Production of Sound
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Sound Production
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome, everyone! Today, we're going to talk about how sound is produced. Can anyone tell me what sound is?

Isn't sound just noise, like when I listen to music?

Great question, Student_1! Sound is actually a form of energy that produces the sensation of hearing. It originates from vibrations.

What do you mean by vibrations?

Excellent inquiry! Vibrations are rapid to-and-fro motions. For example, when you clap your hands, they vibrate, producing sound. Remember: 'Vibrate to create!' can help you remember this.

And how does that relate to energy?

Good point! Energy conservation tells us that energy can't be created or destroyed, only transformed. So, when you clap, mechanical energy turns into sound energy. Let's keep this in mind!
Experiments and Observations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

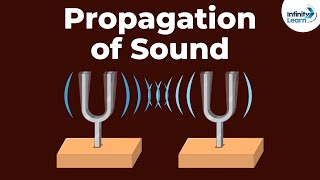
Now, let's perform an activity with a tuning fork. When we strike the fork, what do we observe?

It starts to vibrate!

Exactly! When these prongs vibrate, they create sound. Let's try touching it to a table tennis ball!

The ball moves! What does that show us?

Great observation! It shows us that vibrations transfer energy. We can say, 'Vibration moves energy!'
Understanding Sound Behavior in Water
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s submerge the tuning fork's prongs into water. Watch what happens!

Wow! The water ripples more when both prongs are submerged!

Exactly! This is because sound energy is transferred through the water. 'Sound travels better in water!' helps us remember this.

Why can't we hear sound in a vacuum?

Great question, Student_3! Sound needs a medium, like air or water, to travel. In a vacuum, there are no particles to carry the sound waves.

So, all sounds must come from something vibrating?

Exactly, Student_4! We've learned 'Sound = Vibration + Medium.' Remember that!
Linking Vibrations to Instruments
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s discuss musical instruments. Can anyone name an instrument and what part vibrates to create sound?

How about a guitar? The strings vibrate!

Correct! Each instrument has a vibrating part, translating energy into sound. Remember, 'Strings, membranes, air columns!' refers to vibrating instrument parts.

What about our vocal cords?

Yes, absolutely! Our vocal cords vibrate to produce speech. Well done!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Sound is a form of energy generated by vibrations, which are essential to sound production. The section highlights how vibrations are transmitted through a medium and how sound is perceived, using practical activities to illustrate these principles.
Detailed
In this section, we explore sound as a form of energy that relies on vibrations for its creation and transmission. Sound originates from vibrating objects, like clapping hands or struck tuning forks, and cannot exist in a vacuum. The principles of energy conservation apply, indicating that energy transforms rather than disappears. Through engaging activities—such as using a tuning fork to create vibrations in water and observing their effects—we learn how vibrations transfer energy. This hands-on approach reinforces key concepts such as the nature of sound waves, how various objects produce sound through vibration, and the importance of a medium for sound transmission.
Youtube Videos








Key Concepts
-
Sound is produced by vibrating objects.
-
Vibrations transfer energy, essential for sound production.
-
A medium is required for sound to travel.
-
Energy conservation principles apply to sound production.
Examples & Applications
Clapping hands creates vibrations that produce sound.
Striking a tuning fork creates sound waves that travel through the air or water.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
If it's making a sound, it’s vibing around!
Stories
A curious child strikes a tuning fork, discovering that it vibrates, sending ripples in the water. This sparks a journey to explore vibrations and sounds in nature.
Memory Tools
S-M-E - Sound is Medium Energy.
Acronyms
VIPS - Vibration In Producing Sound.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Sound
A form of energy that creates the sensation of hearing.
- Vibration
A rapid back-and-forth motion of an object.
- Medium
A material through which sound waves travel.
- Energy Conservation
The principle stating that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
