristics. In girls, estrogen plays a similar role. Can anyone list some changes triggered by these hormones?

Boys get facial hair and their voice becomes deeper!

And girls develop breasts and start their menstrual cycle!

Good observations! So, both hormones create physical and emotional maturation during this crucial development period. Remember, 'TESTO' for Testosterone and 'ESTRO' for Estrogen—it’s an easy way to recall their roles in boys and girls.

That makes it easier to remember!

Before we wrap up this session, let’s summarize: testosterone and estrogen are vital for bodily changes, focusing on sex organ development and secondary sexual characteristics. Is there anything unclear?
Changes During Puberty Summary
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

So, class, now let’s review what we’ve learned about puberty and the development of sex organs. Who wants to summarize the key points?

Puberty starts between ages 11 and 19, and it involves important changes for both boys and girls.

Boys develop testes and penis, while girls' ovaries grow, maturing eggs.

Hormones like testosterone for boys and estrogen for girls trigger these changes.

Excellent summary! This transition is significant in reaching reproductive maturity, marking the shift from childhood to adulthood. Remember the key terms and how they relate to growth and development in both genders during this time. Any questions before we conclude?
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
As individuals enter puberty, significant changes occur in the development of sex organs, marked by hormonal influences that lead to reproductive maturity. Boys experience growth in testes and penis while girls have enlarging ovaries and maturing eggs, alongside secondary sexual characteristics.
Detailed
Development of Sex Organs
During puberty, which typically occurs between ages 11 and 19, humans experience profound physical and hormonal changes indicative of reaching reproductive maturity. This period is characterized by the development of primary sexual organs: in males, the testes and penis develop fully and begin to produce sperms; in females, the ovaries enlarge, maturing eggs and beginning their release.
Hormones play a critical role in these changes. The male hormone testosterone is released by the testes, fostering the development of male secondary sexual characteristics, including facial hair and deepening of the voice. In females, the hormone estrogen, released by the ovaries, facilitates breast development and the maturation and release of eggs. The impact of these hormones is evident not just in reproductive capabilities, but also in the overall physical and emotional maturation of adolescents.
Understanding this process is essential as it not only marks the transition from childhood to adulthood but also prepares individuals for future reproductive health.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Development of Male Sex Organs
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Look up Fig. 6.1 and 6.3 of the previous lesson which show sex organs of humans. At puberty, male sex organs like the testes and penis develop completely. The testes also begin to produce sperms.
Detailed Explanation
During puberty, significant changes occur in the male reproductive system. The testes, which are small glands located in the scrotum, complete their development and begin to function by producing sperm. This is essential for male fertility. The penis, which is the external organ, also grows and matures. These developments enable males to become capable of sexual reproduction.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a tree growing and bearing fruit. Just like the branches and leaves develop before the tree can produce fruit, the male reproductive organs mature before boys can begin producing sperm. This is part of the natural growth process.
Development of Female Sex Organs
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
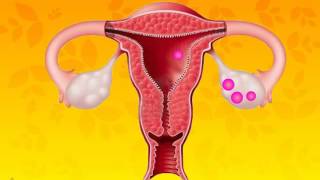
In girls, the ovaries enlarge and eggs begin to mature. Also ovaries start releasing mature eggs.
Detailed Explanation
Similar to boys, girls experience significant changes during puberty that affect their reproductive organs. The ovaries, which are located in the lower abdomen, grow larger and begin to mature eggs. This process is essential for reproduction, as each month, one matured egg is released from an ovary in a process called ovulation. This prepares the female body for potential pregnancy.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a factory preparing products for sale. The ovaries function as factories that produce eggs. Each month, just like a factory might release one product for distribution, the ovaries release one egg, ready for fertilization.
Key Concepts
-
Development of Sex Organs: The reproductive organs mature during puberty, governed by hormonal changes.
-
Hormonal Influence: Testosterone and estrogen are the primary hormones responsible for physical changes and sexual maturation.
-
Puberty Duration: Puberty typically spans from ages 11 to 19, during which critical changes occur.
-
Secondary Sexual Characteristics: Features such as breasts in girls and facial hair in boys develop during puberty.
Examples & Applications
An example of a change during puberty is the growth of facial hair in boys, indicating the influence of testosterone.
As girls enter puberty, they experience breast development and eventual onset of menstruation, influenced by estrogen.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In puberty's stage, we grow tall and wide, / Hormones take charge, a thrilling ride.
Stories
Imagine a caterpillar transforming into a butterfly. Just as the caterpillar undergoes changes to become a beautiful butterfly, children grow and change during puberty to become adults ready for new life.
Memory Tools
PES (Puberty, Estrogen, Testosterone) helps you remember the key components of sexual maturation.
Acronyms
THREE for Testosterone, Hormone, Reproductive, Enlarge, Eggs.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Adam’s Apple
The prominent notch in the throat formed by the thyroid cartilage surrounding the larynx, more pronounced in males post-puberty.
- Adolescence
A period of transition from childhood to adulthood during which significant physical, emotional, and social changes occur, typically between 11 and 19 years.
- Hormones
Chemical substances released by endocrine glands that regulate various functions in the body, including growth and development.
- Testosterone
The male hormone produced by the testes, responsible for the development of male secondary sexual characteristics.
- Estrogen
The female hormone produced by the ovaries, responsible for the development of female secondary sexual characteristics.
- Puberty
The developmental stage during which adolescents become capable of reproduction and physical changes occur.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
