Activity 12.4
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to the Electroscope
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we are going to learn about an exciting device called an electroscope. Can anyone tell me what an electroscope is used for?

Is it used to detect electric charges?

Exactly! The electroscope helps us detect whether an object has an electric charge. First, let's discuss how we can make one using some simple materials.

What materials do we need?

We'll need an empty jam bottle, a cardboard piece, a paper clip, and two strips of aluminum foil. Can anyone think about how these parts will fit together?
Building the Electroscope
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we have our materials, let's start by piercing a hole in the cardboard so the paper clip can fit through. Who can explain why we need this setup?

The paper clip will hold the aluminum foil strips, right?

Correct! Next, we hang the aluminum foil on the paper clip. Once we finish assembling the electroscope, we will charge it with our refill and observe what happens. Can anyone guess what we will see?

The foils might move away from each other!
Observing Charge Transfer
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's charge our refill and touch it to the paper clip. What do you observe with the aluminum foil strips?

They are repelling each other!

Excellent observation! The strips repel each other because they acquire the same charge. This shows us that like charges repel. Can anyone explain why we see this behavior?

Because they are both positively or negatively charged!
Understanding Earthing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's think about what happens if we touch the paper clip with our hand. Why do the foil strips return to their original position?

Is it because touching it discharges the electroscope?

Exactly! This process of transferring charge to the earth is called earthing. Why do you think earthing is important in our daily lives?

It helps prevent electrical shocks!
Summarizing Our Learning
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's summarize what we learned today about electroscopes. What were the main points?

We learned how to build an electroscope!

And that like charges repel while unlike charges attract!

Great! We also talked about earthing and why it's essential for safety.

This is so cool! Can we do more experiments with electricity next time?
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
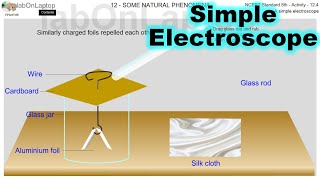
In Activity 12.4, students learn to construct a simple electroscope using a jam bottle and aluminum foil strips. This device helps demonstrate the principles of static electricity, charge transfer, and how like charges repel while unlike charges attract.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
In Section 12.4.1, we engage students in Activity 12.4, where they create a simple electroscope using common household items. The experiment involves taking an empty jam bottle, a piece of cardboard, a metal paper clip, and aluminum foil strips. Students assemble the electroscope and charge the refill, then observe the behavior of the foil strips. The core concepts explored include how charges transfer, the behavior of like and unlike charges, and the use of the electroscope to detect whether an object is charged. Through this activity, students also learn about the practical applications of electric charge in everyday scenarios and the fundamental principles behind static electricity.
Youtube Videos









Key Concepts
-
Electroscope: A tool to detect electric charge.
-
Charge Transfer: Movement of electric charge between objects.
-
Earthing: Removing excess charge by transferring it to the earth.
-
Static Electricity: Accumulated charge on an object.
-
Metal Conductor: Material enabling flow of electric charge.
Examples & Applications
Charging a plastic comb with hair and using it to attract small pieces of paper demonstrates static electricity.
Using an electroscope to determine whether a charged object can induce a charge in it reflects real-world applications of charge transfer.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Charges alike, they shove and fight, but unlike charges hold on tight.
Stories
Once there was an electroscope that could feel the charges around it, like a highly sensitive pet. Whenever visitors came close, it would swing its 'arms' to show whether they were charged or not.
Memory Tools
Remember E.C.E - Electroscope Can Earth (referring to the functions of the electroscope).
Acronyms
ELECTRO
Electroscope Learns Electric Charges Through Reactions of Objects.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Electroscope
A device used to detect electric charge through the movement of charged conductors.
- Charge Transfer
The movement of electric charge from one body to another.
- Earthing
The process of removing charge from an object by transferring it to the earth.
- Static Electricity
Electric charge that accumulates on the surface of an object.
- Metal Conductor
A material that allows the flow of electric charge due to the mobility of electrons.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
